Both zero coupon and coupon bonds are debt obligations, there are obvious and some technical differences in their fundamentals and implications. Let us understand their differences through the comparison below.
Table Of Contents
Zero-Coupon Bond, also known as Pure Discount Bond or Accrual Bond, refers to those bonds which are issued at a discount to their par value and makes no periodic interest payment, unlike a normal coupon-bearing bond. In other words, its annual implied interest payment is included in its face value which is paid at the maturity of such bond.
Therefore, this bond is the one where the sole return is the payment of the nominal value on maturity. In the secondary market, zero coupon bond prices are quite discounted, hence, investors, look to buy at a lesser price and experience gains at maturity. Since the payment can only be redeemed at maturity, these bonds experience high volatility in price.
Zero coupon bonds are debt security instruments that do not pay interest like conventional bonds. Some bonds are issued as zero coupon whereas, some bonds are initially issued as regular bonds but are later converted into zero coupon bonds after a financial institution strips them of their coupons.
These Bonds are initially sold at a price below the par value at a significant discount, and that’s why the name Pure Discount Bonds referred to above is also used for these Bonds.
Since there are no intermediate cash flows associated with such Bonds, these types of bonds don’t result in reinvestment risk because there are no cash flows prior to maturity that must be reinvested. These calculations can be done using zero coupon bond calculators available on the internet.
Such bonds possess the greatest duration, which is equivalent to the maturity of such bonds and, as such, are subject to the greatest level of Interest Rate Risk.
Since the Interest accrued is discounted from the Par value of such Bonds at purchase, which effectively enables Investors of Zero Coupon Bonds to buy a greater number of such bonds compared to any other Coupon Bearing Bond.
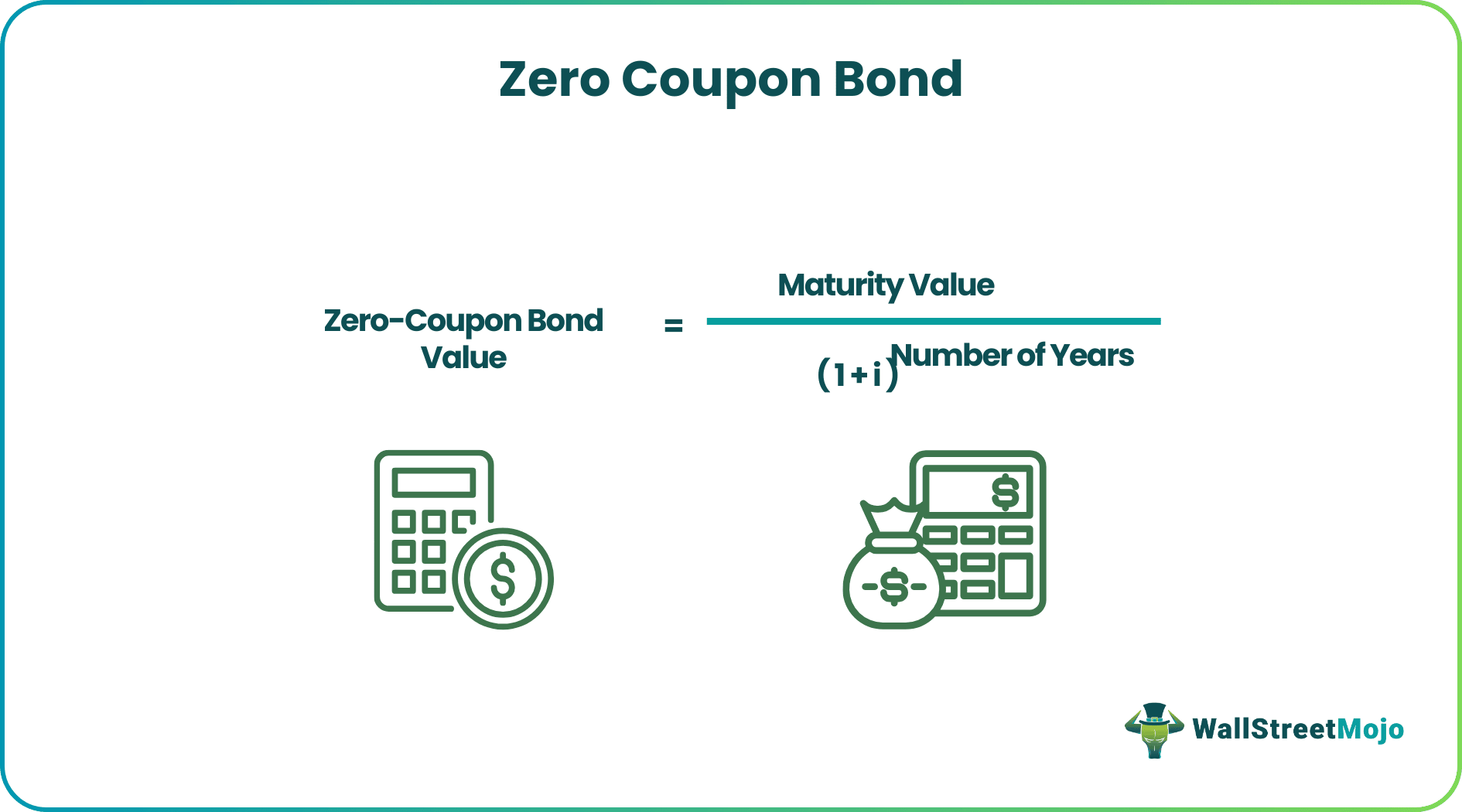
Let us understand the formula to use a zero coupon bond calculator. This shall act as the basis for calculations and understanding the intricacies of the concept.
Zero-Coupon Bond Value =Maturity Value/(1+i)^ Number of Years
Now that we understand the basics of zero coupon bond prices, its formula and basic ideology, let us apply them to a couple of examples to widen our rnage of understanding of the concept and its related factors.
Cube Bank intends to subscribe to a 10-year this Bond having a face value of $1000 per bond. The Yield to Maturity is given as 8%.
Accordingly,
Zero-Coupon Bond Value =

= $463.19
Thus, the Present Value of Zero Coupon Bond with a Yield to maturity of 8% and maturing in 10 years is $463.19.
The difference between the current price of the bond, i.e., $463.19, and its Face Value, i.e., $1000, is the amount of compound interest that will be earned over the 10-year life of the Bond.
Thus Cube Bank will pay $463.19 and will receive $1000 at the end of 10 years, i.e., on the maturity of the Zero Coupon Bond, thereby earning an effective yield of 8%.
When we talk about bond markets, we usually talk about the bond market in the United States or in the UK where both market has matured for quite some time. Let us take a deep dive into one of the largest emerging markets for bonds with a market value of over $1 trillion- India.
Post-COVID-19, the bond demand for zero coupon bonds has skyrocketed in the sub-continent which has been majorly caused by insurers to match their assets and liabilities in a better manner.
Moreover, it also helps them manage their cash flows better as these bonds can be traded as principal and coupons separately.
While the investor does not pay any sum towards the bond until maturity, they might still be subject to federal, state, or local taxes as the interest for these bonds is accrued every year.
This form of taxation is because the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) considers zero coupon bonds like original issued debt obligations.
Let us understand the advantages of using a zero coupon bond calculator and investing in them through the discussion below.
This offers predetermined returns if held till maturity, which makes them a desirable choice among investors with long term goals or for those intending assured returns and doesn’t intend to handle any type of Volatility usually associated with other types of Financial Instruments such as Equities, etc.
These Bonds avoid the risk of Reinvestment of Coupon Bonds as Interest Rates keep changing with the passage of time, which impacts the Yield to Maturity of such coupon-bearing Bonds. Since there are no interim cash flows, the investor is assured of a fixed rate of return.
Usually, these Bonds are issued for a longer time frame, which can be used by a potential investor to align with their life goals such as Marriage, Children Education, and retirement, and so on. Thus a smart investor based on their time horizon can invest in different maturity Zero-coupon Bonds by paying a smaller amount initially (as Zero-coupon Bonds are issued at deep discounts, one can buy more with lesser amount) and stagger them as per their career and life goals without getting impacted by the volatility.
Despite the advantages mentioned above, there are factors from the other end of the spectrum that prove to be a disadvantage for investors and regulators when it comes to zero coupon bond price and accrual. Let us understand the disadvantages through the explanation below.
Not all Zero-coupon Bonds have a ready secondary market, which results in illiquidity. Furthermore, in case of any urgent need funds, it is difficult to liquidate the same without getting a major haircut in value.
They have a single cash inflow for the Investor, which happens at the maturity, and as such, these bonds have the greatest Duration, which results in Interest Rate Risk. Further, These are issued with call provisions that allow the issuer of such Bonds to redeem the bonds prior to their maturity at dates and prices, which are predetermined at the time of the issue of such Bonds. In such cases, the Investor is left with the risk of reinvesting the proceeds at the rates available at the time of redemption, which will obviously be less than the earlier slated yield on the redeemed bonds.
It doesn't offer any regular source of income and is a complete misfit for those looking for a stable regular source of Income. Furthermore, one has to pay tax on the accrued interest on such bonds every year. However, it is pertinent to note here that there are certain categories of Zero Coupon Bonds, which can overcome the taxation problem.
Both zero coupon and coupon bonds are debt obligations, there are obvious and some technical differences in their fundamentals and implications. Let us understand their differences through the comparison below.
| Basis | Zero-Coupon Bond | Regular Coupon Bearing Bond |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Meaning | It refers to fixed Income security, which is sold at a discount to its Par value and doesn't involve any cash flow during the life of the Bond except on maturity. | It refers to fixed Income security, which involves regular payment in the form of coupons and may be issued at a discount or premium depending upon market dynamism. |
| 2. Coupons | No Interest Coupons during the lifetime | Regular Coupons semi-annually or annually. |
| 3. Duration | The duration of a Zero-coupon Bond is equal to the maturity of the Bond. | The duration of the Regular bond will always be less than its maturity. |
| 4. Interest Rate Risk | Involves the greatest level of Interest Rate Risk due to the high duration of the Bond. | Comparatively less than Zero Coupon Bond. |
| 5. Reinvestment Risk | There is no Reinvestment Risk in a Zero-coupon Bond as there are no cash flows during the life of the Bond. | Suffers from Reinvestment Risk due to regular cash flow in the form of coupon payments during the life of the Bond. |