Table Of Contents
What Is Withholding Tax?
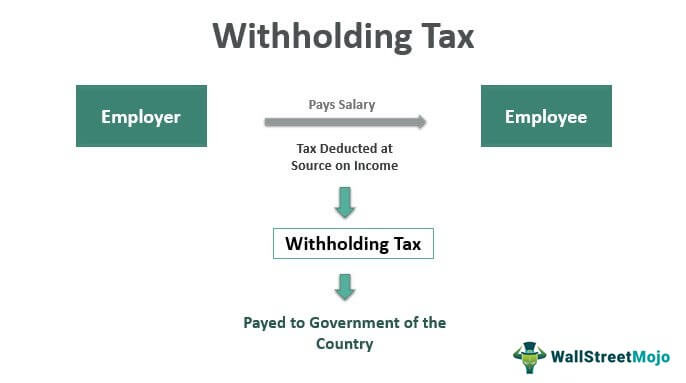
Withholding tax, or retention tax, is usually deducted from the source of income by the payer. The payer may include people who are residents of another country on an employee of a domestic company. The income may be interest income and dividend income as per the tax laws of the country charging withholding tax. The tax is then remitted to the government of the country.
This tax collection system ensures that the process is efficient and transparent. The primary responsibility is with the payer, and the tax rates vary from country to country, depending on the tax laws. It is also applicable to individuals who are non-residents and who are earning in another country.
How Does Withholding Tax Work?
The withholding tax or retention tax is a type of tax deducted at source. The tax can be on interest, dividend and other income of the recipient by the payer of such income and then remitted to the government directly.
Further, the receiver on which it is applied can be a person, either Resident or Non-resident of that country. For the purpose of residential status, the country’s tax norms are taken into consideration. Also, retention tax is deducted from the income having its source in the deducting country itself which may be a dividend withholding tax or tax on interest income.
Withholding tax is usually deducted at source on income by the payer on various parties including people resident of another country and the same is very important from the perspective of both the government as well as the general public in terms of property tax management and early collection of taxes from residents and non-residents as well as salaried employees.
Types
Following are the various types of withholding tax imposed on numerous persons as per the tax norms of country charging such tax:
#1 - Withholding Tax on Payments to Foreign Persons
- Retention taxes on the income of the foreign person is deducted at source at a fixed rate of 30% on the Gross amount of income.
- These are the retention taxes which are deducted at source by the federal government of the USA on the foreign person on their certain kinds of receipts.
- Also, partnership firms pay the taxes off on the incomes earned by the foreign partners from the partnership firms.
- Interest income of the non-residents, dividend withholding tax from domestic companies, and compensation for services, rent receipts, royalties, and annuities are certain kinds of payments that are subject to withholding taxes on the non-residents of the country deducting the retention taxes.
#2 - Wages Withholding tax
- Wages withholding taxes are the graduated tax rates, and hence higher wages will be liable for higher withholding taxes. In contrast, the lower retention tax will be responsible for lower withholding tax, and therefore there is fair treatment of every class of employees.
- The employers are deducting it on the salary and wages of the employee.
- Further, withholding allowances on the retention taxes are a part of the calculation of retention taxes since the withholding allowances are the tax exemptions on withheld no retention taxes are deducted.
#3 - Backup Withholding on Dividends and Interest
- Backup withholding taxes, as the name suggests, are deducted on the dividend and interest of the recipient.
- Here, federal income tax is being deducted at source on such interest dividends and other kinds of incomes at the time of payment to the stocks and other instrument holders.
- Applicability: Backup retention taxes are applied if the recipient is a foreign person as well as either the person does not provide the Tax Identification Number under form W 9, or the person has been notified by the Indian revenue service as the person on whole retention tax is required to be deducted.
How To Calculate?
The withholding tax computation process of this type of tax varies from country to country and depends on the tax laws of the specific jurisdiction. These are calculated and deducted based on two things, the amount of income earned and the details provided by the employee to the employer in term W-4.
Let us look at some basic steps.
- Determine the tax rate – According to the guidelines, the tax rate has to be determined as per the type of income. Rates also depend on the residential status of the recipient.
- Payment calculation to charge tax – The amount of income on which the tax will be charged should be calculated properly.
- Apply the tax rate – The next step is to multiply the payment or income with the tax rate. This step shows the amount of withholding tax percentage that should be withheld.
- Deduct the tax from the gross payment – The final step is to deduct the tax amount from the gross payment to get the net amount of income that will be paid to the recipient.
However, there may be other rules of exemptions that should be taken into account while making the calculation.
For each category of recipients, withholding tax computation is done differently. For example, the retention tax on wages is calculated as per the withholding table and publication 15. In contrast, retention tax on an individual is calculated on various regular income as well as lottery, betting, etc. using the withholding estimator and expected income.
Examples
Now let us understand the calculation with the help of a withholding tax example.
Suppose Mr. X earns a salary of $ 36,000 per year. With the yearly salary of $ 36,000 his monthly income comes to $ 3,000 ($ 36,000 / 12).
However, a 10% withholding tax is deducted from the same; hence, he takes home only $ 27,000 ($ 30,000 – $ 3,000), and the balance of $ 3,000 is deducted at source as the withholding tax percentage is 10%.
Why Is It Charged?
Let us look at some reasons why this kind of tax is charged.
- The most crucial reason for charging the retention tax is that it relieves a person from paying massive amounts all together in a single month. Hence, it is a type of advance tax that is deducted and paid by the payer to the government every month, etc.
- Thus like an insurance policy where a smaller amount is paid periodically for a considerable shelter in the future, retention tax works the same way.
- Also, for the government, it becomes a huge relief since their day to day expenses can be made out of such periodic payments instead of waiting for so long.
How To File?
The withholding tax example given above shows the calculation but there are some procedures to file it.
Even though the filing of the tax return is based on the rules and tax laws of the jurisdiction, there are some common steps that should be followed while doing so. Let us study the steps.
- Filing requirements – it is necessary to understand and be familiar with the rules of filing tax returns in that country. The frequency of filing and the deadline of submitting the same should be adhered to strictly.
- Collect documents – The documents and the records required to file is very important and should be gathered on time. Such records include the calculation details, the payee details, and any other supporting forms or certificates.
- Complete the form – Then comes the step of filling up the correct form given by the tax authority. The information should be accurate and complete so that there is no mismatch or problems later on. The instructions for filling up the form should be followed for proper reporting.
- Form submission – The completed form must be submitted to the designated tax authority within the deadline. It may be done electronically or through post.
- Payment of tax – If the return indicates that extra tax is to be paid then it has to be done. If there is a refund because the withheld tax is more than the liability, it will be settled as per the rules.
Withholding Tax Rates
In the United States of America, withholding tax is generally deducted at 30% on miscellaneous income of non-residents like interest, royalty, etc. Thus most of the payments to foreign persons are deducted @30% with certain exemptions. But specific reduced rates depend upon those exemptions, including exemptions by the internal revenue code or the tax treaties between governments of various countries.
Withholding Tax Vs Tax Deducted at Source (TDS)
There is a thin line difference between withholding tax and tax deducted at source (TDS) where the retention tax term is usually more prevalent in case of out of country payment or the payment made to non-residents. The same is the amount the payer deducts well before the actual price and then deposits to the government as per the due date. At the same time, tax deducted at source is the amount deducted when making payments and paid to the government on behalf of the recipient.
