Table Of Contents
Wire Fraud Definition
Wire fraud is a federal crime involving defrauding an individual or a party using electronic communication such as chat rooms, emails, phone calls, and fax. In addition, the fraudster may use deception techniques to gain money, property, or other benefits from the victim unlawfully. This cybercrime is punishable with severe penalties.
In the United States, the geographical span of the crime also defines wire fraud. According to the constitution, it specifically occurs across state lines. Even though it involves a vast spectrum of crimes, some common examples of wire fraud are online phishing, identity theft, catfishing, credit card frauds, telemarketing scams, etc.
Table of contents
- Wire Fraud Definition
- Wire fraud is a crime wherein individuals use electronic means such as email or phone calls to defraud individuals or other entities such as financial institutions in other states. The elements of this fraud include a wired communication system, the intent to defraud a person, and the usage of the wire communication system for making a deception.
- Phishing, telemarketing frauds, Nigerian prince scams, identity thefts, etc., are common examples of wire fraud.
- The wire fraud penalty depends on whether it was an individual or financial institution that the fraudster targeted. For individuals, a single act of fraud can result in a prison sentence of up to 20 years. For financial institutions, the fine can be up to a million dollars, and the individual can get a jail time of a maximum of 30 years.
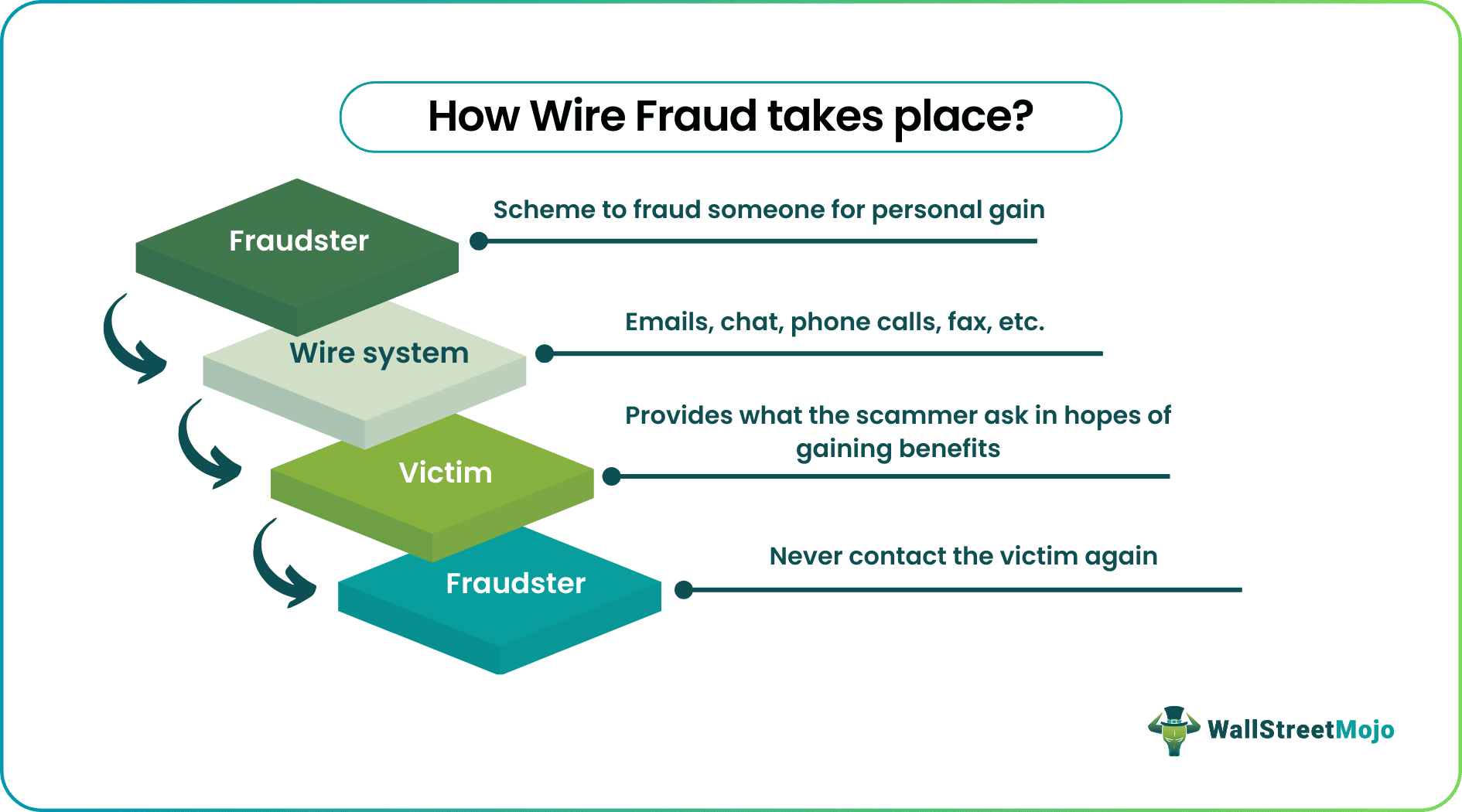
How Does Wire Fraud Work?
Wire fraud occurs when a person willingly/intentionally uses an electronic means of communication to defraud someone else. In most cases, the fraudster may be looking for monetary gain. But they can also demand any items of value. The fraudster subjects the aggrieved party to promise or deception, encouraging them to transfer valuable property to them. The process of convincing the other individual usually occurs through electronic means of communication, but the victim can send the benefits in various ways. The fraudster can even come to pick up cash or other valuables after the fraudster has convinced them to give it up. Wire fraud is criminal because, after the transfer of the property, the fraudster does not keep his promise.
An act of wire fraud is characterized by:
- An intent to deceive someone
- A wire communication system
- The actual usage of interstate wire communication system to make the deception.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
When is a person convicted of Wire Fraud?
The law can convict a person of a wire fraud felony even if they didn’t receive any cash or valuable items in hand. The act of attempting to receive valuable property from someone across state lines through deception is enough to convict the individual. In this scenario, the victim does not have to have suffered any loss; they only need to have been approached by the fraudster who promised something in exchange for money but had no intention of providing the said goods or services.
One might have tried to defraud more than one party in a wire fraud felony. In this case, the court treats each case as a different offense. It might result in long sentences if the fraudster defrauded or attempted to defraud more than one party. The court may not allow the defendant to carry out the sentences consecutively since each case is a charge on its own. If three fraud cases are committed, the court would treat it the same way three counts of robbery with violence carried out over several months would be treated.
Examples
One of the examples of wire fraud is the Nigerian Prince Scam. In this type of fraud, a potential victim receives an email from a purported wealthy individual. They ask for help in the form of a relatively small amount of money so that they access their funds. They then promise to send the individual a large sum of money as thanks for helping them. However, once an individual falls prey to the scam and sends money, the scammers stop having any contact with them.
In the Nigerian email scam, the fraudsters may advise the victim to send money in the form of a wire transfer or through the purchase of coupons. Generally, the scammers attempt to get the funds irreversibly. Despite being the oldest trick in the book, the Nigerian email scam is still in full swing around the globe.
Although it is the Nigerian scam(or a “419” scam), individuals from any part of the world can initiate it. This scam was first incepted in Nigeria, where scammers would pose as a wealthy Nigerian prince who could not access his money. The specialty of this scam is Emails with grammatical errors so that illiterate people can fall for it easily.
Another example is phishing, where the fraudster tricks the victim into sharing their crucial personal information. They do this by pretending to be someone the victim tends to trust. The scammer can then use the data to steal from the victim, misuse their identity or conduct unauthorized activities in the victim’s name. Many consider phishing as the most common type of cybercrime today.
Wire Fraud Video Explanation
Wire Fraud Statutes & Limitations
The statute of limitation for wire fraud is five years. However, if the aggrieved party is a financial institution, the statute of limitation is ten years.
The crime must be initiated in one state and completed or targeted at parties in other states. One potential limitation of prosecution is the proof of the defendant’s good faith or belief. It is the argument that they believed they could offer the services they were asking for compensation for.
Wire Fraud Penalty
The wire fraud penalty in the United States is a fine and a jail term that does not exceed 20 years. The fines charged can be up to $250,000 for individuals and $500,000 for organizations. If the fraud involved a financial institution, penalties could be as much as a million dollars in fines and a maximum of 30 years in prison for each fraud case.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Wire fraud is a punishable act of cybercrime that can bring severe fines and jail sentences under federal law. It can invite a jail time of no more than 20 years in the United States.
Nigerian prince scam is a very common case which, still, people fall prey for. Other examples of wire fraud include phishing, telemarketing frauds, identity thefts, catfishing, credit card fraud, etc. The spectrum of these crimes is a little broadly-defined, and any act of gaining personal benefit from a person under false promises through a wired electronic system can be considered criminal.
Both are fraudulent white-collar crimes punishable under the rules of federal law in the United States; but they are not the same. Embezzlement is the misuse of assets entrusted to a person, while wire fraud is defrauding someone under false promises through electronic means.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to what is Wire Fraud & its definition. Here we explain how does it work along along with examples, penalty, statutes & limitations. You can learn more about from the following articles –

