Table Of Contents
What is Risk Management?
Risk management is the prediction and mitigation of potential risks associated with a particular business. Risk managers develop and implement solutions to either completely avoid the risk or minimize its negative impact.
Every company needs a risk management plan to deal with business risks, if and when they occur. Risks could be security issues, financial loss, reduced productivity, labor crisis, inventory shortage, or a tarnished reputation. Investors must operate within the limits of their risk appetite.
- Risk management involves the identification of potential risks and taking strategic actions to mitigate those risks.
- Business operations are risky by design. In finance, acknowledging the constant presence of risk at every turn is considered the right approach. There is always a chance of uncertain and unfortunate occurrences.
- Risks are primarily classified into three types—business risks, non-business risks, and financial risks.
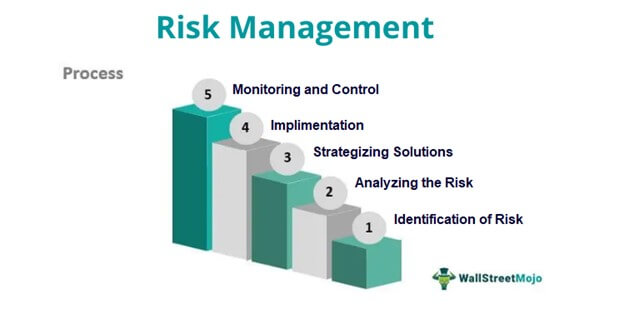
- The risk mitigation process comprises—risk identification, risk analysis, strategizing solutions, implementation, and the monitoring of the results.
Risk Management in Finance Explained
Risk management in finance is all about anticipating the risks involved in a particular scenario. For example, a fund manager hedges derivatives, a retail investor buys bonds for the first time without any proper analysis and fundamentals, and people take enormous debts and then default on payments. In all those scenarios, there is a varying level of risk involved.
When investors fail to prepare for risks, it can cost them severely. In finance, acknowledging the constant presence of risk at every turn is considered the right approach. If investors can anticipate risks, they can also take appropriate measures to mitigate them. Investors are highly recommended to operate within the limits of their risk appetite.

However, risks are uncertain; therefore, every organization needs to prepare risk management strategies, beforehand. A financial loss is the most severe form of damage a company can incur. Business operations constantly require debts, payments, and credit.
To mitigate risks associated with them, every firm needs a risk management plan. With planning and preparation, potentials risks can be predicted—risk mitigation strategies can be executed in time.
Examples
Let us look at some examples to understand the practical application of this concept.
Example #1
Janice has invested a reasonable amount of money in a company. She has followed the company's progress for years and has detailed knowledge - market capitalization, goodwill, and future growth prospects. But in the aftermath of the pandemic, the company deteriorated—sales declined, and product quality went down.
To make matters worse, the company took huge debts from different creditors and lenders. Meanwhile, new alternatives were made available to the company’s target customers. Due to poor customer service, the company’s long-term customers started buying from its competition.
Janice reads about the problems, predicts potential risks, and decides to sell her holdings. Soon the company's share price dropped, but Janice secured her investment.
In risk management, this is referred to as a risk-avoidance strategy. Janice identified the problems, analyzed the risks, and implemented decisions.
Example #2
A chocolate company has been a market leader in the food industry for years; suddenly, new companies enter the market. The market leader had a considerable market share.
But, a recent survey highlighted a growing taste for the competitor's product. Also, the newly introduced products were priced much lower.
The management identifies a potential risk in time. They reanalyze numbers to ascertain any new trends. The data shows a noticeable decline in sales. To mitigate risks, the company takes action—a new flavor of chocolate is introduced into the market. In addition, the market leader announces a discount price on all its other products.
Soon, the company witnesses a sharp increase in its revenue. Eventually, the new entrant is pushed out of the market.
Risk Management Process
Firms need a structure to deal with potential risks if and when they arrive. The process involves the following steps:
#1 - Identification of Risks
There are different types of risks—legal risks, market risks, regulatory risks, and environmental risks. A firm can face one issue or multiple risks at once. Therefore, the nature of the risk needs to be understood first. It is then conveyed to company stakeholders.
#2 - Analyzing the Risks
Whenever a firm anticipates a threat, it comes with a scope of impact linked to direct and indirect factors. Once the risk is identified, its severity is determined based on potential impact. The impact could range from minor errors to the entire business coming to a standstill.
#3 - Strategizing Solutions
Based on the analysis, the firm comes up with multiple solutions. Ultimately, the best possible solution is selected. The risk management strategy functions like a roadmap—from identifying the threat to rectifying it.
#4 - Implementation
Before implementing the best possible solution, its pros, cons, conflicts, and consequences are considered. When firms take action to mitigate risk, the action in itself can cause a chain reaction damaging other operations. The mitigation strategy should be inexpensive, doable, and realistic to market scenarios.
#5 - Monitoring and Control
After taking action, the impact is recorded and monitored to understand how it brings the necessary changes. The firm determines whether the expected results are shown or not. In addition, firms lookout for any negative impacts brought out by the risk mitigation strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The process involves the identification and elimination of potential risks. Business is risk-prone by design. Alternatively, if the risk cannot be eliminated completely, they are minimized. There are various kinds of risk; firms develop a risk management plan to deal with potential risks.
The five components of risk mitigation are as follows:
1. Risk identification
2. Risk assessment
3. Risk mitigation
4. Risk monitoring
5. Risk governance.
When investors fail to prepare for risks, it can cost them severely. In finance, acknowledging the constant presence of risk at every turn is considered the right approach. If investors can anticipate risks, they can also take appropriate measures to mitigate them.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What is Risk Management & its Definition. We explain risk management plans, meaning, process, trading, & finance examples. You can learn more about accounting from the articles below –
