Table Of Contents
What is Weighted Mean?
The weighted mean equation is a statistical method that calculates the average by multiplying the weights with their respective mean and taking its sum. It is a type of average in which weights assign individual values to determine the relative importance of each observation. The weighted mean formula statistics are useful across sectors such as finance, education, and economics.

The weighted mean allows for the incorporation of varying degrees of importance or significance among data points in a dataset. By assigning weights to each value, the weighted mean reflects the relative importance of different elements, making it a valuable tool in situations where certain values carry more weight or relevance than others.
Key Takeaways
- The weighted mean equation is a statistical approach for calculating the average by multiplying the weights with their respective mean and taking its sum.
- It is a type of average where weights are assigned individual values to find each observation's relative importance.
- One may determine the weighted mean by multiplying the weight with the quantitative outcome and adding all the products.
- If all the weights are equal, then the weighted and arithmetic mean are the same.
- The weighted mean may help an individual make decisions where some characteristics have more significance than others.
Weighted Mean Formula Explained
The weighted mean, also known as the weighted average, is a statistical measure that calculates the average of a set of numbers, where each number is assigned a weight indicating its relative importance or contribution to the overall average. Unlike the simple arithmetic mean, where each value carries equal weight, the weighted mean assigns different weights to each value based on predetermined criteria.
To calculate the average weighted mean formula, one multiplies each value by its corresponding weight and then divides the sum of these products by the sum of the weights. This method allows for the prioritization of certain values over others, reflecting their significance or relevance in the context of the data set.
Weighted means are commonly used in various fields, such as finance, economics, and education, where certain data points may carry more significance than others. For example, in financial analysis, the weighted mean may be used to calculate the average return on investment in a portfolio, with each investment's weight reflecting its proportion of the total portfolio value.
In educational settings, teachers may use weighted means to calculate final grades, assigning different weights to exams, quizzes, and homework assignments based on their importance in assessing student performance. Similarly, in economic analysis, the weighted mean may be used to calculate composite indices, such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI), where the weights reflect the relative importance of different goods and services in measuring inflation.
Overall, the weighted mean provides a flexible and customizable approach to calculating averages, allowing analysts to account for varying degrees of importance or significance among the data points in a given dataset.
Formula
The weighted mean formula statistics are calculated by multiplying the weight with the quantitative outcome and adding all the products. If all the weights are equal, then the weighted mean and arithmetic mean will be the same.
Weighted Mean = ∑ni=1 (xi*wi)/∑ni=1wi
It implies that Weighted Mean = w1x1+w2x2+…+wnxn/w1+w2+…+wn
Where
- ∑ denotes the sum
- w is the weights and
- x is the value
In cases where the sum of weights is 1,
Weighted Mean = ∑ni (xi* wi)
How To Calculate?
Let us understand the step-by-step process of calculating the average weighted mean formula through the points below.
List the numbers and weights in tabular form. Presentation in tabular form is not compulsory but makes the calculations easy.
Multiply each number and the relevant weight assigned to that number (w1 by x1, w2 by x2, and so on).
Add the numbers obtained in Step 2 (∑x1wi).
Find the sum of the weights (∑wi).
Divide the total of the values obtained in Step 3 by the sum of the weights obtained in Step 4 (∑x1wi/∑wi).
Note: If the sum of the weights is 1, then the total of the values obtained in Step 3 will be the weighted mean.
Examples
Now that we understand the basics of weighted mean formula statistics, let us also understand the practicality of the concept through the examples below.
Example #1
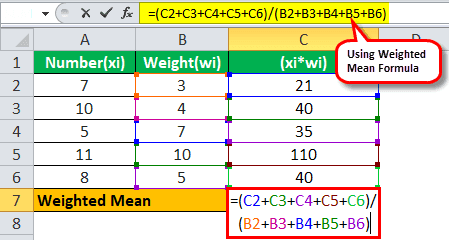
The following are 5 numbers and the weights assigned to each number. Next, calculate the weighted mean of the above numbers.
Solution:



WM will be -

Example #2
The CEO of a company has decided that he will continue the business only if the return on capital is more than the weighted average cost of capital. The company makes a return of 14% on its capital. The capital consists of equity and debt at 60% and 40%, respectively. The cost of equity is 15%, and the cost of debt is 6%. Advise the CEO on whether the company should continue with its business.
Solution:
Let us first present the given information in tabular form to understand the scenario.
We will use the following data for the calculation.


WM =0.60*0.15 + 0.40*0.06
= 0.090 + 0.024

Since the return on capital at 14% is more than the weighted average cost of capital of 11.4%, the CEO should continue with his business.
Example #3
It is difficult to gauge the future economic scenario. The stock returns could get affected. The finance advisor develops different business scenarios and expected stock returns for each scenario. Therefore, it would enable him to make a better investment decision. Calculate the weighted mean average from the above data to help the investment advisor showcase the expected stock returns to his clients.
Solution:
We will use the following data for the calculation.



=0.20*0.25 + 0.30*(-0.10) + 0.50*0.05
= 0.050 – 0.030 + 0.025
WM will be -

The expected return for the stock is 4.5%.
Example #4
Jay is a rice merchant who sells various types of rice in Maharashtra. Some rice grades are of higher quality and sold at a higher price. He wants you to calculate the weighted mean from the following data:
Solution:
We will use the following data for the calculation.

Step 1: In Excel, there is an inbuilt formula for calculating the products of the numbers and their sum, which is one of the steps in calculating the weighted mean. Select a blank cell and type this formula = SUMPRODUCT(B2: B5, C2: C5), where the range B2: B5 represents the weights and the range C2: C5 represents the numbers.

Step 2: Calculate the sum of the weights using the formula =SUM(B2: B5), where the range B2: B5 represents the weights.

Step 3: Calculate =C6/B6,


WM will be -

It gives the WM as Rs 51.36.
Relevance and Uses
Weighted mean can aid an individual in making decisions where some attributes have more significance than others. For instance, one generally uses it to calculate a specific course's final grade. In courses, the comprehensive exam typically has more weight on the grade than chapter tests. Thus, if one performs poorly in chapter tests but does well in final exams, the weighted average of the grades will be relatively high.
One may use it in descriptive statistical analysis, such as calculating index numbers. For instance, stock market indices such as Nifty or BSE Sensex are computed using the weighted average method. One can also apply it in physics to find the center of mass and moments of inertia of an object with a known density distribution.
People in business often calculate the average weighted mean formula to evaluate the average prices of goods purchased from different vendors where the quantity is considered the weight. It gives a businessman a better understanding of his expenses.
One can apply the weighted mean formula to calculate the average returns from a portfolio comprising different financial instruments. For instance, let us assume equity consists of 80% of a portfolio and debt balance 20%. The returns from equity are 50% and from debt are 10%. The simple average would be (50%+10%)/2, which is 30%.
It gives a wrong understanding of the returns, as equity constitutes most of the portfolio. Hence, we calculate a weighted average, which works out to be 42%. This number of 42% is much closer to equity returns of 50%, as equity accounts for most of the portfolio. In other words, the returns pull by an equity weight of 80%.
Weighted Mean Vs Mean
Let us understand the differences between weighted mean and mean through the comparison below.
Weighted Mean
- Incorporates weights assigned to each value based on their relative importance or contribution.
- Calculated by multiplying each value by its corresponding weight and dividing the sum of these products by the sum of the weights.
- Useful when certain values have more significance or relevance than others in the dataset.
- Commonly used in finance, economics, and education to calculate averages where some data points carry more weight.
Mean
- A simple average is calculated by summing up all values and dividing by the total number of values.
- Treats each value equally without considering their relative importance or contribution.
- Suitable for datasets where all values have equal significance.
- Widely used in basic statistical analysis and everyday calculations.
- It may not accurately reflect the true average when certain values significantly deviate from the others or have varying degrees of importance.