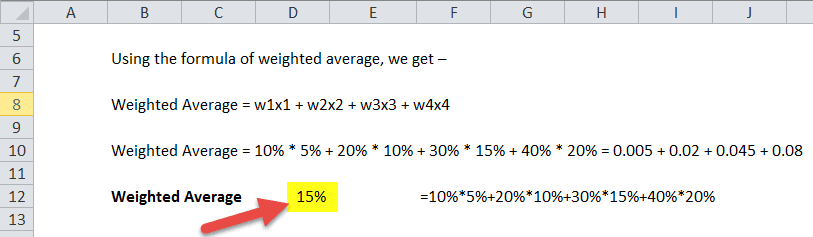Table Of Contents
How Is Weighted Average Calculated?
The weighted average is an average that considers the relative importance of each value under consideration. One may calculate it by multiplying the respective weights (in percentage terms) with their corresponding value. The weighted average is used to determine portfolio returns, inventory accounting, and valuations.

Each quantity in the simple weighted average formula is assigned a weight. These weights thereby determine the importance of each quantity of the average. These figures help especially in situations where the inventory or any other data points are intertwined and complex. Inventory accounting methods such as FIFO and LIFO are also significant in the weighted average.
Key Takeaways
- The weighted average is an average that considers each value's relative importance.
- One may compute it by multiplying the respective weights in percentage with their adjacent value.
- Calculating the weighted average capital, equity, and debt cost are considered. One may calculate the WACC based on the company's capital structure.
- One may also utilize the weighted average method for calculating the outstanding shares accessible in the year.
Weighted Average Formula Explained
On a simple average, we don’t pay heed to the weight. The result becomes too generic when we calculate the simple average. However, in the weighted average, we pay the right emphasis on the right weight, and we portray the weight in terms of percentages.
If you look at the weighted average formula, you will see that the value is multiplied by the right amount of weight, which is the beauty of the weighted average.
- For example, if we need to find the average of 10, 13, and 25 on a simple average, we will add three numbers and divide them by 3. Simple average of the above three numbers would be = (10 + 13 + 25) / 3 = 48 / 3 = 16.
- The result would be quite different if we took the same example with weight. Let’s say that the weight of number 10 is 25%, 13 is 30%, and 25 is 45%. Weighted average of the above three numbers of would-be = (10 * 25%) + (13 * 30%) + (25 * 45%) = 2.5 + 3.9 + 11.25 = 17.65.
Formula
Weighted Average Formula = W1X1 + W2X2 +......+WnXn
Here, w = respective weight (in percentage), x = value
Example
Let’s take a simple weighted average formula example to illustrate how we calculate a weighted average.
Ramen has invested an amount into four types of investments: 10% in Investment A, 20% in Investment B, 30% in Investment C, and 40% in Investment D. The rates of return for these investments are 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20%. But, first, calculate the weighted average of the rates of return Ramen would receive.
In this weighted average example, we have both w and x.
Using the weighted average formula, we get the following:
- Weighted Avg = w1x1 + w2x2 + w3x3 + w4x4
- Weighted Avg = 10% * 5% + 20% * 10% + 30% * 15% + 40% * 20% = 0.005 + 0.02 + 0.045 + 0.08 = 15%.
Uses
The usage of the weighted average is quite broad. However, let us understand the major uses of weighted average formula accounting through the discussion below.
As for the weighted average example, we can talk about the weighted average cost of capital. In calculating the weighted average cost of capital, we consider the cost of equity and the cost of debt. And depending on the company's capital structure, we calculate the WACC.
Another example where we use the weighted average cost of capital is the issuance of outstanding shares. Let's say a firm issued 100 shares on the 1st of January. And then another 100 shares are issued on the 1st of July.
Now, we will use the weighted average method while calculating the outstanding shares available during the year. Since the first 100 shares are issued on the 1st of January, it would be applicable for the whole year. But the next 100 shares are only issued in the middle of the year. That's why the next 100 shares would be available only for 6 months. And here would be the calculation of weighted average of outstanding shares = (100 * 1) + (100 * 0.5) = 100 + 50 = 150.
Weighted Average in Excel (with Excel template)
Let us now calculate the same example as above in Excel. MS Excel makes weighted average formula accounting simpler and more efficient. Let us discuss:
It is very simple. You need to provide the values of "X" and "Y."
Then, you can easily calculate the ratio in the Weighted Average in the Excel template provided.