Table Of Contents
What Is Wasting Asset?
A wasting asset is a type of asset whose useful life is limited. Therefore, its value decreases over time, including fixed assets like vehicles, plants, property, and equipment or financial instruments like options.
Wasting assets are very commonly encountered in everyday life. Unfortunately, most of the assets we can think of, natural resources like petroleum, car, or even a life insurance policy, most of the assets depreciate with time and usage. Therefore, it is up to the analyst to understand the asset and its usage to determine the method to decrease the asset's value over time.
Key Takeaways
- Wasting assets are a type of asset whose value decreases over time due to limited useful life. Examples of wasting assets include fixed assets like vehicles, plants, property, and equipment or financial instruments like options.
- The ownership of wasting assets can provide advantages, including tax savings, by claiming depreciation against the equipment bought. However, the maintenance cost of an asset may be quite high, especially in the latter stages of its life.
- Options are also considered wasting assets, with their value decreasing over time due to the option's expiration.
Wasting Asset Explained
The wasting assets in accounting are also called depleting assets and can be explain to be the ones that have a very limited useful life. The business expects to consume or use them up within a short time or they get depleted over time on their own. They also reduce due to usage, extraction or through any natural process.
These kinds of assets decrease in their value as they are continuously used. Some very common examples are mines, natural resources, etc, that get exhausted due to extraction. It is important to conder these type of assets both from environmental and economic perspective.
There are various industries that rely to a huge extent on these types of assets, leading to continuous usage. Therefore, these industries should manage and control their operation in a very sustainable manner so that the resources or assets can be used for a longer time frame and available to all equally.
Over extraction or usage also harms the environment in a negative way. Wasting assets like vehicles, or equipment needs energy extracted from natural resources to work properly. Thus, over usage leads to resource depletion on one hand and pollution on the other. Plants also fall under the category of such assets, whose depletion can disturb the balance of nature.
Types And Formula
Now let us look at different kinds of wasting assets and how to calculate their decrease in value over some time (also known as depreciation in some cases)
#1 - Factory/ Buildings / Office Furniture
These wasting assets in accounting are types of fixed assets are generally depreciated equally over their useful life. The straight-line depreciation method is used in this scenario. This is the simplest method of calculating depreciation, and the depreciation expense is the same each year, evenly spread over the years. The formula used for calculating depreciation is
Depreciation Expense = (Cost – Salvage Value) / Useful Life
where,
salvage value is the value (can be the selling value) of the asset at the end of its life.
#2 - Vehicles
Vehicles like cars and trucks also fall under the list of wasting assets and are generally used very heavily in the initial years and, as such, should be depreciated rapidly in the initial years. We use the double-declining method in that case, which is very similar to the straight-line method apart from the fact that the depreciation rate is twice that of the first method. It assumes that the equipment depreciation rate is higher in the initial years as the machine is used more initially. The formula used for calculating depreciation is
Depreciation Expense = Beginning book value x Rate of Depreciation
where,
Rate of depreciation = 100%*2/Useful Life
#3 - Machinery
The value of plant and machinery decreases over time due to depreciation. Depreciation is the term used to describe the rreduction in the value of these assets and needs to be accounted for in the books of accounts of wasting asset corporation so that the fair value of the asset is reflected in the financial statements.
Machines/production equipment and the depreciation is calculated based on the number of units produced and are depreciated by the Units of Production method.
Depreciation Expense = (Number of Units Produced / Life in Number of Units) x (Cost – Salvage Value)
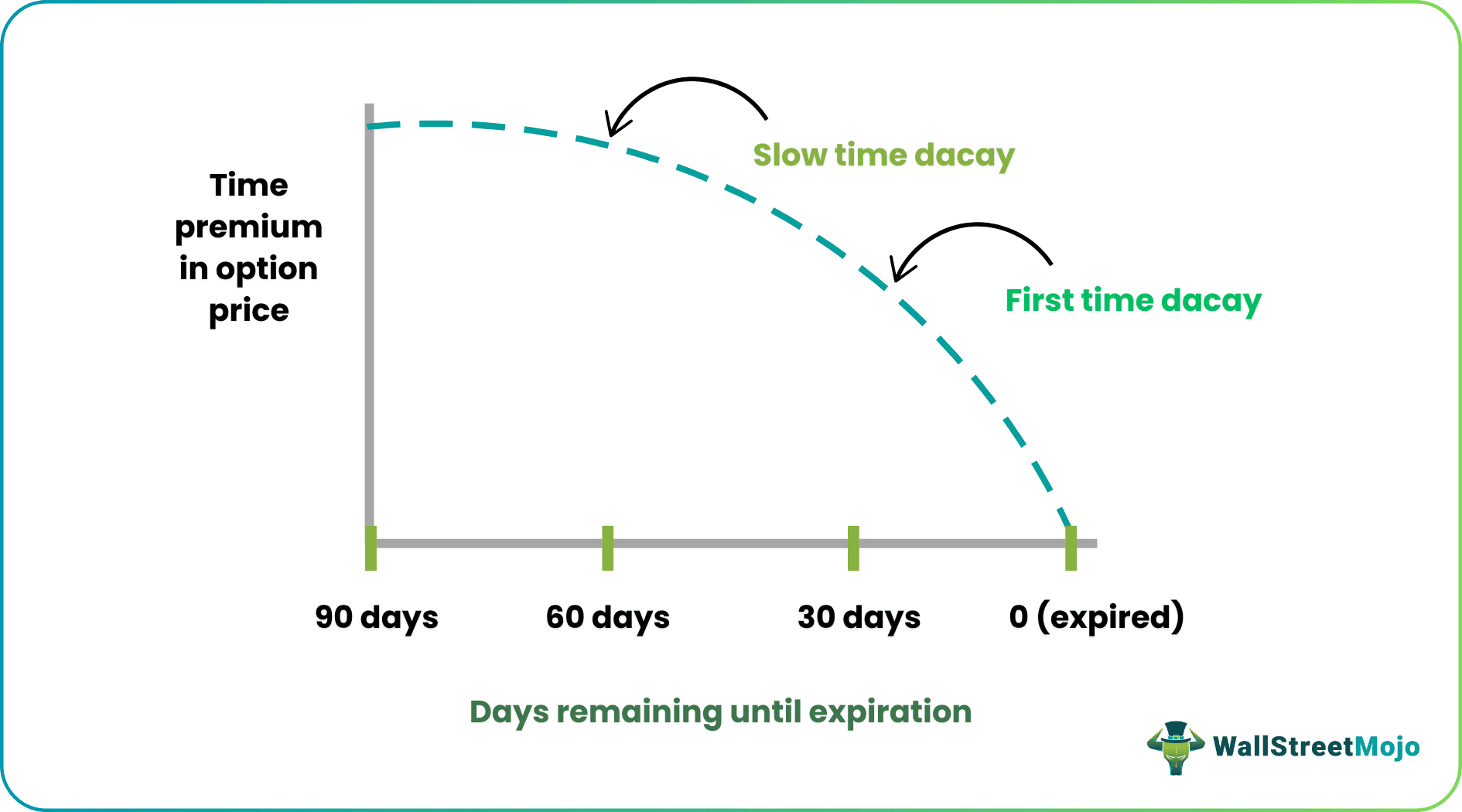
#4 - Options
Enough of depreciation, we have completely ignored the other type of wasting asset called options, which we will briefly describe.
In layman's terms, a term option is a type of instrument which allows the owner of the option to buy or sell a share at a certain price called the strike price. The price of an option depends on a few factors, the most important of which are
- Difference between the strike price and the current price of the stock: This is because if, for an example, the buyer has the option to buy a share price of $100 for $60, he is making a profit of $40 (the difference between the strike price and exercise price)
- The options have an expiry associated with them, after which the owner can no longer exercise them, and here comes the concept of time decay of options. The closer the options get to the expiry date, the lesser the owner's probability of making a profit. Finally, the option's value becomes zero on the day of expiry.
#5 - Natural Resource
Natural resources like petroleum reserves, coal mines, etc., are depleted over time based on the quantity extracted. This is because they are finite in nature and takes an extremely long time period to get replenished. But compared to the time taken to get replenished, the usage takes place faster.
Examples
Let us understand the concept with the help of some suitable examples.
Example #1
Consider a building with an initial value of $1000 and a useful life of four years. Then, considering a salvage value of $200 at the end of its life, we can calculate the depreciation expense each year as (1000-200)/4 = $200 and create a depreciation schedule as given in the following table.

Example #2
Consider a car with an initial value of $1000 and a useful life of four years.
In this method, the rate of depreciation is 2*100%/4 = 50% each year. So in the first year, the depreciation expense will be 1000*.5 = $500; in the 2nd year, it will be $500*.5 = $250, and so on.

Another method of calculating accelerated depreciation is the sum of the years' depreciation method.
In this method
Depreciation Expense = (No of Years Remaining / Sum of Years) x (Cost – Salvage Value)
Consider a car with an initial value of $1000, a salvage value of $100, and a useful life of four years.
So in the first year, the remaining years will be 4, and the sum of the years will be 1+2+3+4 =10, and the depreciation will be four*(1000-100)/10 = $360.

Example#3
Let us suppose a piece of equipment of wasting asset corporation that produces five, six, four, and ten units respectively in the four years and has a salvage value of $100.
The depreciation expense for the first year would be given as five*(1000-100)/(5+6+4+10)= $180 and so on.

Example#4
Consider a coal mine in which a mining company acquired for $10 million and used another $5 million to develop the site. Finally, consider the mining company that can sell the mine after it has extracted the coal for a certain period for a residual value of $3 million.
Now consider the mining company's plans to extract 1000 tons of coal from the mine.
Then the depletion per ton is (10+5-3)*10^6/1000 = $12,000
This is then multiplied by the tons of coal extracted per year to calculate the yearly depletion expense.
If you can remember, this method is very similar to the method of units of production used for equipment described above.

Therefore, the above examples give us a very clear idea about the various types of list of wasting assets and assets that are finite in nature and how they are accounting for in the books. The calculations state the formula used in various situations for calculating the amount of reduction in value that takes place at regular intervals.
Please refer to the above template for the detailed calculation of wasting assets.
Problems
Let us try to understand the problems of the concept.
- Buying an asset may not be possible for a business with low capital if the initial cost of an asset is high.
- The maintenance cost of an asset may be quite high, especially in the latter stages of its life.
- Since most of such assets are finite, they can be overexploitation can lead to very fast depletion and fall in future availability.
- Excess use and lead to environmental effects like pollution, habitat loss and disturbance in the balance of nature.
- Over reliance of such assets can be detrimental to the business because if they are not available on time, then they affect the business process negatively causing disruption and rise in costs.
- Technological advancemets may lead to overuse of wasting assets because there is an increase in demand for better productivity and efficiency.
- Wasting assets often face the problem of demand and supply due to price fluctuation in the market and assets like plant, machinery or equipment becoming obsolete due to technological advancement.
Solutions
Some important solutions to the problems of such kind of assets are as given below:
- The primary advantage of owning an asset is its ownership and the fact that owning an asset costs much less than leasing in the long run.
- Tax savings can be made by claiming depreciation against the equipment bought.
- Sutainable management practices should be strictly followed and proper rules and regulations should be put in place so as to use them within sustainable limits.
- Assets like vehicles and machinery that use a large quantity of fuel, should be upgraded and maintained properly so that the fuel is used efficiently without wastage and cause less pollution.
- Businesses should always try to make alternate arrangements in situations where there is a possibility of non-availability of assets so that the operation does not get affected.
- Responsible usage of assets should be planned by the management to as to meet demand as well as reduce cost.
- Planning and setting aside funds for replacement and upgradation so that there is less loss due to assets becoming obsolete and price fluctuations and volatility can also be controlled through diversification.
Thus, the above details give us an idea about the various factors responsible for negative impact of such assets and how it is possible to efficiently solve them without causing much damage. It is necessary to address these problems and solutions within a combination of regulatory framework, sustainanble practice, social engagement and strategic long term planning. All stakeholders should collaborate with each other in a responsible way.

