Table Of Contents
What Is Volatility Expansion?
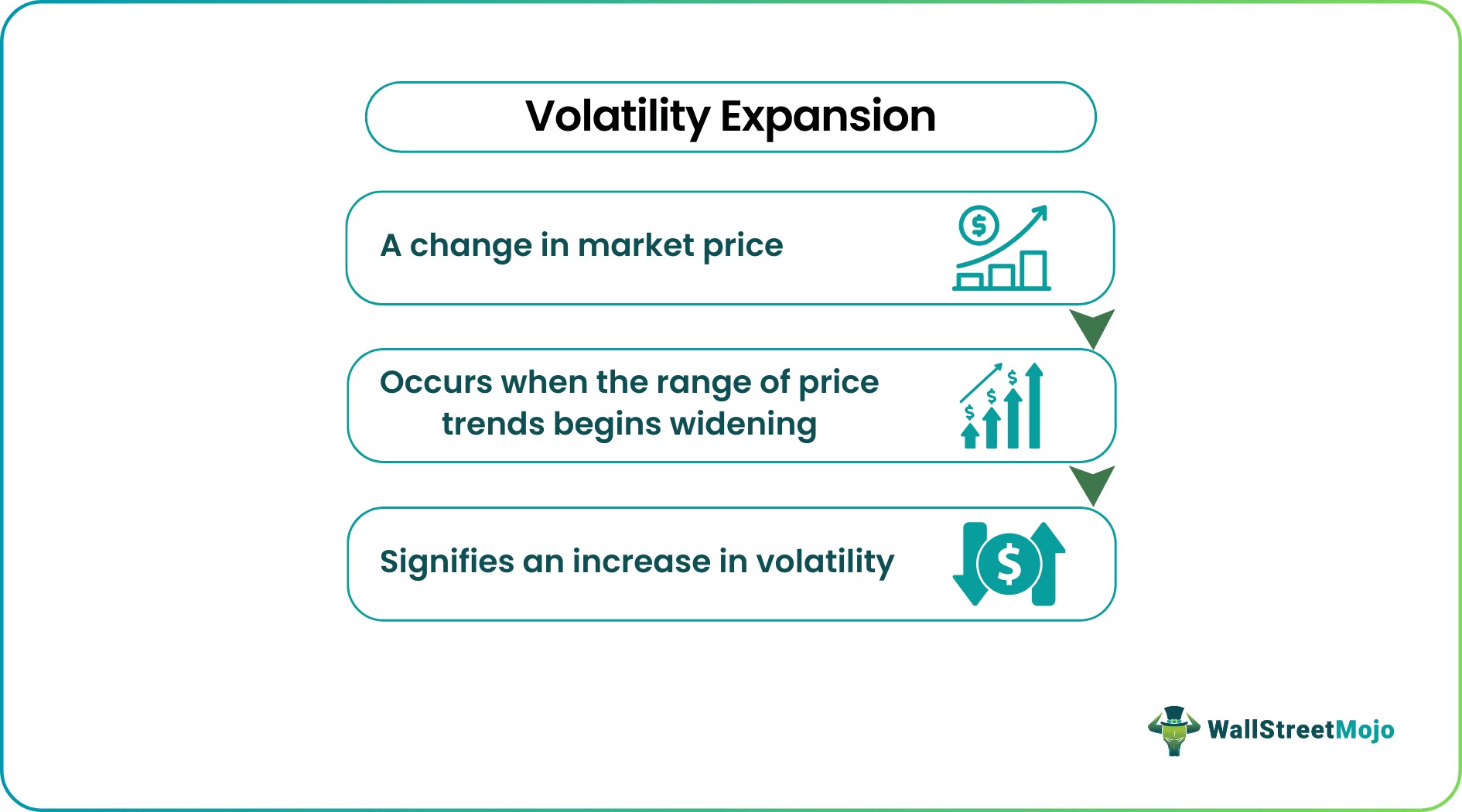
Volatility expansion is a rise in market volatility that signifies the extent to which prices have spread out. It occurs when the spectrum of price trends starts to extend. This expansion signifies a fluctuation in a measure of market volatility.
This expansion includes a surge in the daily trading range or a strong up or down price gap at the open. When investors sell options in a high-volatility environment, they anticipate that the volatility will decline and return to an expected average range.
Table of Contents
- What Is Volatility Expansion?
- Volatility expansion is an increase in volatility in the market. It represents the extent to which the market prices have expanded. It occurs when the range of price trends starts to expand.
- These indicators aid traders in determining the likelihood of unfavorable consequences of an investment and in establishing practical risk-reward trade-offs. Additionally, volatility patterns may be utilized to identify profitable trading opportunities.
- Several factors, including the economic scenario and government decisions, can influence this expansion. It may lead to market opportunities. However, it may also result in significant losses for investors.
Volatility Expansion Explained
Volatility expansion is an upsurge in fluctuations in markets at specific periods. This increase may provide opportunities for options traders. For instance, throughout the returns season, a company's stock price may fluctuate drastically due to unpredictability in the market. Several options strategies, including long straddles or strangles, may profit from an abrupt increase in volatility. Recognizing volatility is essential for effective risk management and developing efficient trading strategies.
Volatility expansion indicators help investors analyze the possible adverse risk of an investment and make appropriate risk-reward trade-offs. Furthermore, volatility patterns may be employed to determine profitable opportunities, including volatility expansion trading approaches. Investors could enhance their confidence in the financial markets by incorporating volatility analysis into their decision-making process.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Causes
Some causes of volatility expansion include the following:
- The government of a nation can play a significant role in controlling the market. Their decisions related to legislation, economic policies, and trade agreements may have a substantial impact on the financial markets. Any event, such as speeches and elections, may trigger a reaction among the traders, leading to a fluctuation in the stock prices and eventually resulting in this expansion.
- The economic landscape may impact this expansion. Economic elements, including inflation rates, monthly job reports, consumer spending data, and quarterly GDP evaluations, may influence market performance. When the economy performs well, traders generally react positively. However, when the market does not perform up to expectations, it leads to this expansion.
- Certain occurrences, like weather changes and natural calamities, may cause this expansion in a specific industry. The events may create a price change in certain commodities, leading to this expansion.
How To Day Trade It?

The Generalized Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity (GARCH) model, as shown in the chart from TradingView, is a model in statistics employed to predict a financial asset's volatility. This volatility expansion indicator considers the variations in the market volatility over a particular period. It acknowledges that the market can fluctuate in a heteroskedastic way. This implies that fluctuation occurs in a non-constant manner and can be impacted by historical events. The GARCH model enables investors to evaluate an asset's future volatility. If the GARCH experiences a rise in value, it implies that the asset volatility is likely to increase. When the GARCH value sees a decline, it indicates that the asset volatility will decrease.
Examples
Let us study the following examples to understand the volatility expansion indicator:
Example #1
Suppose the stocks of a transportation company were priced at $150 per share. However, there was a natural calamity in the area from where this company got its oil supply. The oil prices experienced a sharp increase, which also led to an increase in the transportation company's expenses. Since fuel prices increased steeply, transportation companies had to incur higher expenses. As a result, the transportation company's asset prices were significantly impacted, and they fell to $75 per share. This is an example of volatility expansion.
Example #2
Adrian Mowat noted that bond market volatility is going to be a significant cause of concern. The bond market in the United States witnessed changes in early December 2023. The US bond yields were around 5%. They went beyond 5% intraday before rallying back to 4.2%. It is one of the most significant risks at present. The prices are increasing at a solid nominal pace, and the Fed is unlikely to change its reference interest rate in 2024, indicating that bond yields are mispriced. They are unacceptably low.
Effects
The effects of volatility expansion are:
- This expansion may signify market opportunities. It offers entry points to investors that can act as an advantage for them. An increase in downward volatility may allow traders to purchase additional assets at lower prices. Conversely, during a period of upward volatility, investors may use the opportunity to sell out. These circumstances can allow investors to generate substantial returns in the long run.
- The expansion may cause substantial losses to investors as it is not always possible to predict the market timing accurately. Market volatility may aggravate losses. However, the best days may have a massive impact on the market. It may have a significant influence on the long-term returns.
- Financially strong organizations with robust foundations usually perform better during such expansions. Investors may withstand such high volatility periods as such companies usually perform better after coming out of these circumstances.
Volatility Expansion vs Volatility Contraction
The differences between the two are as follows:
Volatility Expansion
- Volatility expansion is a spike in market volatility at specific points in time. This increase may generate opportunities for options traders.
- It indicates a rise in volatility, or how quickly and widely prices spread out.
- Volatility metrics can assist investors in evaluating the possible adverse risks associated with an investment and making suitable risk-reward decisions.
Volatility Contraction
- A Volatility contraction is a possible breakout moment in stock trading. It indicates corporate accumulation within a base, which might result in a significant upward rise in the stock price.
- This pattern's significant features include tightening from left to right within the base, relative strength and accumulation signals, volume dry-ups and bursts upwards within the base, and a very tight final contraction.
- The Volatility Contraction Pattern (VCP) is a valuable technique for traders seeking to profit from stock breakouts. It is an approach that has the potential to deliver substantial returns.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The approach constructs a channel employing the average True Range of the last X bars multiplied by a factor. The indicator's options allow users to modify both the average length and the factor. The channel is constructed by adding and subtracting the result from the close.
Larry Williams, a prominent United States trader and author of multiple trading books, designed the Volatility Breakout method. The Volatility Breakout techniques are based on the idea that if the market moves by a specific amount in a short period, the trend will continue to persist for some time.
This expansion in digital assets, or crypto, implies the quick and unanticipated fluctuations that affect the cost of cryptocurrencies over a certain period. It demonstrates how much a security's market price swings around its average price. However, the overall cryptocurrency market is far more volatile than traditional finance. As a result, prominent cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum often have their volatility index. Usually, investing in an asset with higher volatility is riskier.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what is Volatility Expansion. We explain its causes, examples, effects, how to day trade, & comparison with volatility contraction. You may also find some useful articles here –

