Table Of Contents
Vicarious Liability Meaning
Vicarious liability is a term that indicates how one party is legally responsible for the acts of another party, which the former could not control or take due care of. Though the latter holds liability for the losses incurred or the wrongs done, the first party is the one that fails to exercise its controls, causing the business to suffer.
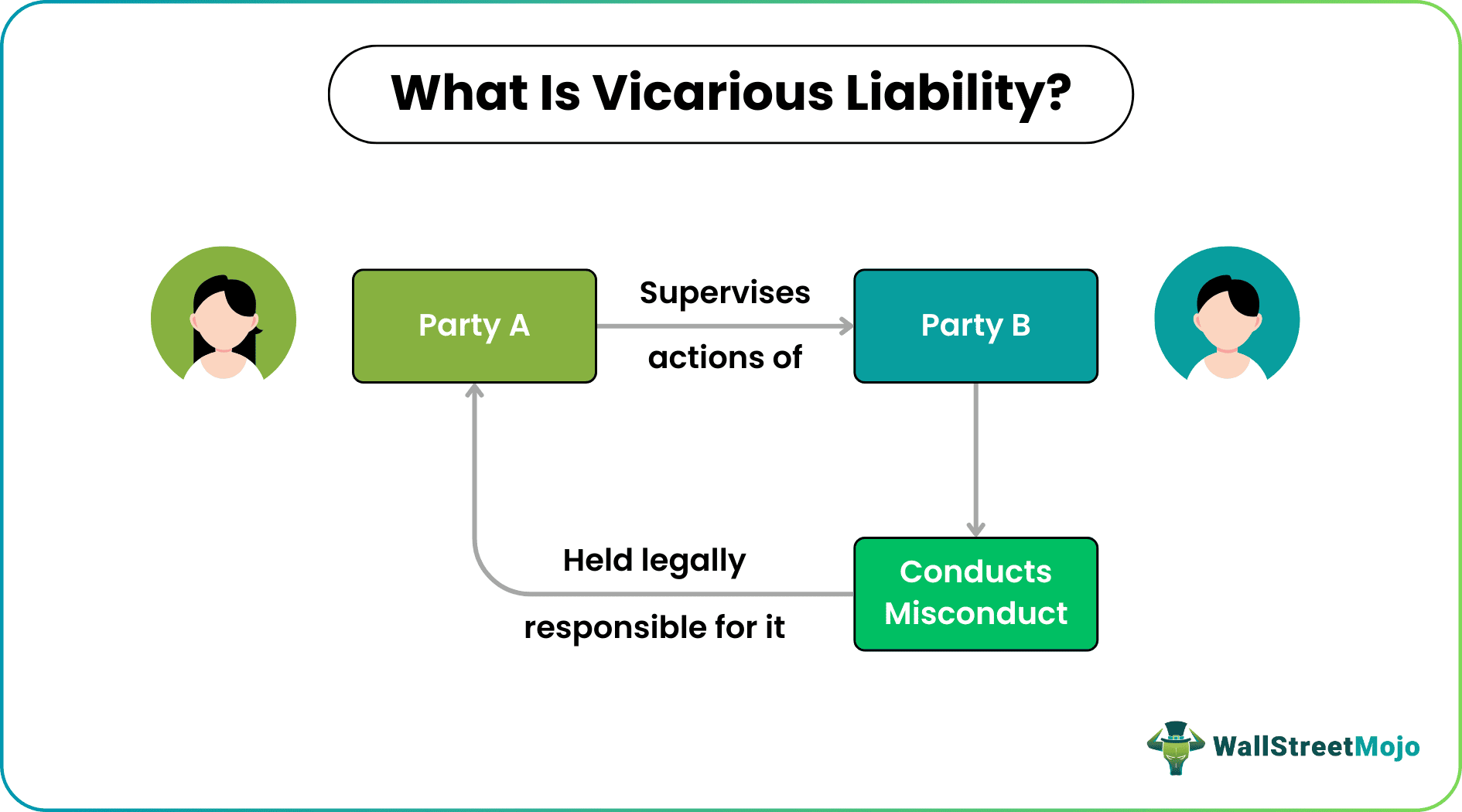
Also known as imputed liability, the concept ensures the authoritative or supervising party remains alert and keeps a check on the subordinate individuals or entities so that they do not involve in any misdeed and work in accordance with the standard ethics and regulations followed in the industry.
Key Takeaways
- Vicarious liability is a term that indicates an authoritative party's legal responsibility for their subordinates' wrongdoings.
- Principal, Parental, and Employer liability are the three types of imputed liability.
- The three elements around which the concept revolves include the employer-employee bond, the act of negligence defined in tort, and the scope and course of employment.
- It differs from strict liability, which holds defendants responsible for a crime, irrespective of their intentions and mental state.
Understanding Vicarious Liability
Vicarious liability is an idea that has been introduced to ensure that subordinates always remain under strict supervision. This is because one unethical action at their end would make their superior authorities pay. The individuals or entities, therefore, have to make sure they have complete control over the subordinates without imposing restrictions on their liberty to work and act. Their function as a monitoring unit is enough to make the other party stick to the ethics and work as per industry rules.
For example, when a child acts wrongly, people directly report to the parents, considering their failure in teaching the kids good life lessons. The concept of vicarious liability runs on the same principle and understanding. Similarly, when an employee does something unethical, the employers are held responsible though they are not directly connected to the misdeed.
A vicarious liability case is mostly reported when the personal benefit of a person is involved in cash or kind. However, it can also occur if a person intends to hit/damage another person, be it physical or reputational, due to a dispute between both parties.
Some of the wrongdoings that fall under vicarious liability are mentioned below:
- Employers' liability for wrongful acts of employees
- Principals' liability for wrongful acts of agents
- Partners' liability for wrongful acts of each other
- Masters' liability for a wrongful act of servants
These wrongful doings could be a copyright violation, sexual abuse, confidentiality breach, physical and mental harassment, etc.
At times, employers find themselves completely unaware of what the employees do and their plans of wrongdoings. The former feels unnecessarily trapped. This is where vicarious liability insurance helps and protects them and their businesses from being dragged into lawsuits involving their employees.
Types
Though these incidents have different traits, they are categorized based on their nature of occurrences. For example, when a kid misbehaves, the parents are held responsible for their children's actions. This is termed parental liability.
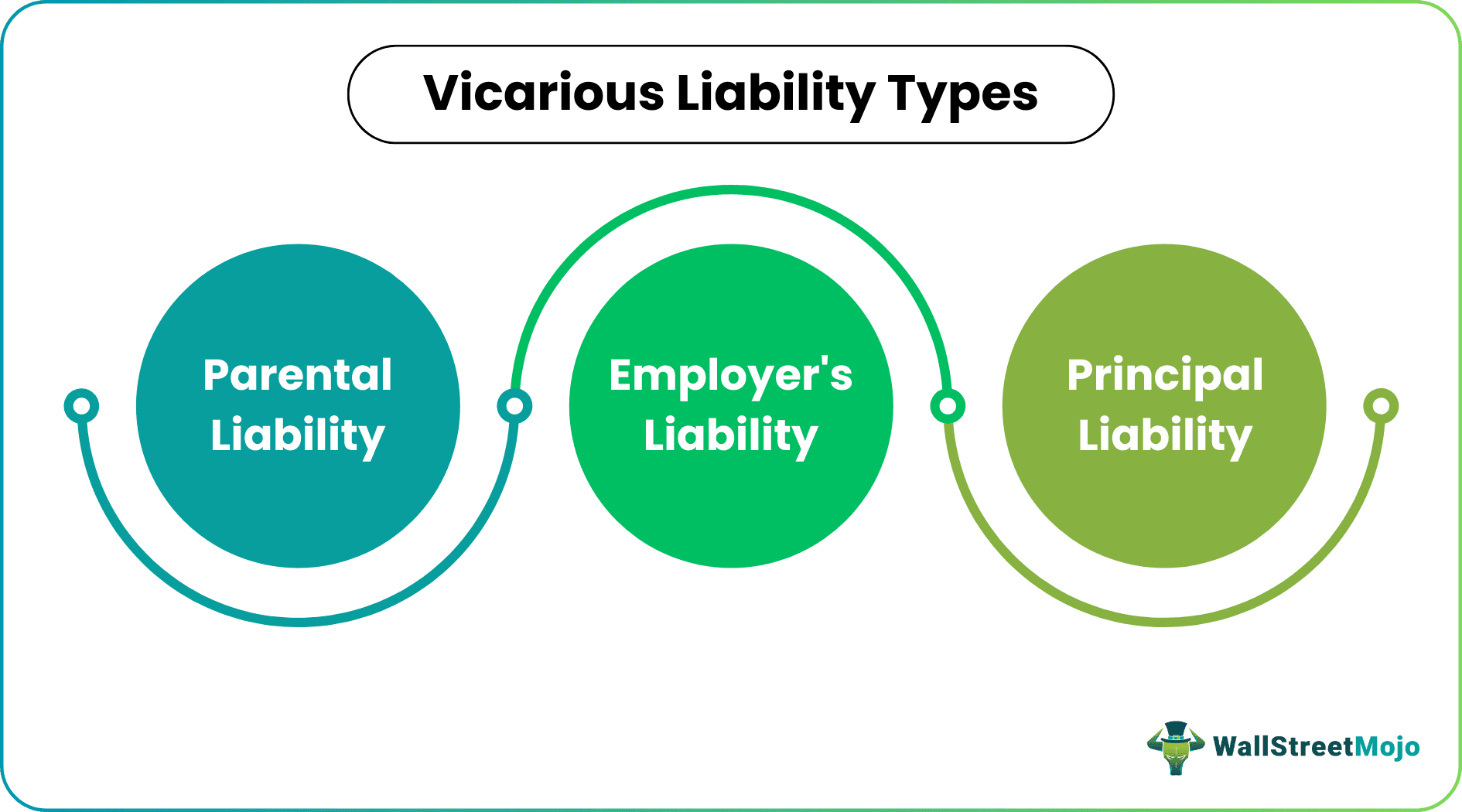
In an organization, vicarious accountability holds employers responsible for an employee's misconduct as the former needs to constantly monitor the happenings and ensure they do not encourage any negativity in the workplace. Therefore, such incidents fall under the employers' liability label.
There are instances where owners allow another individual or entity to use their asset. While using the same, if the latter damages the property, the owner will be held responsible for the action. This is because it's the owners' responsibility to make sure the property is lent to someone trustworthy. Such liabilities are termed principal liability.
Elements
The idea of vicarious liability in the UK revolves around three elements – employer-employee bond, an act of negligence as defined in tort, and the scope and course of employment.
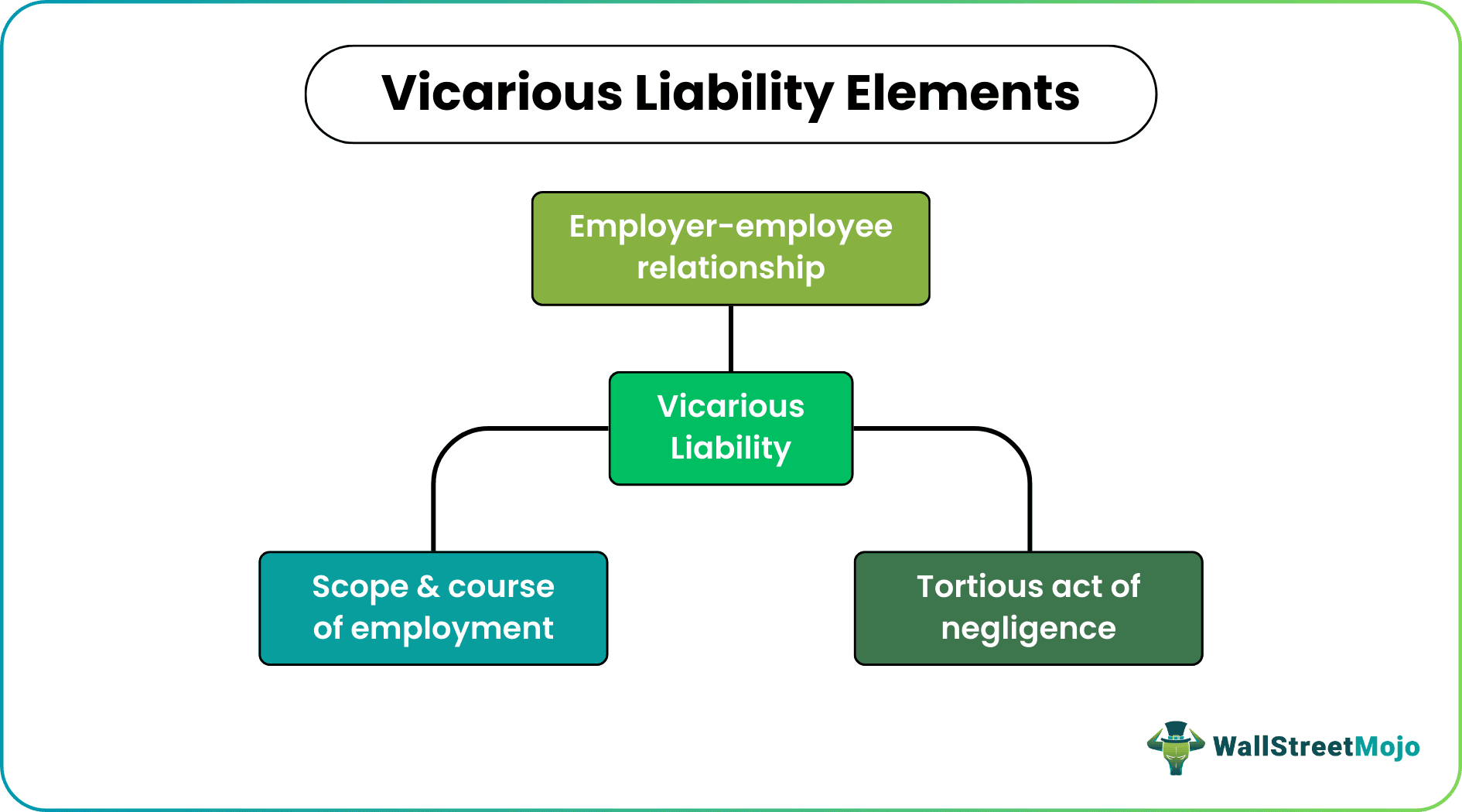
When one party is held responsible for the wrongdoing of its subordinate in an organization, the two parties must share the employer-employee relationship. Secondly, whatever mistakes the subordinate party commits must be recorded within the scope and course of employment. This is to ensure that the person or entity still falls under the subordinate category of the employer or parent entity.
Last but not least is the tortious act of negligence. It applies when one fails to care for something due to careless behavior. In situations where a person handles someone's property carelessly, the latter shares imputed liability being the owner of the asset and for trusting the wrong person with the asset.
Examples
Let us consider the following vicarious liability examples to understand the concept better:
Example #1
Michel, an employee of Company X, a taxation service provider, works under John, his supervisor. They have one client James, who is also a cousin of John, and there is a legal dispute going on between them.
With an intention of making James pay more, John tells Michel to file wrong taxation information about his cousin. Michel refuses to do the same. However, John threatens him that his refusal could lead to his termination. Hence, Michel gives up and agrees to his boss' instructions.
In the above case, John holds the liability for Michel's action.
Example #2
Robert has a JCB Machine Driver, David. If David negligently hits Paul, Robert will be liable. But if Robert hires a JCB Machine, and the driver, David, negligently hits Paul, in that case, Robert will not be liable for Paul. This is because David is not their servant but an independent contractor.
Vicarious Liability vs Strict Liability
Vicarious liability and strict liability are two forms of liabilities that lead to major confusion among people. However, the two concepts differ widely.
Vicarious liability is the legal responsibility the supervising or authoritative party has to take for the mistakes or crimes committed by their subordinates. On the other hand, strict liability, as the name implies, is an unescapable legal liability, which the authorities impose in situations where the mistakes or crimes are hazardous, and the law punishes the one responsible, irrespective of their intentions or mental status.
For example, even if A unintentionally sells a product to a minor, believing him to be over 18, the law holds the seller strictly liable for the crime committed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
In tort, it can be imposed not on the person who committed the wrongful action but on another person who has the authority over the person committing the unlawful act.
Though employers, masters, and principals are responsible for how the employees, servants, and agents behave and comply with the standard ethics and rules, they find themselves trapped by what the latter do. However, through vicarious liability insurance, they can protect themselves against their subordinates' wrongdoings.
An employer has this liability for the wrongdoings of independent contracts only if:
- Employers have been negligent in choosing a suitable independent contractor.
- The tasks assigned to the contractors are non-delegable.
- The mistake or crime is too hazardous.
