Table Of Contents
Variable Declaration in VBA
In VBA, variable declaration are necessary to define a variable for a certain data type so that It can hold values. Any variable not defined in VBA cannot hold values. There is an option to require the DIM keyword does variable declaration and variable declaration in VBA.
What are the variables in VBA?
The word "variable" defines variables as the name of memory in your location, which holds some value. You can pass a value in a code based on the variable type. The value will be used while executing the code, and you will get the output.
What is the use of Variable?
Creating a program or a code consists of instructions that pass the information to the system about what to do with data. The data consist of two types of values, fixed and variable. Fixed values are also called "constant." One may define variables by certain data types: Integer, Byte, String, etc. It helps us to identify the nature of the data we are entering, i.e., Text, Number, Boolean, etc.
How to Declare a Variable?
To declare a variable in code, you should assign a name to that variable. You can assign any name to a variable. However, selecting a variable name that relates to data is advisable so that other users can understand it easily. For example, if you need to pass Integer data in the code, then the name variables like i_count or out. If you need to pass a string value, you can name that variable like strName.
One can declare variables anywhere in the VBA code. However, the coder must declare them at the start of the code so that every user can understand the code very easily. The variable should be declared using Dim.
Examples of VBA Variable Declaration
Here are some examples for you to understand the VBA data type. Then, you can try it on your computer.
Add a module in VBA Editor. Then, copy and paste the below codes one by one to see the result.
VBA Variable Declaration Example #1 - Integer
One may need the VBA Integer when one needs to store the whole numbers. For example, integers can store values between 32,768 to 32,767. If you need to pass values beyond this, use the Long Data type in VBA.
Code:
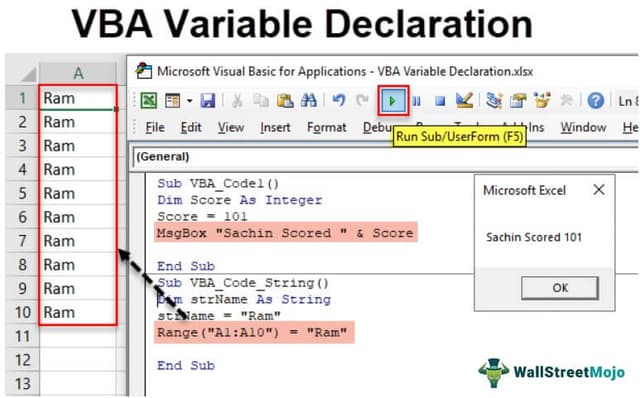
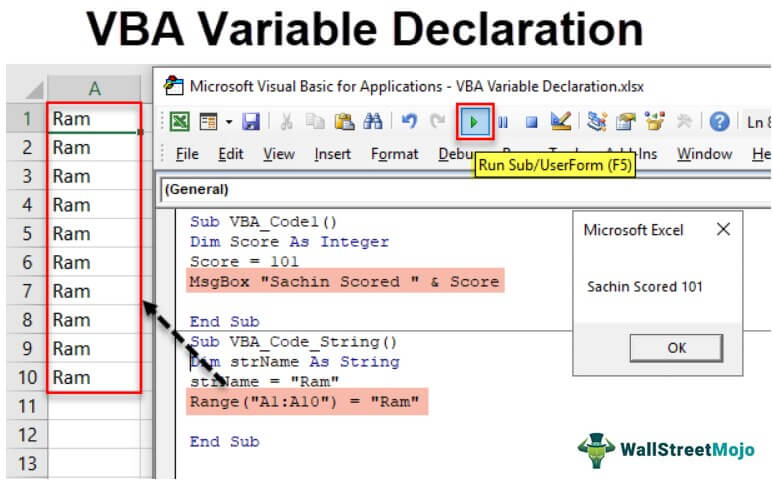
Sub VBA_Code1() Dim Score As Integer Score = 101 MsgBox "Sachin Scored " & Score End Sub
The above code's result will show “Sachin Scored 101.” See below.

VBA Variable Declaration Example #2 - String
The VBA string data type can store data as text.
Code:
Sub VBA_Code_String() Dim strName As String strName = "Ram" Range("A1:A10") = "Ram" End Sub
When you run the above code, this will enter "Ram" in every cell between Range A1:A10.

VBA Variable Declaration Example #3 - Date
The date data type in VBA can store data like the date. Therefore, it will be in the format of MM/DD/YYYY.
Code:
Sub VBA_Code_Date() Dim DOB As Date DOB = "04/04/1990" MsgBox "I was born on " & DOB End Sub
When you run the above code, this will show the result below.

VBA Variable Declaration Example #4 - Boolean
Boolean Datatype in VBA has only two values True or False.
Code:
Sub VBA_Code_Boolean() Dim bgender As Boolean bgender = False If bgender = True Then Range("A1") = "Male" Else Range("A1") = "Female" End If End Sub
When you run the code, the result in the A1 cell will be "Female."

VBA Variable Declaration Example #5 - Long
The Data type Long is also used to store numbers. They can store numbers between -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. Here, you must have a question: if Integer and Long can store numbers, why do we use Integer?
Here is the answer. Integer takes two bytes of space. However, Long needs 8 bytes of space. So, you should not use Long when you know one can store a number as an Integer. Else, your program running time will increase.
Suppose you need to show the distance between the North Pole and the South Pole in "Meter." You know that the distance in the meter is outside the range of -32,768 to 32,767. So, you will use the Data type Long.
Code:
Sub VBA_Code_long() Dim distance As Long distance = 13832000 MsgBox "Distance between the North Pole and the South Pole is " & distance & " Meter" End Sub
The result will be "Distance between the North Pole. The South Pole is 13832000 Meter.

If you use an Integer as a data type in the above code, then this will go through an error. You can try it.
Points to Remember
You need to remember some points while declaring the variables.
- A variable name should not be more than 255 characters.
- Variables are not case-sensitive.
- A variable should not start with a number. Instead, we can use the number or underscore in the middle of the variable name.
- VBA variable declaration cannot be an Excel keyword like Sheet, Range, etc.
- VBA variable declaration does not contain special characters.