Table Of Contents
Excel VBA Solver
How do you solve complicated problems? If you are unsure how to go about these problems, then there is nothing to worry about; we have a solver in Excel. In our earlier article, “Excel Solver,” we learned how to solve equations in Excel. If you are unaware, “SOLVER” is also available with VBA. This article will take you through how to use “Solver” in VBA.
Enable Solver in Worksheet
A solver is a hidden tool available under the "Data" tab in Excel (if already enabled).
To use SOLVER in excel, first, we need to enable this option. Follow the below steps.
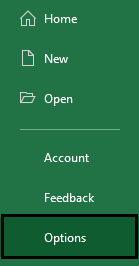
Step 1: Go to the FILE tab. Under the FILE tab, choose "Options."
Step 2: In the "Excel Options" window, choose "Add-ins."
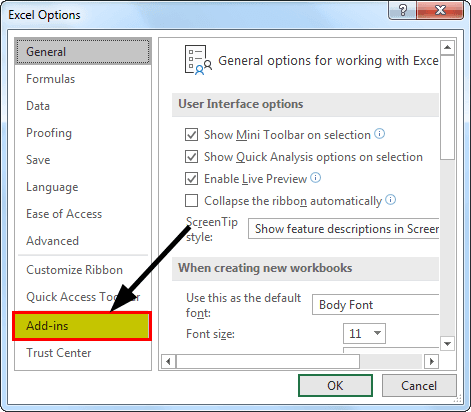
Step 3: At the bottom, chooses "Excel Add-ins" and click on "Go."
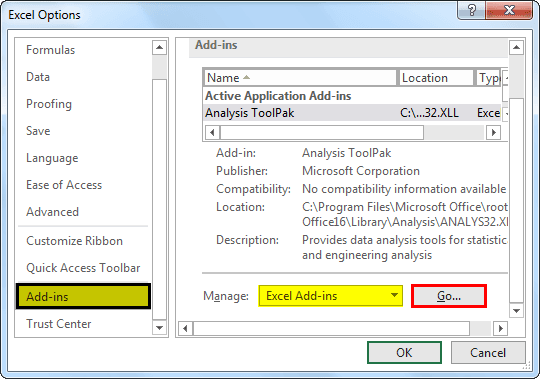
Step 4: Now, check the "Solver Add-in" box. Click on "OK."
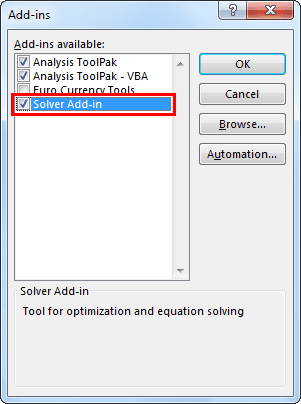
Next, you must see "Solver" under the "Data" tab.
This topic highlights key concepts and provides a broader understanding of the field. If you’re curious to explore these ideas more thoroughly, this Excel Macros Course offers a structured way to do so.
Enable Solver in VBA
In VBA, Solver is an external tool. So, we need to enable it to use it. Follow the below steps to enable it.
Step 1: Go to Tools >>> Reference in Visual Basic Editor Window.
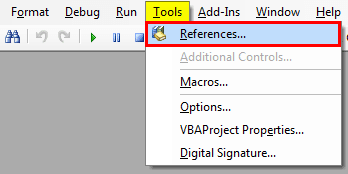
Step 2: From the references list, choose "Solver" and click on "OK" to use it.
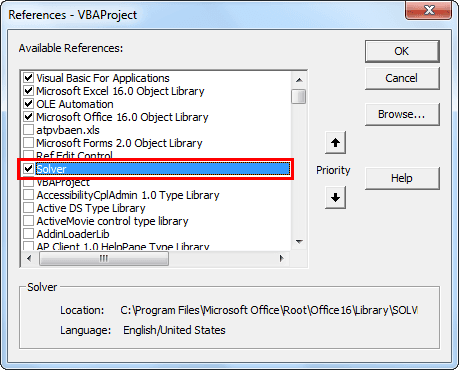
Now, we can use Solver in VBA as well.
Solver Functions in VBA
To write a VBA code, we need to use three "Solver Functions" in VBA: "SolverOk," "SolverAdd," and "SolverSolve."
SolverOk

SolverOk ( SetCell, MaxMinVal, ValueOf, ByChange, Engine, EngineDesc)
SetCell: This will be the cell reference that needs to be changed, i.e., the "Profit" cell.
MaxMinVal: This is an optional parameter. Below are numbers and specifiers:
- 1 = Maximize
- 2 = Minimize
- 3 = Match a specific value
ValueOf: This parameter needs to supply if the MaxMinVal argument is 3.
ByChange: By changing which cells, this equation needs to be solved.
SolverAdd
Now, let us see the parameters of SolverAdd.

CellRef: To set the criteria to solve the problem, what cell needs to be changed?
Relation: If the logical values are satisfied, we can use the numbers below.
- 1 is less than (<=)
- 2 is equal to (=)
- 3 is greater than (>=)
- 4 must-have final values that are integers.
- 5 must-have values between 0 or 1.
- 6 must-have final values that are all different and integers.
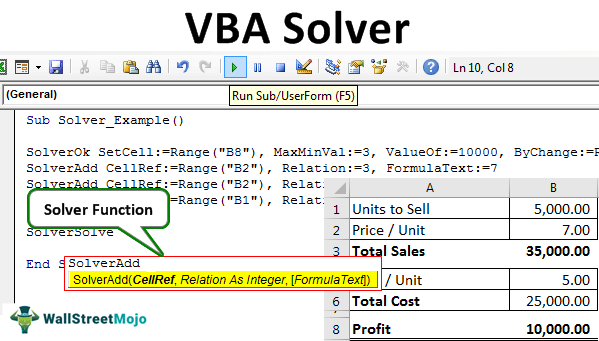
Example of Solver in Excel VBA
Look at the below scenario.
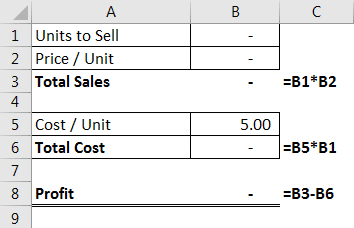
Using this table, we need to identify the "Profit" amount, which needs to be a minimum of 10,000. To arrive at this number, we have certain conditions.
- Units to Sell should be an integer value.
- Price / Unit should be between 7 and 15.
Based on these conditions, we must identify how many units to sell. At what price to get the profit value of 10,000?
Let us solve this equation now.
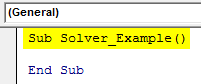
Step 1: Start the VBA sub procedure.
Code:
Sub Solver_Example() End Sub
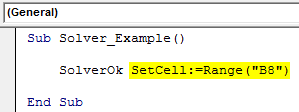
Step 2: First, we need to set the Objective cell reference using the SolverOk function.

Step 3: The first argument of this function is "SetCell," in this example, we need to change the value of the Profit cell, the B8 cell.
Code:
Sub Solver_Example() SolverOk SetCell:=Range("B8") End Sub
Step 4: We need to set this cell value to 10,000. So for MaxMinVal, use 3 as the argument value.
Code:
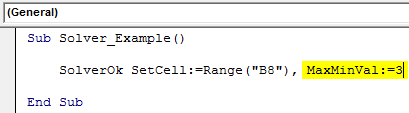
Sub Solver_Example() SolverOk SetCell:=Range("B8"), MaxMinVal:=3 End Sub
Step 5: The next argument ValueOf value should be 10,000.
Code:
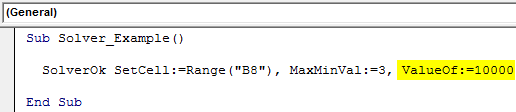
Sub Solver_Example() SolverOk SetCell:=Range("B8"), MaxMinVal:=3, ValueOf:=10000 End Sub
The next argument is ByChange, i.e., by changing which cells this equation needs to be solved. In this case, changing Units to Sell (B1) and Price Per Unit (B2) cells need to be changed.
Code:
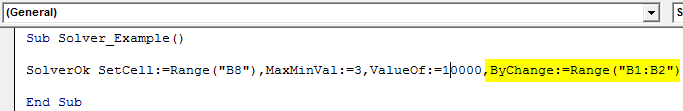
Sub Solver_Example() SolverOk SetCell:=Range("B8"), MaxMinVal:=3, ValueOf:=10000, ByChange:=Range("B1:B2") End Sub
Note: remaining arguments are not required here.
Step 6: Once we set the objective cell, we must construct other criteria. So, for this, open the "SolverAdd" function.
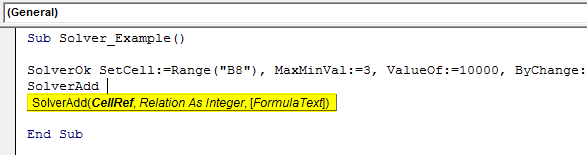
Step 7: First Cell Ref we need to change is Price Per Unit cell, B2 cell.
Code:
Sub Solver_Example() SolverOk SetCell:=Range("B8"), MaxMinVal:=3, ValueOf:=10000, ByChange:=Range("B1:B2") SolverAdd CellRef:=Range("B2") End Sub
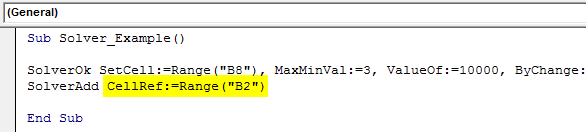
Step 8: This cell needs to be >= 7, so the Relation argument will be 3.
Code:
Sub Solver_Example() SolverOk SetCell:=Range("B8"), MaxMinVal:=3, ValueOf:=10000, ByChange:=Range("B1:B2") SolverAdd CellRef:=Range("B2"), Relation:=3 End Sub
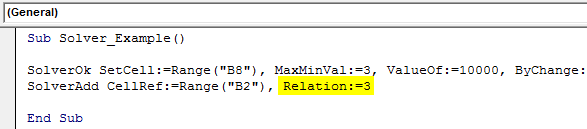
Step 9: This cell value should be >=7, Formula Text = 7.
Code:
Sub Solver_Example() SolverOk SetCell:=Range("B8"), MaxMinVal:=3, ValueOf:=10000, ByChange:=Range("B1:B2") SolverAdd CellRef:=Range("B2"), Relation:=3, FormulaText:=7 End Sub
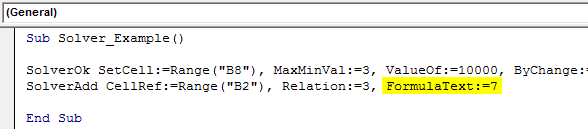
Step 10: Similarly, the same cell needs to be less than 15, so for this relation is <= i.e. 1 as the argument value.
Code:
Sub Solver_Example() SolverOk SetCell:=Range("B8"), MaxMinVal:=3, ValueOf:=10000, ByChange:=Range("B1:B2") SolverAdd CellRef:=Range("B2"), Relation:=3, FormulaText:=7 SolverAdd CellRef:=Range("B2"), Relation:=1, FormulaText:=15 End Sub
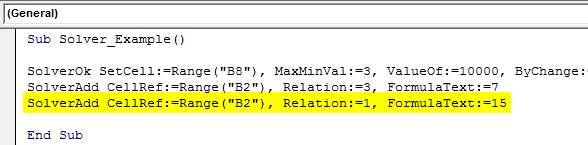
Step 11: The first cell, "Units to Sell," must be an Integer value. So, for this, also set up the criteria below.
Code:
Sub Solver_Example() SolverOk SetCell:=Range("B8"), MaxMinVal:=3, ValueOf:=10000, ByChange:=Range("B1:B2") SolverAdd CellRef:=Range("B2"), Relation:=3, FormulaText:=7 SolverAdd CellRef:=Range("B2"), Relation:=1, FormulaText:=15 SolverAdd CellRef:=Range("B1"), Relation:=4, FormulaText:="Integer" End Sub
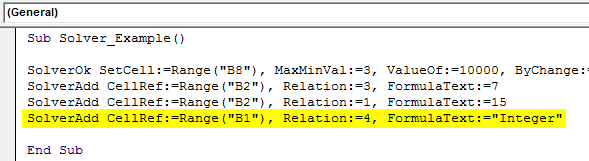
Step 12: In one final step, we need to add the SolverSolve function.
Code:
Sub Solver_Example() SolverOk SetCell:=Range("B8"), MaxMinVal:=3, ValueOf:=10000, ByChange:=Range("B1:B2") SolverAdd CellRef:=Range("B2"), Relation:=3, FormulaText:=7 SolverAdd CellRef:=Range("B2"), Relation:=1, FormulaText:=15 SolverAdd CellRef:=Range("B1"), Relation:=4, FormulaText:="Integer" SolverSolve End Sub
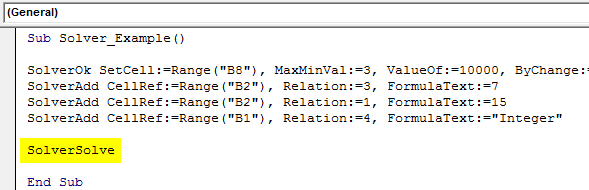
Run the code by pressing the F5 key to get the result.
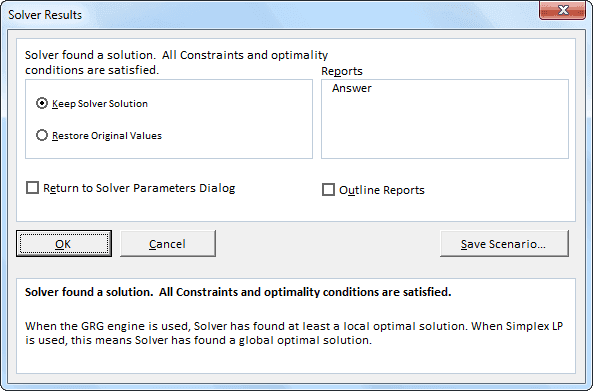
When you run the code, you will see the following window.
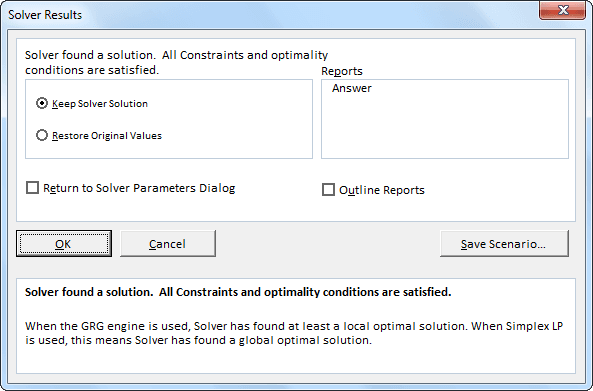
Press "OK." You will get the result in an Excel sheet.
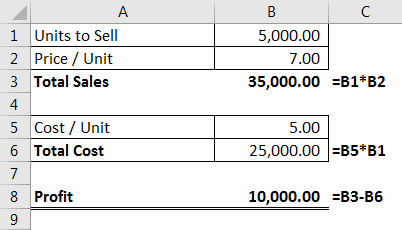
So, to earn a profit of 10,000, we need to sell 5,000 units at 7 per price where the cost price is 5.