Table Of Contents
Excel VBA Row Count
In VBA programming, referring to rows is most important as well, and counting them is one thing you must be aware of when it comes to VBA coding. We can get a lot of value if we understand the importance of counting rows with data in the worksheet. This article will show you how to count rows using VBA coding.
How to Count Rows in VBA?
Example #1
To count rows, we need to use the RANGE object. In this object, we need to use the ROWS object. In this, we need to use the COUNT property.
Look at the below data in Excel.

From the above data, we need to identify how many rows are there from the range A1 to A8. So first, define the variable as an Integer to store the number of rows.
Code:
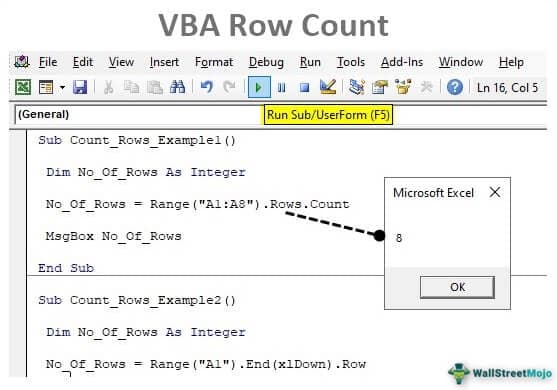
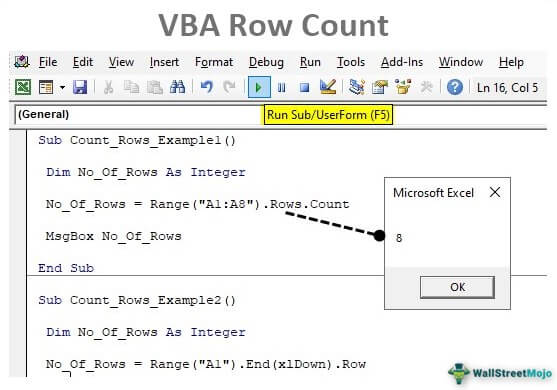
Sub Count_Rows_Example1()
Dim No_Of_Rows As Integer
End Sub
We will assign row numbers for this variable, so enter the variable name and the equal sign.
Code:
Sub Count_Rows_Example1()
Dim No_Of_Rows As Integer
No_Of_Rows =
End Sub
We need to provide a range of cells, so open the RANGE object and supply the range as “A1:A8”.
Code:
Sub Count_Rows_Example1()
Dim No_Of_Rows As Integer
No_Of_Rows = Range("A1:A8")
End Sub
Once we supply the range, we need to count the number of rows, so choose the ROWS property of the RANGE object.

We are counting several rows in the RANGE object's ROWS property, so choose the "COUNT" property now.

Now in the message box, show the value of the variable.
Code:
Sub Count_Rows_Example1()
Dim No_Of_Rows As Integer
No_Of_Rows = Range("A1:A8").Rows.Count
MsgBox No_Of_Rows
End Sub
Now, run the code and see the count of rows of the supplied range of cells.

There are 8 rows supplied for the range, so the row count is 8 in the message box.
Example #2
We have other ways of counting rows as well. For the above method, we need to supply a range of cells, showing the number of rows selected.
But imagine the scenario where we need to find the last use of any column. For example, take the same data as seen above.

To move to the last used cell from cell A1, we press the shortcut excel key “Ctrl + Down Arrow,” so it will take you to the last cell before the empty cell.
First, supply the cell as A1 using the RANGE object.
Code:
Sub Count_Rows_Example2()
Dim No_Of_Rows As Integer
No_Of_Rows = Range("A1")
MsgBox No_Of_Rows
End Sub
From this cell, we need to move down. We use Ctrl + Down Arrow in the worksheet, but in VBA, we use the END property. Choose this property and open the bracket to see options.

Look there with the END key. We can see all the arrow keys like "xlDown, xlToLeft, xlToRight, and xlUp" since we need to move down and use the "xlDown" option.
Code:
Sub Count_Rows_Example2()
Dim No_Of_Rows As Integer
No_Of_Rows = Range("A1").End(xlDown)
MsgBox No_Of_Rows
End Sub
It will take you to the last cell before any break. We need the row number in the active cell so use the ROW property.
Code:
Sub Count_Rows_Example2()
Dim No_Of_Rows As Integer
No_Of_Rows = Range("A1").End(xlDown).Row
MsgBox No_Of_Rows
End Sub
Now, this will show the last row number, which will be the count of the number of rows.

So in rows, we have data.
Example #3 - Find Last Used Row
Finding the last used row is important to decide how many times the loop has to run. Also, in the above method, the last row stops to select if there is any breakpoint cell. So in this method, we can find the last used row without any problems.
Open CELL property.
Code:
Sub Count_Rows_Example3()
Dim No_Of_Rows As Integer
No_Of_Rows = Cells(
MsgBox No_Of_Rows
End Sub
Now, we need to mention the row number to start with. The problem here is we are not sure how many rows of data we have so that we can go straight to the last row of the worksheet, for this mention, ROWS.COUNT property.
Code:
Sub Count_Rows_Example3()
Dim No_Of_Rows As Integer
No_Of_Rows = Cells(Rows.Count,
MsgBox No_Of_Rows
End Sub
Next, we need to mention in which column we are finding the last used row, so in this case, we are finding it in the first column, so mention 1.
Code:
Sub Count_Rows_Example3()
Dim No_Of_Rows As Integer
No_Of_Rows = Cells(Rows.Count, 1)
MsgBox No_Of_Rows
End Sub
At this moment, it will take you to the last cell of the first column. We need to move upwards to the last used cell from there onwards, so use the End(xlUp) property.
Code:
Sub Count_Rows_Example3()
Dim No_Of_Rows As Integer
No_Of_Rows = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp)
MsgBox No_Of_Rows
End Sub
So, this will take you to the last used cell of column 1, and in this cell, we need the row number, so use the ROW property to get the row number.
Code:
Sub Count_Rows_Example3()
Dim No_Of_Rows As Integer
No_Of_Rows = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
MsgBox No_Of_Rows
End Sub