Table Of Contents
VBA Match Function
VBA Match function looks for the position or row number of the lookup value in the table array, i.e., in the main excel table.

In a worksheet, lookup functions are an integral part of Excel. Some important lookup functions are VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, INDEX, and MATCH. Unfortunately, we do not have these functions as VBA functions. However, we can use them as worksheet functions in VBA.
In this article, we will show you how to use one of the worksheet lookup functions, MATCH in VBA, as a worksheet function.
How to Use MATCH Function in VBA Excel?
We will show you a simple example of using the Excel MATCH function in VBA.
Example #1
In VBA, we can use this MATCH formula in excel as a worksheet function. Follow the below steps to use the MATCH function in VBA.
Step 1: Create a sub procedure by giving a Macro name.
Code:
Sub Match_Example1()
Step 2: In the E2 cell, we need the result, so start the code as Range (“E2”).Value =
Code:
Sub Match_Example1() Range("E2").Value = End Sub

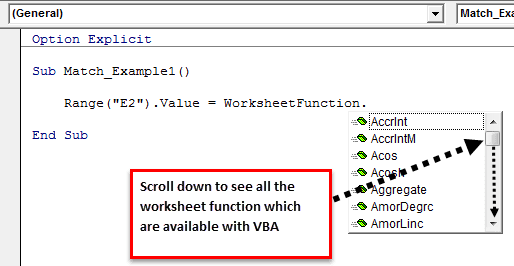
Step 3: In E2, the cell value should result from the MATCH formula. So, to access the VBA MATCH function, we need to use the property “WorksheetFunction” first. In this property, we will get all the available worksheet function lists.

Step 4: Select the MATCH function here.
Code:
Sub Match_Example1() Range("E2").Value = WorksheetFunction.Match( End Sub

Step 5: The problem starts because we do not get the exact syntax name. Rather, we get syntax like “Arg1, Arg2, Arg3”. So, it would help if you were sure of the syntaxes here.
Our first argument is LOOKUP VALUE. Our LOOKUP VALUE is in cell D2, so select the cell as Range (“D2”).Value.
Code:
Sub Match_Example1() Range("E2").Value = WorksheetFunction.Match(Range("D2").Value, End Sub

Step 6: The second argument is Table Array. Our table array range is from A2 to A10. So, select the range as “Range (“A2: A10”).”
Code:
Sub Match_Example1() Range("E2").Value=WorksheetFunction.Match(Range("D2").Value,Range("A2:A10"), End Sub

Step 7: Now, the final argument is MATCH TYPE. We need an exact match, so enter the argument value as zero.
Code:
Sub Match_Example1() Range("E2").Value = WorksheetFunction.Match(Range("D2").Value, Range("A2:A10"), 0) End Sub

Run the Macro. We will get the position of whatever the year name is there in cell D2.

Example #2 - VBA Match From Another Sheet
Assume the same data set from the above is on two different sheets. For example, the table array is in the sheet name called “Data Sheet,” and Lookup Value is in the sheet name called “Result Sheet.”
In this case, we need to refer to worksheets by their name before we refer to the ranges. Below is the set of codes with sheet names.
Code:
Sub Match_Example2() Sheets("Result Sheet").Range("E2").Value = WorksheetFunction.Match(Sheets("Result Sheet").Range("D2").Value, Sheets("Data Sheet").Range("A2:A10"), 0) End Sub

Example #3 - VBA Match Function with Loops
If the result we want is in a single cell, then no problem, but if the result has to come in more than one cell, then we need to use a VBA loop to get the result in all the cells.
Assume you have data like this.

Writing lengthy codes is arduous in these cases, so we switch to loops. Below is the set of codes that will do the job for us.
Code:
Sub Match_Example3() Dim k As Integer For k = 2 To 10 Cells(k, 5).Value = WorksheetFunction.Match(Cells(k, 4).Value, Range("A2:A10"), 0) Next k End Sub

This set of codes will get the result in just the blink of an eye.