Table Of Contents
Excel VBA Hide Columns
Hiding is simple, but you need to understand the concept here. To hide the column using VBA, we need to determine which column we need to hide. To specify the column to be hidden, we need to use the RANGE object.
Range("A:A")
Then, we need to use the Property “Entire Column.”
Range("A:A").EntireColumn
We need to use the “Hidden” property in the column property.
Range("A:A").EntireColumn.Hidden
Then, we need to set the Hidden property to TRUE.
Range("A:A").EntireColumn.Hidden = TRUE
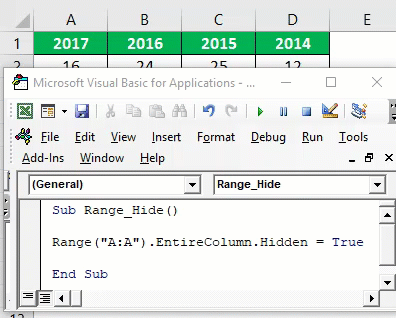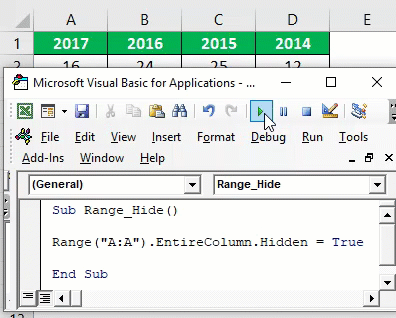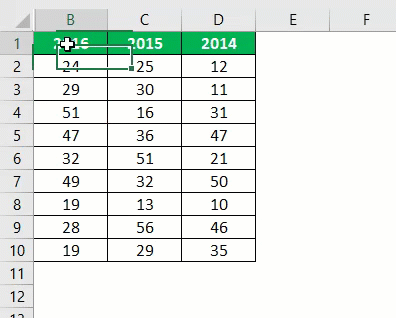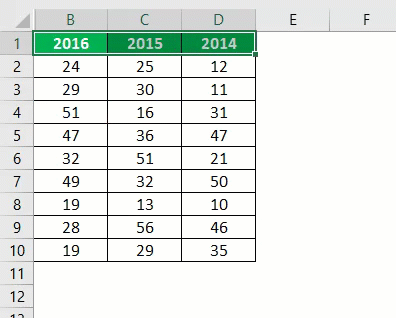
It will hide column A.
How to Hide Columns in VBA?
We can hide columns in several ways. We can hide a column using a Range object using the CELLS property. We need to construct our VBA code based on the method we use.
Example #1 - Hide using Range Object
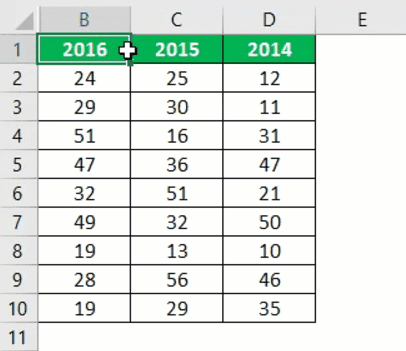
If you want to hide a particular column, then specify the column inside the RANGE object. For example, look at the below data.

Now, we will hide the entire column A using the following code.
Code:
Sub Range_Hide() Range("A:A").EntireColumn.Hidden = True End Sub
So, when we run the code, we will get the following result.
Example #2 - Hide using Columns Property
If you want to hide the column using the Columns property, then the below code is for you.
Code:
Sub Range_Hide() Columns("B").Hidden = True End Sub
It will hide column B. Here, you must be thinking about where the Entire Column property is. When you use the Columns property, it is unnecessary to use the Entire Column property.
We can still use the Entire Column property but not necessarily required. And code for the same is given below.
Code:
Sub Columns_Hide() Columns("B").EntireColumn.Hidden = True End Sub
It also should work fine.
We can use the column number as well instead of an alphabetic reference. And code for the same is given below.
Code:
Sub Columns_Hide() Columns(4).EntireColumn.Hidden = True End Sub
It will hide Column D.

Example #3 - Hide Multiple Columns
We can hide multiple columns at a time as well. We need to mention the first and the last column so that in between columns also will be hidden. Using the following code to hide multiple columns for the same data as example #1.
Code:
Sub Columns_Hide() Range("A:C").EntireColumn.Hidden = True End Sub
It will hide column A to C.
We can also use the following code to hide multiple columns in Excel VBA.
Code:
Sub Multi_Columns_Hide() Columns("A:C").EntireColumn.Hidden = True End Sub
The above methods will hide the first three columns: A, B, and C.

Example #4 - Hide Columns with Single Cell
We can also hide a column based on a single cell reference. We do not need to give the full column reference to hide the column. With just a single cell reference, we should be able to hide a column.
Code:
Sub Single_Hide() Range("A5").EntireColumn.Hidden = True End Sub
It will hide the entire column A.

Example #5 - Hide Every Alternative Column
Assume you have data, something like the below image.

We need to hide every alternative column, which is blank. We need to use loops; the below code will do the job for us.
Code:
Sub AlternativeColumn_Hide() Dim k As Integer For k = 1 To 7 Cells(1, k + 1).EntireColumn.Hidden = True k = k + 1 Next k End Sub
It will hide every alternate column.

Example #6 - Hide Every Empty Column
In the previous example, every other alternative column was blank. So we have hidden it easily. But look at the below data.

Here, the empty columns pattern is not standard. In these cases, the below code will hide all the empty columns. It does not matter what the pattern is.
Code:
Sub Column_Hide1() Dim k As Integer For k = 1 To 11 If Cells(1, k).Value = "" Then Columns(k).Hidden = True End If Next k End Sub
When you run the code, you will get the result as follows.

Example #7 - Hide Columns Based On Cell Value
Now we will see how to hide columns based on the cell value. For example, look at the below data.
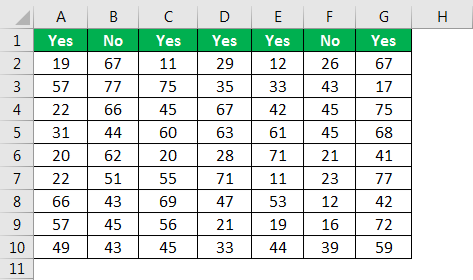
Here, we want to hide all the columns if the heading is “No.” The below code will do it for me.
Code:
Sub Column_Hide_Cell_Value() Dim k As Integer For k = 1 To 7 If Cells(1, k).Value = "No" Then Columns(k).Hidden = True End If Next k End Sub
When you run the code, you will get the result as follows.