Table Of Contents
Excel VBA For Each Loop
VBA For Each Loop goes through the collection of objects or items and performs similar activities. It will consider all the available specified objects and perform instructed activity in each object.
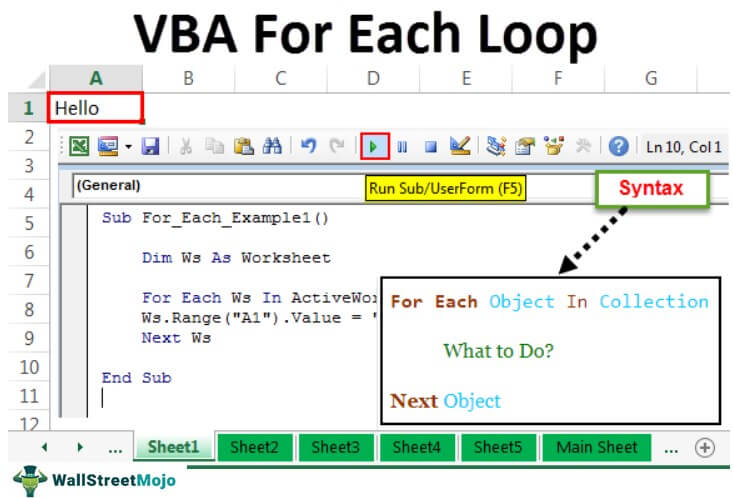
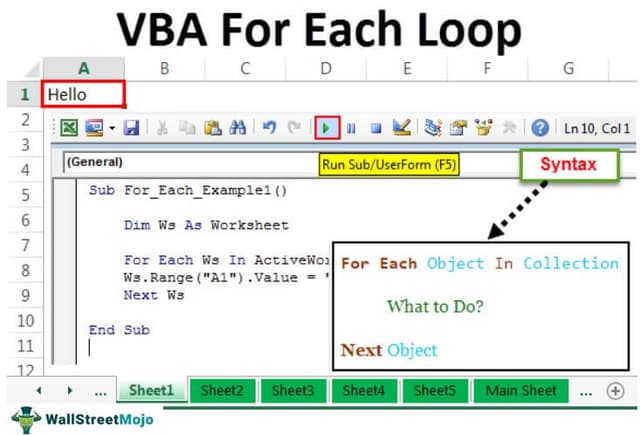
In VBA, it is mandatory to understand the loops. A loop allows you to conduct the same activity for many cells or objects in excel. Today's article will concentrate on the For Each Loop mechanism.
Syntax
VBA For Each Loop can loop through all the set collections of objects or items. For example, a group means "All the opened workbooks," "All the worksheets in a workbook," and "All the collection of shapes and charts in the workbook."
Let us look at the syntax.
For Each Object In Collection What to Do? Next Object
For example, you have 10 sheets in your workbook. You want to hide all the worksheets except the one you are in. Can you hide it manually? Yes, you can, but what if you have 100 sheets? Isn't that a tedious and time-consuming task to do? So instead, you can do this using VBA For Each Loop.
How to use For Each Loop in VBA? (Examples)
Example #1 - Insert Same Text in All the Sheets
We will see how to use FOR EACH in VBA with a simple example. Assume you have 5 worksheets in a workbook, and you want to insert the word "Hello" in all the worksheets in cell A1.

We can do this with FOR EACH LOOP. You must remember that we are performing this activity on each worksheet, not on the same worksheet. Follow the below steps to write the VBA code.
Step 1: Start the excel macro.
Code:
Sub For_Each_Example1() End Sub

Step 2: Since we are referring to the worksheets, declare the variable "Worksheet."
Code:
Sub For_Each_Example1() Dim Ws As Worksheet End Sub

Step 3: Now, using FOR EACH LOOP, we need to refer to each worksheet in the active workbook.
Code:
Sub For_Each_Example1() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets Next Ws End Sub

Step 4: Write what we want to do on each worksheet. In each worksheet, we need to put the word "Hello" in cell A1.
Code:
Sub For_Each_Example1() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets Ws.Range("A1").Value = "Hello" Next Ws End Sub

Step 5: Run this code manually through the option or press shortcut key F5. It does not matter how many sheets you have; it will insert the word "Hello" in all the worksheets.

Example #2 - Hide All the Sheets
As told earlier in the post, what if you have hundreds of sheets to hide except the one you are in? Using VBA For Each Loop, we can hide all the sheets in Excel.
Step 1: Start the macro with your name.
Code:
Sub For_Each_Example2() End Sub

Step 2: Declare the variable as “Ws.”
Code:
Sub For_Each_Example2() Dim Ws As Worksheet End Sub

Step 3: Now, in each worksheet, you need to hide the sheet.
Code:
Sub For_Each_Example2() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets Ws.Visible = xlSheetVeryHidden Next Ws End Sub

Step 4: Running the above code will hide all the sheets, but Excel needs at least one sheet visible. So, we need to tell which sheet not to hide.
Code:
Sub For_Each_Example2() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets If Ws.Name <> "Main Sheet" Then Ws.Visible = xlSheetVeryHidden End If Next Ws End Sub

The operator symbol <> means not equal to in VBA.
So, the code says when you are looping through all the worksheets in the active workbook, hide if the sheet name is not equal to the "Main Sheet."
We can do this by using the IF statement in VBA. First, write the code as IF Ws.Name <> "Main Sheet" Then hide, or if it is equal to the sheet name "Main Sheet," then do not hide.
Step 5: Run the code using the F5 key or manually. Then, it will hide all the worksheets except the one named "Main Sheet."

Example #3 - Unhide All the Sheets
We have seen how to hide all sheets except the one we are in. Similarly, we can unhide all the worksheets as well.
We need to change the code from xlSheetVeryHidden to xlSheetVisible.
Code:
Sub For_Each_Example3() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets Ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Next Ws End Sub

We do not need the IF condition here because we are unhiding all the sheets. However, if you do not want to unhide any specific sheet, you can use the IF condition and supply the sheet name.

Example #4 - Protect and UnProtect All the Sheets
Protect All Sheets: We can protect all the sheets in the workbook with just a piece of code. All the principles are the same, the only thing we need to do here is instead of Ws. Visible, we need to put the code Ws. Then, protect and type the password.
Code:
Sub For_Each_Example4() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets Ws.Protect Password:="Excel@2019" Next Ws End Sub

Unprotect All the Sheets: We can also unprotect all sheets protected in the workbook using VBA. We need to put the words "Unprotect" and "Password."
Code:
Sub For_Each_Example6() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets Ws.Unprotect Password:="Excel@2019" Next Ws End Sub

Things to Remember
- VBA For Each Loop is for the collection of objects.
- It will consider all the specified objects in the specified workbook.
- While declaring the variable, we need to know which object we refer to—for example, worksheet, workbook, chart, etc.