Table Of Contents
What is the Variance Analysis Formula?
Variance analysis refers to the investigation, due to deviations, in the financial performance from the standards set by the company in the budget. It helps the company's management to keep an eye on and a control check on its operational performance.
Variance Analysis can apply to many variables, but they are generally and broadly categorized into the following different types:
- Material Variance
- Variable Overhead Variance
- Labor Variance
- Sales Variance
- Fixed Overhead Variance
Below are some of the Variance Analysis formulae that one can apply:
- Material Cost Variance Formula = Standard Cost – Actual Cost = (SQ * SP) – (AQ * AP)
- Labor Variance Formula= Standard Wages – Actual Wages = (SH * SP) – (AH * AP)
- Variable Overhead Variance Formula = Standard Variable Overhead – Actual Variable Overhead = (SR – AR) * AO.
- Fixed Overhead Variance Formula = (AO * SR) – Actual Fixed Overhead.
- Sales Variance Formula = (BQ * BP) – (AQ * AP)

NOTES:
Where,
- SQ = Standard Quantity for actual output,
- SP = Standard Price
- AQ = Actual Quantity
- AP = Actual Price
- SH = Standard Hours
- AH = Actual Hours
- SR = Standard Rate
- AR = Actual Rate
- AO = Actual Output
- BQ = Budgeted Quantity
- BP = Budgeted Price
Explanation of the Variance Analysis Formula
There are various aspects of the variance analysis formula, as mentioned above. The difference between the direct material's standard cost and the direct material's actual cost that the firm uses for its production can be termed Material Variance (Cost Variance). The first term in every formula is associated with a set standard, and the second term in every formula state actually. The difference gives us whether that Variance is favorable or adverse. When the result is positive, that is favorable, versus the result that comes in negative is adverse.
Examples of Variance Analysis Formula (with Excel Template)
Let’s see some simple to advanced examples of Variance Analysis Formula to understand it better.
Example # 1
Below is the summary extracted from ABC Ltd., which manufactures steel. You are required to do material and labor variance analysis.
Below is given data for the calculation of variance analysis.

Calculation of Standard Quantity for AO

Calculation of Standard Hours for AO

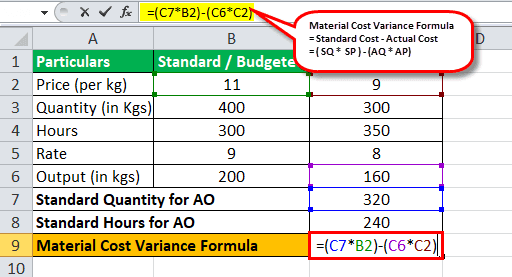
Calculation of Material Cost Variance

Material Cost Variance Formula = Standard Cost – Actual Cost
= (SQ * SP) – (AQ * AP)
= (320*11) – (300*9)
Material Cost Variance will be -

=2080 (Favorable)
Calculation of Labor Variance

Labor Variance formula = Standard wages – Actual Wages
= (SH * SP) – (AH * AP)
= (240*9) – (350*8)
Labor Variance will be -

=640 (Adverse)
NOTE: Whenever there is a negative figure in variance analysis, then it should be written as Adverse and not negative.
Example # 2
Prashant industries, a well-renowned company in the manufacturing of copper cables, is worried about its actual performance due to an increment of overhead expenses and has provided you the below data and asked you to conduct overhead analysis for both fixed and variable.
Below is given data for the calculation of variance analysis.

Calculation of Variable Overhead Variance

Variable Overhead Variance = Standard Variable Overhead – Actual Variable Overhead = (SR – AR) * AO
= (25 – 27) * 80
Variable Overhead Variance will be -

=160 (Adverse)
Calculation of Fixed Overhead Variance

Fixed Overhead Variance = (AO * SR) – Actual Fixed Overhead
=(80 * 25) - 2500
Fixed Overhead Variance will be -

=500 (Adverse)
Example # 3
Silver ltd has been trying to analyze its issue related to performance as it is not able to analyze why it shortfall with meeting its street estimate profits, and upon initial investigation, it found out that its operating profit is fluctuating year on year. Hence, the driver for the same was gross profit, and hence it decided to review its production-related issues, if any. You are required to conduct all the variance analysis and advise the management of Silver ltd where the issue lies.

Below is given data for the calculation of variance analysis.
Calculation of Standard Quantity for AO

Calculation of Standard Hours for AO

Calculation of Material Cost Variance

Material Cost Variance Formula =Standard Cost – Actual Cost
=(SQ * SP) – (AQ * AP)
=(1080*3.55) – (2700*4)
Material Cost Variance will be -

=6966 (Adverse)
Calculation of Labor Variance Formula

Labor Variance formula = Standard wages – Actual Wages
= (SH * SP) – (AH * AP)
=(12960*2) – (11000*1.5)
Labor Variance will be -

= 9420 (Favorable)
Calculation of Variable Overhead Variance

Variable Overhead Variance = Standard Variable Overhead – Actual Variable Overhead = (SR – AR) * AO
=(2 – 1.5) * 2700
Variable Overhead Variance will be -

=1350 (Favorable)
Calculation of Fixed Overhead Variance

Fixed Overhead Variance = (AO * SR) – Actual Fixed Overhead
=(2700 * 2) – 7000
Fixed Overhead Variance will be -

=1600 (Adverse)
Calculation of Sales Variance

Sales Variance = (BQ * BP) – (AQ * AP)
=(2500*5.6) – (2700*5.5)
Sales Variance will be -

=850 (Adverse)
Relevance and Uses
It can be said that variance analysis involves the isolation of different causes for variation in budgeting when compared with actual outcomes. Variance analysis aids in management by exception concept by depicting all the deviations from standards affecting the firm's financial performance. If variance analysis is not performed, such exceptions may cause a delay in action from the management, which was very much necessary in that situation. The performance of every responsibility assigned to different departments is measured and evaluated against standards concerning areas that are within its direct control.