Table Of Contents
What Is A Value Trap?
A value trap is when the stock's current price appears to be undervalued based on fundamental valuation parameters like Price to Earnings, Price Book Value, and Price to cash flow ratio over time; however, these stocks are not worthy investments. For such stocks, periods of low price can be coupled with low multiples as well.
This could be because the company doesn't have much to offer in the future, lacks future planning of product line, company's competitive behavior, innovation in the field of operations, ability to manage cost, etc. Moreover, the historical performance of value trap stocks in the open market and otherwise also has to be taken into consideration in this situation.
Value Trap Explained
A value trap refers to a situation where an investment appears to be undervalued based on traditional financial metrics like price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, price-to-book (P/B) ratio, or dividend yield, but it turns out to be a poor investment choice due to underlying problems or negative factors that aren't immediately apparent.
Investors falling into a value trap may see a stock's low valuation and believe it's a bargain, only to find that the company faces fundamental issues such as declining earnings, deteriorating financial health, technological obsolescence, poor management, or industry disruptions.
Failing to identify value trap indicators can lead to significant losses as the stock's price continues to decline, even though it seemed cheap initially. To avoid falling into a value trap, investors should conduct thorough research beyond just financial ratios.
Analyzing the company's competitive position, industry trends, management quality, growth prospects, and potential risks is essential. Distinguishing between a temporarily depressed stock and a genuinely undervalued opportunity requires a comprehensive understanding of the company's fundamentals and its long-term prospects.
For any investors, it is crucial to understand and analyze from all aspects instead of concentrating on attractive market prices compared to some multiples. Often, even expensive investment at higher prices turns out to be better than looking at cheap investment options.
Suppose an investor wants to look for such value investment in undervalued companies. In that case, they must ask a particular question, i.e., Why has the market price of such investments been low over so much time, what are future aspects of business, holding patterns in stocks, comparison with peers, and past, present, and future analysis and forecast of business. It can be avoided if an investor understands and performs research on the business before making any investment decision.
Characteristics
Let us understand the characteristics of value trap stocks through the explanation below.

- Available at Attractive Price Compare to Valuation Metrics: Such investments are priced lower in the market than valuation metrics like Price to Cash flow, Price to Earnings, Price to book value, etc.
- Inconsistent Profit: If investors decide to research more in such stocks, they will find inconsistency in profit over multiple years. The growth of stocks depends on earnings consistency and growth; if it's not there, it results in the degradation of stock in terms of valuation.
- No Future Planning: For every business, it is essential to plan its future process; whenever a company is in the product, which, although trending today but a future requirement product is uncertain, such stocks look attractive today but prove to be a value trap for investors.
- No Control Over Cost: Due to various factors or developments in technology, that are not adopted by the company, the cost of production is still high. If the company cannot manage its cost structure, face problem in the future.
- Bad Management: Good management is the business's life to survive and prosper in the future.
- Accounting Issues: Due to manipulation, tactics used in accounting such value trap business looks attractive in books compare to their market price.
Examples
Now that we understand the basics of the concept and its intricacies, let us understand the catastrophic effect of failing to understand value trap indicators through the examples below.
Example #1
Stock ABC Ltd is available at an attractive price compared to its earnings of 5X, compared to its average of 20X earnings for the last year. In addition, ABC's price-to-book value ratio has dipped below 1 for the last nine months. Previously it was around 2.
Such indicators mean an undervalued company and a good investment opportunity in value investing for many investors. However, many investors suffer a loss due to a lack of studying the company's complete fundamental analysis.
Example #2
Trinity Place Holding Inc. is a New York-based real estate company that deals with risk-adjusted real estate investments in the United States. In August 2023, it was trading on the exchange at $0.45 per share. This value was a 26.51% increase after a dramatic 17.08% decrease in the previous three months. According to the GF value evaluation, its fair was estimated at $11.11 per share.
However, a more detailed analysis revealed the underlying factors of risk that simply cannot be overlooked. As a result, an Altman Z-Score of -0.49 indicated such risks. Therefore, experts suspect that the seemingly value-adding stock might well be a value trap.
Causes
Let us understand the causes that end up creating a value trap stock through the discussion below.

- Lack of Research and Development in Product Line: Every company needs to perform research and development to survive and grow in the future. If a company does not continuously research new products and services and make them available in the market, it may look attractive today but won't survive in the long run. Historical performance should be analyzed and compared with the present, and for an investor, it is essential to understand the business's future planning.
- Less Focus on Investors: Companies often focus on large investors and concentrate on them. At the same time, a higher portion of ownership of shares is by insiders and large investors, resulting in ignorance towards the common investor. An investor must understand holding patterns in the company before investing.
- Various Small Factors: Many parameters affect investment decisions on an institutional level to invest in certain companies like stock price revenue, etc. many institutions prefer to invest in a company after it shows a certain level of growth in the market. Many small companies in which institutional investors are not yet involved look attractive from a price point of view but turns out to be a value trap.
- Control Over Holding: Often, it is considered a good sign if the company owns a large part of its shares in the market. But, if institutions like mutual funds or hedge funds don't own enough percentage of stocks to influence decision making or ability to generate the right amount of votes on disagreement in business management, it results in a lack of interest in institutional investors, and such stocks become value traps for retail investors.
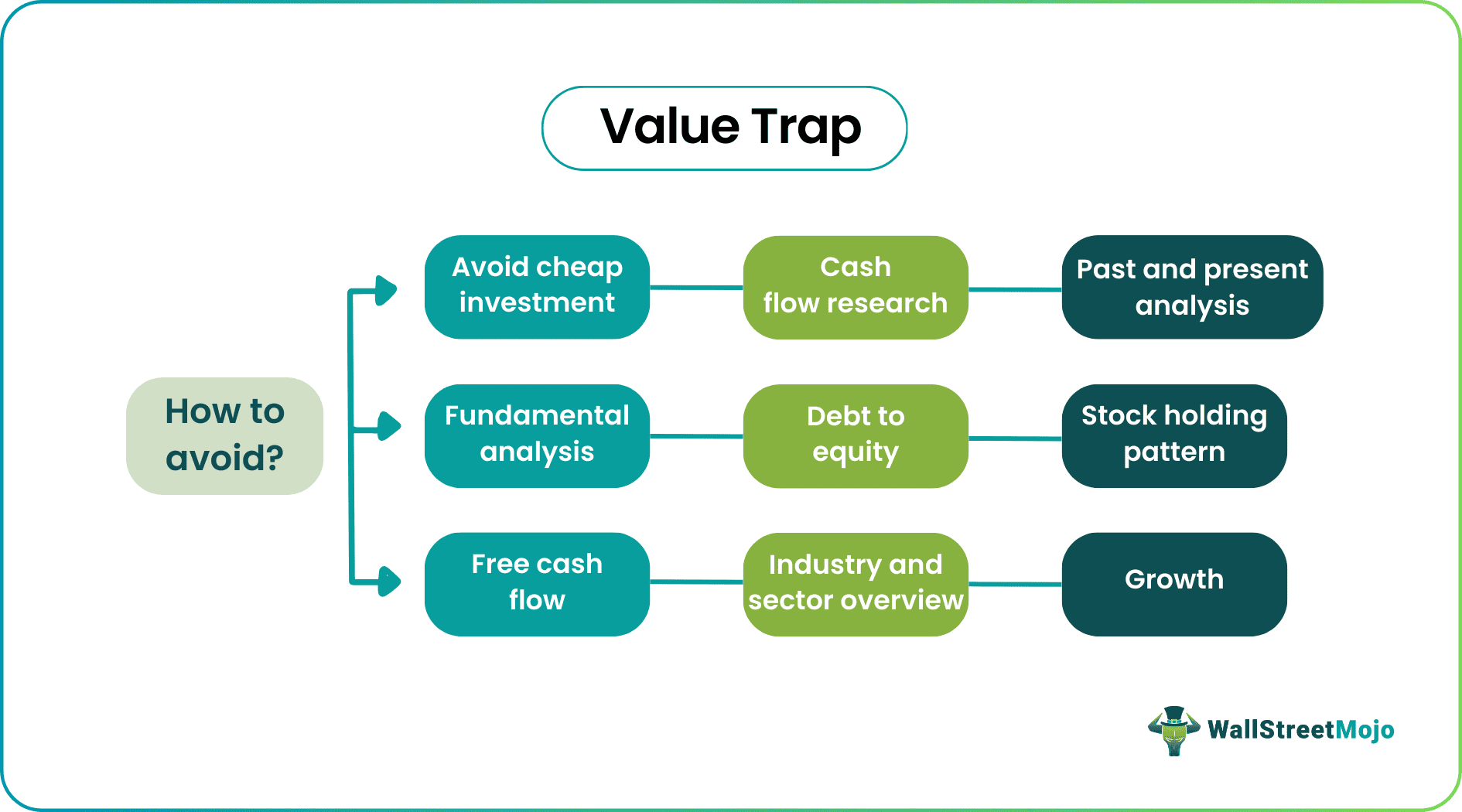
How to Avoid?
Now that we have a detailed understanding of value trap indicators and the concept’s intricacies. Let us learn how to avoid them through the detailed explanation below.
- Avoid Cheap Investment: Investors should concentrate on value and growth instead of price. Companies with the combination of both components, i.e., value and growth, prove to be a much better investment.
- Fundamental Analysis: 360-degree analysis of the company is critical before making any investment decision. And such analysis should include all pros and cons of business from various points of view.
- Free Cash Flow: How much does the company have after paying out its free cash flow and how they are utilizing it.
- Cash Flow Research: How much cash flow comes from operating activities, investing activities, etc. as such information tells the usability of business operations and investment decisions.
- Debt to Equity: Asset vs. liability comparison is significant in the analysis. For an investor, it is vital to understand all rations and not to depend on a specific ration in the decision process.
- Industry and Sector Overview: Understand Industry and sector overview its pros and cons in the market. How peers of the company are performing in comparison.
- Past and Present Analysis: The Company's past, present, and future analysis is essential and can be done by observing the decision process in business, performance, and a thorough understanding of financial statements.
- Stock Holding Patterns: Understanding stock holding patterns in a company is essential for investment decisions. Often, the value trap results from an alteration in holding patterns in the company's shares.
- Growth: Growth in terms of revenue, profit, and future aspects of innovation is vital for any business to survive in today's market
Advantages
Let us understand the advantages of value trap stocks through the points below.
- Cheap Investment: Cheap investment opportunity, which looks like today's value trap, might turn into a valuable investment and can create massive wealth for value investors if done correctly.
- Undervalued Investment Opportunity: If investors do enough research, such value traps can be an excellent opportunity to invest in undervalued stocks and, over the period, generate wealth from such investment.
Disadvantages
There are factors that prove to be a hassle for investors as well. Let us understand the disadvantages of failing to understand value trap indictors through the points below.
- High Risk: This investment can result in the loss of entire capital. If an investor is not careful, they will lose wealth due to the attractive market price of the investment.
- Uncertainty: These are uncertain; some might turn out to be good investment decisions while others may be bad.

