Table of Contents
Value Exchange Definition
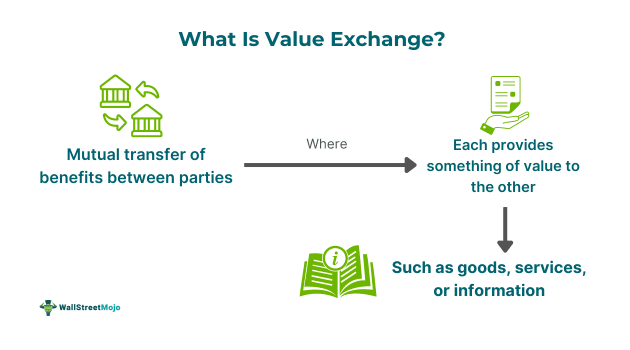
Value Exchange refers to the arrangement where individuals, entities, and originations exchange or trade something of value. Value in the world of finance can take different forms. It could mean products, services, information, money, or assets. It refers to things that have inherent worth that can be exchanged.
The system of exchanging things of value between parties is the basis of economic interactions, which also translate into social interactions. The concept revolves around the day-to-day activities of an individual, entity, or organization. It gives insights into how the economy, trade, and exchange of goods and services work and is the foundation of many businesses.
Key Takeaways
- Value exchange refers to the exchange of things of value, such as products, services, money, information, and assets. It happens between individuals and organizations and forms the basis for social and economic interactions.
- Value exchange systems involve the exchange of products and services for money or data. Businesses offer experiences, relevant communication, and quality offerings. Customers reciprocate with loyalty, repurchases, and reviews.
- It is a mutually beneficial transaction arrangement that helps in building customer trust and brand value and results in economic growth and development.
Value Exchange Explained
Value exchanges are the exchange or delivery of goods, services, information, assets, etc. They include anything that is considered valuable between the parties involved. The exchange shows what businesses could deliver to their customers. This forms the basis of a customer's reaction or loyalty towards the brand. Value exchanges are reflected in all aspects of a business and require careful consideration from stakeholders in implementation.
From a company's perspective, value is delivered through customers' experiences by providing accessible, effective, and enjoyable interactions. It is done by providing high-quality products and services that are helpful to the consumers. Value is provided through relevant communication and quick resolution of issues. Business efforts through promotions and rewards are considered valuable when customers turn because of the factors mentioned above. Customers, as a result, reciprocate their efforts with loyalty. They repeat purchases, try new products or services, refer them to known circles, and provide positive reviews. These, in turn, bring respect, recognition, and status to the business.
Therefore, the value exchange system can be described as the system of exchange of valuable things between businesses and enterprises to customers. Businesses provide customers products and services, giving them money or data in exchange—money and data (reviews, preferences, recommendations), etc., resulting in a profit. In essence, businesses produce products and services to fill the market needs and customers. If they find it useful, the exchange is made, and in most cases, the exchange of value is money.
Types
Exchange of value can be off the following types:
- Customer experience-based exchange of value: This type involves data exchange in return for enhanced customer experience. It means personalization and access to consultation with experts. Customers provide data, and businesses using this data create tailored solutions and experiences with the brand.
- Content-based exchange of value: This type involves exchanging data in return for provided information or content. Customers provide data and receive content that helps solve issues in return.
- Social and community-based exchange of value: This type of exchange involves data exchange in return for access to particular communities, platforms, or networks. Customers provide data to gain access to groups of like-minded people. Referrals can be a part of it.
- Incentive-based exchange of value: This exchange is done for offers as returns. Data is exchanged for discounts, offers, and competition entries. Customer data is provided, and incentives are provided to nudge action.
Examples
Let us look at some examples to understand the concepts better.
Example #1
Imagine Dan is a food enthusiast who wants to eat healthily. He searches for a subscription model of places where they provide nutritious meals all day according to his health status. He used the value exchange system in e-commerce websites for that. Dan went to a nutritionist's website, checked out their books and clothing accessories to stay motivated, and opted for a meal plan, too. Luckily for him, through the value exchange system in the e-commerce website of nutrition, he could get all the things he desired to set for his healthy journey.
This arrangement involves two major things: data provision and money value exchange. Data such as height, weight, age, and health condition details are shared to make a customized plan. On the other hand, money value exchange provides the base of exchange for something valuable, such as the return of services.
Example #2
Retailers and brands are increasingly recognizing the immense value of consumer data as a critical asset for delivering seamless and personalized consumer experiences. According to an EY (Ernst & Young) article, leveraging connected data offers numerous benefits, including the mitigation of costs by optimizing media spend, pricing strategies, and promotions, thereby reducing waste and duplication. By integrating data from both retailers and brands, companies can gain a holistic, real-time view of the consumer, enabling them to make more informed decisions and drive impactful consumer experiences.
Moreover, connected data enhances customer loyalty by allowing businesses to tap into post-purchase opportunities, fostering deeper relationships with consumers. It also enables the identification of upselling opportunities through optimal product bundling and personalized marketing efforts. This comprehensive approach to data not only improves product innovation but also helps companies better understand consumer behavior, ultimately leading to more efficient operations and a stronger connection with their target audience.
Importance
Given below are some of the points that highlight the importance of the exchange of value:
- It builds trust with the customers as they understand what they get in return for their data.
- Value exchange in marketing boosts customer engagement through positive interactions.
- It builds the company's brand image, and the value it offers makes it stand out from its competitors.
- Customer data helps decide on the best products and services for the market, which in turn helps customers solve their problems.
- It gives rise to mutually beneficial partnerships. In this exchange, both customers and businesses stand to benefit.
- A successful value exchange in marketing results in conversions and revenue.
- It enhances the brand value and provides a good reputation.
- Businesses that provide value may also consider societal concerns to portray themselves as socially responsible companies. This could result in upliftment actions in society.
- It helps with economic growth, development, and sustainability.
