Table Of Contents
Value Creation Meaning
Value creation refers to creating beneficial products from raw inputs that have unique selling points and more worth than the inputs. Its purpose is to create unique products with special features to attract more customers, build long-lasting relationships, and ensure non-stop selling of the product to generate revenue and profits for a firm.
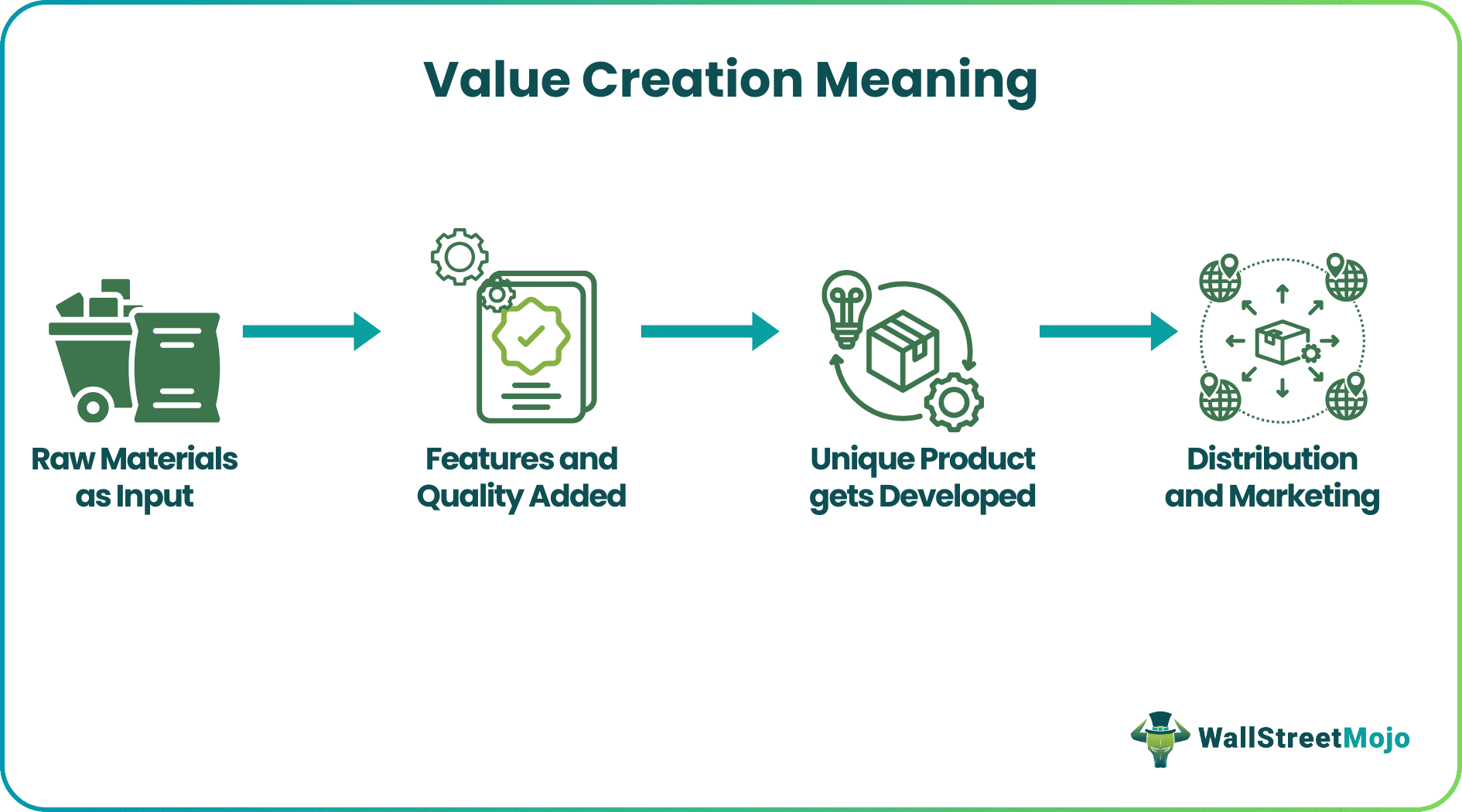
It depends on the understanding of one's business and potential customers and is the backbone of every good sold in the market. The sales team provides valuable insight into the development of the value of a product. It includes behaviors, norms, raw materials, and the production efficiency of a firm. Finally, the end product is more valuable than the inputs used for making it.
Key Takeaways
- Value creation is the process of turning raw materials into unique and useful goods with a higher value than the raw materials themselves.
- The two main types of value creation are customer and shareholder value creation.
- The four main states of creating value are development, marketing, manufacturing, and distribution.
- Value creation aids in establishing long-lasting relationships with customers, whereas value capture collects the value already generated in a product to make it lucrative.
Value Creation Process Explained
Value creation is stated as creating or producing something of more value than the inputs used so that it may attract customers. It also motivates customers to pay more for the product. The value added gets calculated by subtracting the amount spent on inputs purchased and the selling price of the product. Many businesses do it to give value to the customer for their purchase of the product or services.
In some cases, businesses undertake shared value creation for their stakeholders. It is because if customers feel that a brand is highly valuable, then they are willing to pay more for the product. It is essential for the success of a business or entrepreneur. Value is determined by three factors, namely utility, egoism, and rarity. Value creation is done by creating a product that is badly needed by consumers is rare, or adds value to the buyers' social status.
It has three steps, namely:
- Transformation - Here, the raw materials are converted into useful products or services.
- Distribution - It refers to converting a product into a product that the customer easily buys.
- Consumption - It entails the usage of the value-added product in the way the product has been designed to be used by the consumers.
Value creation is quite important to all businesses as it helps increase the firms' profits and customer satisfaction. It can be understood as a long-term investment that yields long-term benefits.
The formula for calculating and quantifying the value creation is:
Value Creation = Cash Flow / (WACC – Growth Rate of cash flow)
where WACC is the weighted average cost of capital.
Stages
One can divide the value creation model into four stages:
- Development - This stage consists of the development of a product using the input after careful deliberation of value addition of the newly created product.
- Marketing - Here, the firm producing the value-added product does the marketing to take the best features and qualities of the product to the masses and create a want to buy the product.
- Manufacturing - After the marketing is over, the firm starts manufacturing the product on a large scale to cater to the demands created by the marketing of the product.
- Distribution - Then, the firm prepares a comprehensive road map to take the product to various markets to sell to customers.
Types
There are two main types of value creation:
#1 - Customer Value Creation
It means providing the customer with a valuable product that makes the customers pay more for it. For it to happen, companies must add more value to their product or services. It does not only add value to the basics of the product like quality, features, customer service, timely resolution of complaints, good interactive customer care, and branding of the product. The revenue generated shows the value delivered to the customers.
#2 - Shareholder Value Creation
It means creating value for the shareholders of the company. It always forms the focal point of all other business matrices. The net income of a company represents shareholder value creation. It has the potential to become the soul of overall strategic planning by a company. Since management has been an agent of stakeholders, they accord higher priority to shareholder value creation.
Examples
Let us understand the topic using a few business examples.
Example #1
Google created the best search engine by figuring out how to make it work by enhancing the search functionality to give search results in a few seconds from across the web. The search function added a great deal of value for customers. Moreover, Google worked hard and integrated AdWords into its search engine, which created a huge amount of value for businesses in advertising their products. Both these functionalities gave Google the capacity to monetize its search functions by auctioning ads onto it. Thus, it created a unique product that was beneficial to both – customers as well as the business leading to high revenue and growth for Google.
Example #2
Another example is that of ride-sharing service Uber. Uber created a unique platform to connect drivers and passengers easily and quickly. The services of Uber made it easier for passengers to book a cab and allowed drivers to get passengers without waiting for them. It made it the leading cab rental service provider in the world.
Importance
The importance of value creation lies in the following aspects:
- It helps one to gain customer affinity.
- It creates trust between the brand and the customer.
- It also builds a loyal customer base for the firm.
- A strong bond is created between a product or service and the target audience.
- As a result, the sales of the product or services become quite fast and in large numbers like Apple’s iPhone.
- The company is assured of revenue generation without any losses.
Value Creation vs Value Capture
Value Creation
- It helps one to understand the customer
- It facilitates a firm to know the needs of a customer.
- Here the word innovate is the pillar of the process
- The form offers beneficial offers to the customers
- The product created is unique
- It helps builds a long-term relationship with the customer.
- Customers become loyal to the brand
Value Capture
- It helps in setting and managing the value-based levels of price.
- It basically sells on product value
- It helps build a long-term relationship with the customer.
- It captures the existing value-created product to turn it profitable
- It deals with the monetization of a product by a firm successfully.
- It relates to the effective pricing of a product or goods appropriately to reap; profits on their sales.
- It also enables the monetization benefits as liquidity to shareholders of the firm.
