Table Of Contents
What Is Valuation Of Intangible Assets?
Valuation of Intangible Assets refers to ascertaining the economic value of non-physical assets like goodwill, customer relationships, patents, and brand reputation. Individuals or entities conduct this evaluation to determine the worth of intangible assets so that they can make informed decisions about investments, strategic planning, financial reporting, mergers or acquisitions, and licensing deals.
Valuation of intangible assets is vital to ensuring accuracy in financial representation, guiding investment decisions, and optimizing a competitive edge in business operations. Effectively leveraging intangible assets enables owners to create fruitful strategies and plan business operations better for increased productivity and profitability.
Key Takeaways
- Valuation of intangible assets is all about determining the economic worth of intangible assets such as brand image, goodwill, customer relationships, and patents.
- It involves assessing the value of intangible assets to help entities make well-informed decisions about investments, strategic planning, financial reporting, mergers and acquisitions, and licensing agreements.
- The main valuation methods for intangible assets are the relief from royalty method (RRM), with and without method (WWM), multi-period excess earnings method (MPEEM), real option pricing, and replacement cost method less obsolescence.
- Its importance lies in identifying competitive advantages, strategic decision-making, accurate financial reporting, risk management, and boosting investor confidence.
Valuation Of Intangible Assets Explained
Valuation of intangible assets involves the calculation of the economic worth of any intangible assets to assess the actual value of a company and make better decisions. An intangible asset is classified into two categories - identifiable intangibles like trademarks and patents and value-increasing intangibles like proprietary processes and skilled management. The working and valuation of such assets have become a complex process for many because of their unique traits. However, when the right method is used, it can be achieved.
Proper valuation of such assets can impact investment attractiveness and stock prices of companies by influencing how businesses appear to investors and in the market. Many companies use it to secure financing and allocate resources to make further strategic decisions for their businesses and operations. Moreover, if the method of valuation of intangible assets and shares is implemented effectively, then it impacts the corporate valuations and investment strategies of companies.
Methods
Five main methods define multiple approaches to the valuation of intangible assets. They have been discussed below:
#1 - Relief from Royalty Method (RRM)
RRM, as the name implies, is the method in which entities figure out the amount of royalty that they are not liable to pay just because they own such assets. In this case, the total present value of the royalty they save becomes the value of the intangible assets they hold. This is the most recommended method of valuation for companies that use non-physical assets requiring licenses, like patents, copyrights, trademarks, etc.
RRM consists of the elements of-
- income approximation of tax rates, revenue, and growth.
- market rates of royalty about comparable assets.
For calculation, the following formula can be used:
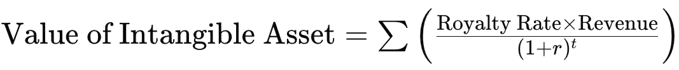
Here
- r= discount rate
- t= time period
#2 - With and Without Method (WWM)
One can easily calculate the value of intangible assets using this method, which finds the difference between a discounted cash flow model with and without assets for the organization. This difference is considered as the value of the intangible asset in question.
The formula used to figure out their value is:
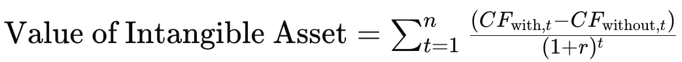
Where:
- CFwith,t = Cash flow with the intangible asset for those number of years
- CFwithout,t = Cash flow without the intangible asset for those number of years
- r = Discount rate
- t = Time period (in terms of years)
- n = Useful life of the intangible asset
#3 - Multi-Period Excess Earnings Method (MPEEM)
MPEEM is considered a type of analysis similar to discounted cash flow that separates cash flow related to a particular intangible asset and then obtains the present value using discounts. It has often been used when a company's value has its base in a single asset, where the asset's cash flow can be separated from total cash flows.
MPEEM can be used to value intangible assets like customer relationships and software.
#4 - Real Option Pricing
It helps in the valuation of those intangible assets that have the potential to generate cash flows in the future but are not doing so currently. Such a model can record the time value of intangible assets like underdeveloped patents.
#5 - Replacement Cost Method Less Obsolescence
It relies on setting a fresh replacement cost for the intangible asset, just like the cost approach. This means the cost it would take to prepare a new intangible from zero is calculated, and then it is adjusted for obsolescence, like the cost of depreciation in the cost approach.
Examples
Let us use a few examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
Let us assume that company XYZ has its trademark that is likely to produce
the following revenue over the next 3 years:
1st year: $500,000
2nd year: $600,000
3rd year: $700,000
The royalty rate being = 5%
Then, the annual royalty savings for:
1st year, R1= $500000 * 0.05= $25000
2nd year, R2 = $600000 * 0.05 = $30000
3rd year, R3 = $700000 * 0.05 = $ 35000
let us assume that the discount rate = 10% (0.10)
As the revenue and royalty rate are known to the firm, the RMM formula would best fit in the situation to calculate the value of its intangible assets.
Hence, using the formula:
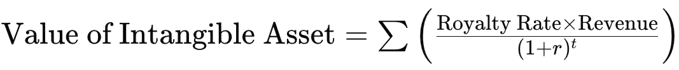
The present value (PV) of every royalty saving can be calculated individually:
PV for R1
$25000/ (1+0.10)
=25000/1.10
=22,727.27
PV for R2
$30000/ (1+0.10)2
=30000/1.21
=$24,793.39
PV for R3
$35000/ (1+0.10)3
= $35000/1.331
=$26,297.52
Hence, the value of trademark (which is the intangible asset in this case)
= PV for R1 + PV for R2 + PV for R3
= 22,727.27+24,793.39+26,297.52=$73,818.18
Therefore, the value of the trademark = $73,818.18
Example #2
An online article published on 2 November 2023 noted an 8% increase in intangible assets globally to $61.9 trillion in 2023 from $57.3 trillion in 2022. The report revealed how the treatment of the workforce directly influences the valuation of intangible assets. The publication also discussed the intangible asset valuation data of 2022, which signified a sharp decline, given the layoffs and waning investor sentiments.
In the list, Apple has maintained its topmost position with an intangible asset valued at $2.7 trillion, while the list saw the addition of a new entrant—Microsoft—into its second spot with a net $2.3 trillion of intangible assets.
Other than these, the E-cigarette and tobacco sector has been the leader in the list, with 91% of its net enterprise value associated with intangibles. In terms of country-wise attributes, the USA has seen the maximum increase in intangible value by the stock exchange, with the NYSE valued at $2.5 trillion.
Example #3
Let us assume a software firm called Innovad out of Old York City is verifying and valuing intangible assets. It has a patent for a unique AI algorithm worth $700 million. The same company has a strong brand identity worth $300 million and extremely skilled human resources valued at $200 million, which contributes $200 million to its value.
The company's customer relationship, especially with major international retailers, is valued at $150 million due to the long-term contract. Hence, after adding the values of all the company's intangible assets, Innovad reaches a valuation of $1,350 million. Moreover, such huge intangible assets will be a crucial factor in its merger with the European Tech giant.
Importance
The significance of the valuation of intangible assets differs with the type and nature of the industry in which it is conducted. Some of the common ones have been listed below:
- It is an important factor in enforcing intellectual property rights and managing intellectual property assets.
- It helps in strategic decision-making through the revelation of the real economic value of intangible assets.
- It enables more accurate and better financial reporting, giving a wholesome and clear picture of a company.
- It allows easier risk management through quantification and identification of possible vulnerabilities concerning intangible assets.
- Investors increase their confidence using transparent information regarding an organization's intangible assets.

