Table Of Contents
What Is Unlimited Liability?
Unlimited liability means the business owners' legal commitment as they are liable for all business debts if the assets of the firm/ business cannot meet its debts or liabilities. In short, the liability of the owners towards the business is unlimited.
The general partners/ sole proprietors are responsible for the business actions. It may end up even confiscating their assets' if the business cannot pay off their liabilities. So with unlimited liability, owners may not have the confidence of taking risky decisions which can impact the growth of business and many opportunities will be lost.
Key Takeaways
- Unlimited liability refers to business owners' legal obligation to bear all debts or
- liabilities of the business if its assets are insufficient to satisfy them. This means the owners' assets may be at risk of satisfying business debts.
- It is generally considered unfavorable because it exposes the owners' assets to business liabilities.
- Unlimited liability may be suitable for small businesses with lower risks and rewards. However, as the business grows and the risks increase, converting to a limited liability structure may be advisable to protect the owners' personal assets.
Unlimited Liability Explained
Unlimited liability in partnership is the concept in which the members of a firm are all equally responsible for the risks of loss or any 1 debt the company has taken to meet its operating expenses.
In business, has its advantages and disadvantages. The formation of a business regarding its liability has to be considered based on the nature of the business, owners’ capacity considering finance, skills, investment, etc. Unlimited liability is suitable for small businesses as the risk and rewards are less.
When the business grows, then it is better to convert it into a limited liability as the risk grows if the volume of business is huge, otherwise the risk ownership becomes difficult to bear and the partners may starting avoiding business opportunities that have very good future potential but has high risk currently. Thus this kind of thought process affects the business negatively and becomes a hindrance in future expansion process.
Examples
Let’s see some unlimited liability examples to understand the concept.
Example #1
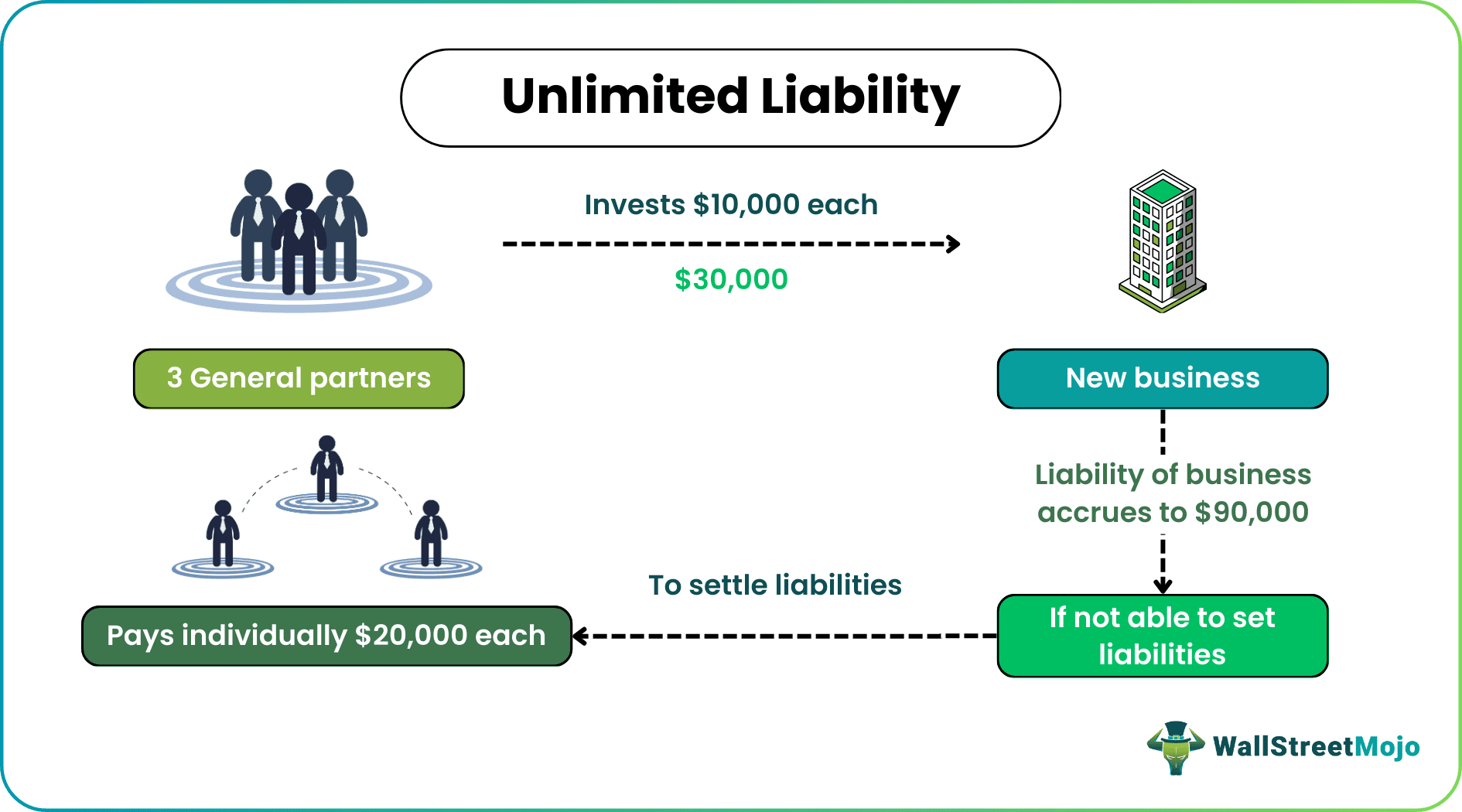
Three individuals work as partners, and each invests $10,000 into the new business they own jointly. Over the period, the liability of the business accrues to $90,000. That means apart from the initial investment of $10,000. Each partner needs to invest another $20,000 to settle the firm's liabilities. If the firm (business) cannot settle the liabilities or defaults on the payments to be made, then all three partners are equally liable to settle the liabilities.
Analysis
The above example indicates how unlimited liability in partnership works. If the business cannot meet its liabilities, the owners are responsible for paying them. The risk is more in this, as even the owners can also be seized for business liabilities.
Example #2
Lawsuits can greatly impact the sole proprietor/ general partners with unlimited liability. If any client sues against the business and cannot settle the dues to be paid post-judgment, then the client can sue the general partners/ proprietor to settle the dues. If they don’t have enough funds to settle the dues, personal assets will be seized.
Unlimited liability is not considered favorable as it can involve the owners' assets. It is one of the major reasons for forming limited liability partnerships and limited liability companies as they offer some protection to the owners against the business's liabilities. Registered companies and corporations work with the limited liability of the shareholders, which indicates that the business's liabilities are not guaranteed, and the same cannot be forced on the shareholders.
Example #3
Joe started a new restaurant. He took place for rent, took furniture, and other facility requirements on hire. The business went well for the first year. Due to the increasing competition, the business was not doing well. So Joe decided to shut down the business. When he closed down the business, he had to pay his creditors $20,000. The initial investment made by him was $10,000. So Joe now has a further liability of $10,000. Since it was a sole proprietorship, the left out of liability of $10,000 needs to be settled from his assets.
Analysis
In the above case, unlimited liability in business is not favorable to Joe since his assets (i.e.) cash of $10,000 is being used for a business purpose on the closure of a business. If the business were carried out on a limited liability basis, then for the liability of $20,000, which is to be paid, $10,000 the initial investment of Joe alone would have been considered for the settlement of dues and his assets will remain untouched for the business actions.
Thus the above unlimited liability examples clearly explain the concept.
Advantages
Some advantages of unlimited liability in business are as follows:
- Owners have the ultimate power and complete control over the business. They are free to make all business decisions within the law.
- Establishing and organizing sole proprietorship and general partnership firm is easy. This is because the partners equally share the risk and contribute equally to the capital. Such liability is ideal for small businesses.
- Dissolving the business is easy as the owners take all decisions. Dissolution has a number of steps which becomes less time consuming and smooth if the firm size and number of partners is small.
- Since owners contribute capital and share the risk equally, there is no outside interference. So, the owners can take all the income generated from the business.
- Complete confidentiality of the business can be maintained as the owners have complete control. There is no outside party to whom the entity is liable or to whom that need to share the company information.
- Management decisions will be improved and cautious as there is a risk of personal liability for the business actions. Such steps are very important otherwise business owners may take undue risk in the hope of generating greater returns and in the process, the business may face an uncertain future.
- Creditors and other stakeholders will have more confidence in the business, as the owners have to follow the unlimited liability clause. The business owners will also be careful in business operations as they have complete responsibility.
- The share capital and the initial investment are at the flexibility of the owners as there will not be any pressure for fixed contribution.
Disadvantages
Some disadvantages of unlimited liability are as follows:
- Unlimited liability makes the owners legally responsible for all the debts and liabilities of the business. They may have to face negative consequences in case the decisions are not able to meet the target.
- In a business with unlimited liability, both the business and personal assets of the owners may be at risk. Thus, along with the business, the owners are also personally liable to face any negative consequence.
- With unlimited liability clause, the owners will be careful in decision making, which can slow down the developments of the business as they will refrain from taking any risky business decisions. The business can even lose some good opportunities because of this.
- Acts of all stakeholders can impact the owners (e.g.). Even an act of an employee which is unlawful can put the owners at risk. In this case the liability of the partners increase further, putting them at greater risk not only financially but also legally.
- The growth of the business is purely in the hands of owners, as the business will cease to exist if the owner leaves, retires, or dies. It becomes very difficult to carry the entity forward with confidence and make future plans for its growth and expansion because there is no guarantee that it will continue existing even if the partners do not exist.
- It has a restrictive structure, as there is no proper legal status and differentiation between the owners and businesses. In other words, business and the owners are the same.
- The results and performance of the business are kept confidential. Mismanagement of the business can never be known to the outside world unless the business goes bankrupt.
Unlimited Liability Vs Limited Liability
- The the case of the former, the partners are liabile for any kind of business risk or debt and no one else will share it, whereas in case of the latter, the liability is limited upto their own contribution.
- In case of the former, the owners are personally responsible for the business obligations but for the latter the partners are not personally liable.
- In case of default in debt payment or any other similar situation, the personal assets of owners may be confiscated for unlimited liability but for limited liability, that will not happen.
Frequently Asked Questions
Unlimited liability for IP (Intellectual Property) infringement refers to the legal responsibility of an individual or entity for damages resulting from unauthorized use, copying, or distribution of intellectual property, such as patents, trademarks, copyrights, or trade secrets. In the case of unlimited liability, there is no cap on the amount that can be claimed for damages. The responsible party may be liable for the full extent of the financial loss suffered by the injured party.
Unlimited liability for breach of confidentiality refers to the legal responsibility of an individual or entity for damages resulting from the unauthorized disclosure or breach of confidential information, such as trade secrets, proprietary information, or sensitive customer data.
The concept of unlimited liability can significantly impact the decision-making process for entrepreneurs when choosing a form of business ownership. In a sole proprietorship, for example, the owner has unlimited personal liability for the business's debts and legal obligations, which may affect their personal assets and financial security, whereas, in a partnership or corporation, the liability may be limited to the business's assets, providing more protection for the owner's personal assets.
