Table Of Contents
What Is Unlevered Beta?
Unlevered beta is a measure to calculate the company's volatility without debt concerning the overall market. In simple words, it is calculating the company's beta without considering the effect of debt. Unlevered beta is also known as asset beta because the firm's risk without debt is calculated just based on its asset.
Key Takeaways
- Unlevered beta quantifies a company's market-related volatility independently of its debt. This metric calculates the firm's risk based solely on its assets, dissociated from debt considerations.
- Unlevered beta tends to be lower than levered beta, as it excludes the debt component, thus magnifying risk. Positive beta appeals to investors during upward market movements, while negative beta attracts them during downturns.
- A positive levered beta aligns with rising stock prices during favorable market conditions, whereas a negative levered beta corresponds to declining stock prices in unfavorable market scenarios.
Explanation
Unlevered Beta is the measurement of the risk of a company without the impact of debt. It is also known as Asset Beta and is used to measure the risk of an unleveraged company to the risk in the market.
- Equity Beta or Levered Beta compares the volatility of a company's stock against the returns of equity markets over a specific period. It measures how sensitive a particular stock is to various macroeconomic factors.
- Since every company has a different capital structure, one must compare how risky an individual company’s assets are, removing any effect that debt has and only measuring how risky the equity of a company is.
- Increasing debt in a company means that it would require more cash flows to service that debt, and hence there is uncertainty about the company's future cash flows. It translates to increased risk for a company due to increasing leverage rather than a result of market or macroeconomic factor risk. Hence, removing the impact of debt can determine the risk of only the company's assets.
- An unlevered beta will always be lower than the levered beta since it strips off the debt component, which adds to the risk. If it is positive, investors will invest in this particular stock when the prices are expected to rise. If the unlevered beta is negative, investors will invest in the stock when the prices are expected to fall.
Unlevered Beta Formula
You can calculate Unlevered Beta using the below formula -
Example of Unlevered Beta Calculation
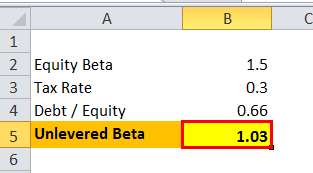
Let us take the example of company X, which has a beta of 1.5 on the market. The Debt/Equity ratio for the company is 2:3, and the tax rate is 30%.
- Unlevered Beta formula = 1.5 / 1 + (1-0.3)0.66

- Unlevered Beta = 1.03
Relevance and Use of Unlevered Beta
- Unlevered beta is used when an investor wants to measure the performance of a stock, which is publicly traded, concerning market movements without the positive effect of debt taken up by the company. A levered beta indicates a company's stock price sensitivity to overall market movements. A positive levered beta indicates that when market performance is good, then stock prices will rise, and a negative levered beta indicates that when market performance is poor, stock prices will fall.
- An unlevered beta formula measures the performance and volatility of stock without the tax advantages of debt. As the effect of debt is removed, companies with varying capital structures can be compared to measure how risky a particular company’s assets are.
- Investors calculate unlevered beta and use it for comparison by stripping off the impact of debt in the company's capital structure.
- Also, various equity analysts use this beta to build multiple financial models for their investors, which provide more information than just a basic scenario.
- Also, another factor to be kept in mind is that if a company has a high debt to equity ratio, all debt is rated AAA. It has inherently less risk than a company with a high debt to equity ratio but has a debt rated below the investment grade.
Conclusion
The Unlevered Beta formula is the measurement of the risk of a company with the impact of debt. It measures the risk of the firm's business, which is unleveraged to the risk of the market. It will always be lower than the levered beta since it strips off the debt component, which adds to the risk.
If the unlevered beta is positive, investors will invest in this stock when the prices are expected to rise. If the unlevered beta is negative, investors will invest in the stock when the prices are expected to fall. It measures the performance and volatility of stock without the tax advantages of debt. As the effect of debt is removed, companies with varying capital structures can be compared to measure how risky a particular company’s assets are.

