Table Of Contents
What is Unit Price?
Unit Price is a measurement used to indicate the price of particular goods or services to be exchanged with customers or consumers for money. It includes fixed costs, variable costs, overheads, direct labor, and a margin of profit to sustain the business activities and earnings of the organization.
Explanation
A unit price is when a product or service is exchanged between the producer, manufacturer, or service provider to the customer or consumer of the goods or services. It is vital for both organizations and consumers. For example, an organization could not sustain selling at lower prices consistently. Similarly, the customers would not purchase the product if the value perceived is lower than the price charged.
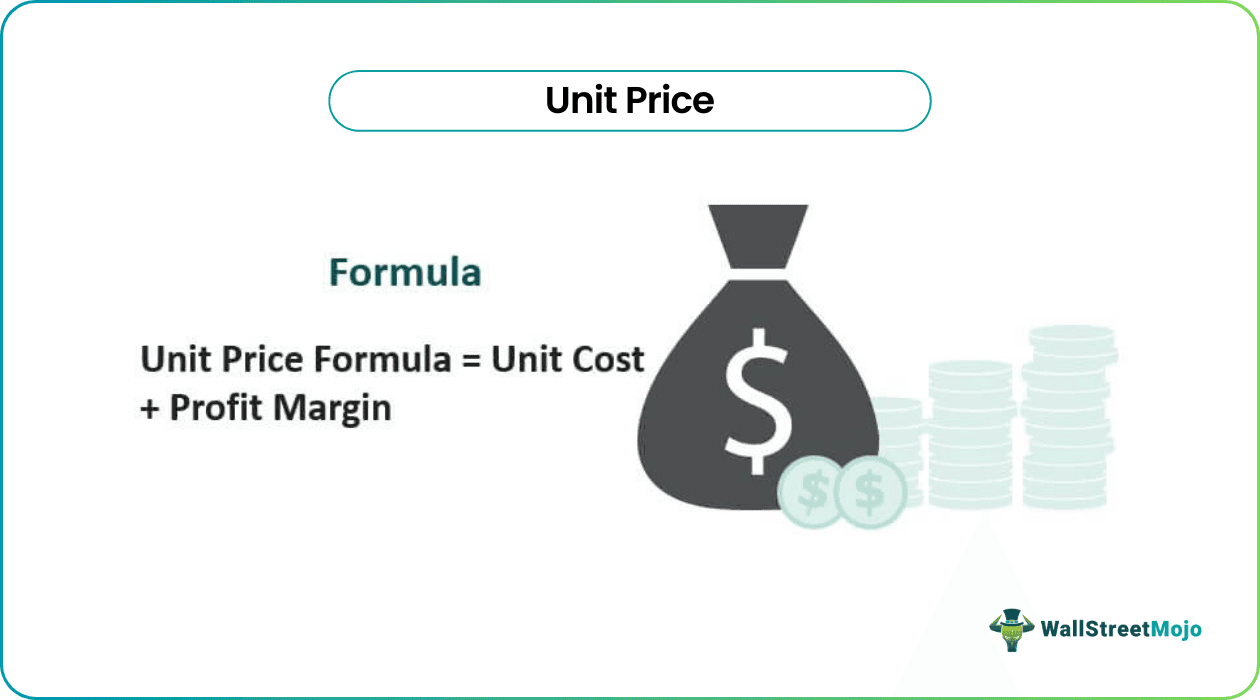
Unit Price Formula
Unit Price Formula = Unit Cost + Profit Margin
The terminology to understand the formula, as mentioned earlier, is as follows:
#1 - Unit Cost
The unit cost indicates the cost of producing the final products when it is readily available to be sold or transferred. The cost of the product mainly consists of the following heads:
- Fixed Costs: Fixed costs are the costs that remain static over the period until a range or level. If the level of production until the fixed cost is static, it tends to increase. Fixed costs could be from various departments such as Production, distribution, Selling, advertisement, etc. A few examples of the fixed costs could be Rent, Depreciation, fixed advertisement programs, etc.
- Variable Costs: Variable costs tend to vary with the production level and the number of units produced. These are fixed for the product and increase or decrease in line with the production of a unit. We divide the variable cost mainly into raw material, labor, and overhead costs. These are directly related to the products manufactured.
#2 - Profit Margin
Apart from including the cost of sales or the total cost incurred to make the product available to sell, a profit portion is also added to arrive at the product's final price or service. The profit portion is generally added to the extent a company sees its product that would create value for the consumers. It depends upon multiple factors such as the brand value of the product, selling strategies, competitive or substitute products, etc.
Example of Unit Price
Let's take an example.
Let's take an example of a product made by XYX incorporation. The product has the following expenses, and the company wants to earn a profit of 20% over the cost of production. The total number of units produced is 100. First, find out the total price of the product.

Solution
To arrive at the final price of the product, the following steps are required:
Calculate Total Cost of Product
To determine the total cost of the product, we need to add all the expenses incurred to make the product ready for sale or transfer.

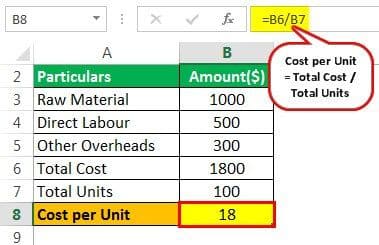
Total Cost = Raw Material Direct Labour + Other Overheads
- Total Cost = 1000+500+300 = $1800
Calculate Total Cost per Unit

Cost per Unit = Total Cost / Total Units
- Cost per Unit = 1800 / 100 = 18 per unit.
Calculate Profit Requirement

Profit Requirement = Total Cost per Unit * Profit Margin
- Profit Requirement = $18*20% = $3.6
Calculate Price per Unit

Price per Unit = Cost per Unit + Profit Requirement
- Price per Unit = 18+3.6 = 21.6
So, the price per unit of the product is $21.6.
Advantages
The unit price helps the company to adequately market its product. Following are some critical advantages of pricing a product:
- Various marketing techniques such as low-cost or predatory pricing are concerned with entering a new market. For using these strategies, the product's unit price should be adequately derived prior so the company could understand its position on the pricing techniques.
- The customers or consumers see the product's value concerning the price they are paying for it. If in the eyes of the customer, the value of the product is lesser than the price charged, it is reasonably possible that the sale would not happen. So, to attract the customers, the product's price needs to be set so that it works for both parties; the company and the customers.
Conclusion
Overall, the product's price is an essential measure for the company in various respects, such as deciding on a new pricing strategy, attracting customers for the product, fighting competition, and creating a market for its products or services. To achieve that, the company should be able to adequately price its product by including all the expenses and a profit margin to sustain the organization for the future.