Table Of Contents
Unit Investment Trust Meaning
A Unit Investment Trust (UIT) is a financial institution that acquires or retains a collection of securities, such as bonds or stocks & offers them to investors in the form of redeemable units. It provides investors with an income or appreciation in their capital.
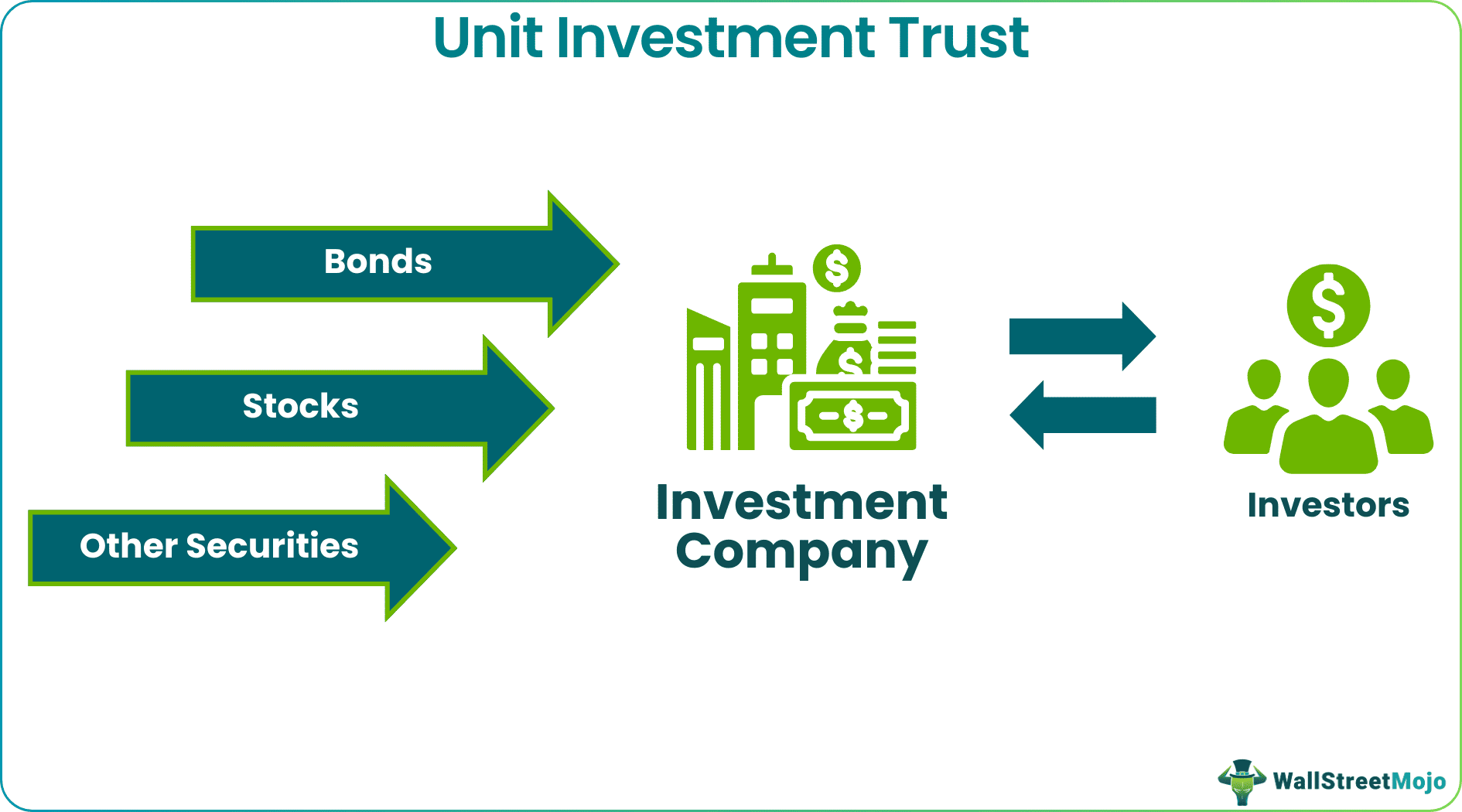
It aims to help investors by offering them securities for trading and later redeeming the units to the trust. This procedure mitigates risk and allows to earn principles and interests on the stakes. Unit investment trust companies have registration with a termination date. On dissolution of trusts, the income is either reinvested in another trust or distributed among unitholders.
Table of contents
- Unit Investment Trust Meaning
- A UIT is a financial company with closed-end funds that collect investors' money and invests it into a broad portfolio of assets. It escalates the capital and curtails the risk of the investors.
- Unit investment trust fund holds several securities with varied investing goals, plans, and portfolios. In addition, investors can redeem their shares depending on the market conditions.
- Although it has several benefits like transparency, diversification, and professional assistance, it bears risks like credit risk, management risk, foreign exchange risk, etc.
How Does Unit Investment Trust Work
UITs raise capital by giving investors "units," or shares, in a single public offering. Each unit reflects a percentage of the trust's ownership and grants the owner a proportional right to the income and capital gains produced by the investments, typically stocks or bonds.
The performance of UITs determines the trust's investment return. These investments are often set, with a UIT keeping the securities it invests in for the fund's duration.
UITs intend to be throughout the fund's duration, but investors can redeem their shares if their investment objectives change.
A fixed unit investment trust purchases a portfolio of securities (such as five or ten individual equities or bonds) and holds them for the duration of the UIT with little to no change. As a result, investors in UITs often know about their endowments.
Characteristics
UITs hold several securities. Different investing goals, plans, and portfolios may apply to various UITs. Some of its highlighting characteristics of it are below.
- UITs themselves are SEC-registered and governed by SEC rules.
- It does not have a board of directors, corporate officers, or financial advisor to provide guidance.
- Similar to a closed-end fund, a UIT makes a single public offering of just a predetermined number of units.
- Typically, a UIT will issue redeemable units, indicating that the UIT will repurchase an investor's units at a price close to their estimated net asset value.
- It will end and dissolve on a specified date. Unsold assets from the investment portfolio are put on sale when a UIT expires, and the investors get the proceeds.
Examples
Let us see some examples of UTIs and understand them better.
Examples #1
Suppose a UIT named QPR Ltd holds 50 diversified portfolios (stocks, bonds, and other securities). These portfolios are further invested in stocks by investors A, B & C with different maturity dates. Investors earn interest on such portfolios and redeem them after maturity. QPR Ltd also holds the portfolio till its maturity date. Portfolios in this way are available for sale, and the principal money returns to the owner.
Example #2
In December 2022, Canadian real estate investment trust Artis was given an average rating of - Hold. Artis invests in private and industrial estates. This rating reflected disciplined performance and growth strategies. Several firms like BMO capital markets, Royal Blood of Canada, and TD Securities lowered their prices on Artis Real Estate Investment Trust shares.
Benefits
Some of the intriguing benefits of UTIs are as discussed:
1) Transparency - Since a unit trust's track records, returns, and investment holdings are all clearly outlined, you can make an informed decision about whether it is a good investment. In addition, the price you pay to buy or sell a unit trust is transparent and depends on the trust's final net asset value (NAV).
2) Separate Holding – As the trustee acts as custodian of the asset's unit, feel safe.
3) Diversification – Diversification of portfolios ensures a guaranteed return for the investors. Portfolios are invested across asset classes and business sectors, mitigating the risk.
4) Liquidity – as investors can enter and exit the market on any business day, the market is highly liquid.
5) Professional Assistance – A highly professional and experienced team manages portfolios here. In addition, they provide time-to-time information and analysis to the investors.
Risks
1) Capital Risk - It alludes to the potential loss of the principal or invested capital. Investors may lose some or all of their principal investment in certain circumstances.
2) Interest Rate Risk - Since interest rates and the value of securities move in opposite directions, any rate increase will result in a decline in the value of debt securities, which will impact the unit trust value.
3) Currency Risk - Foreign exchange risks will be present for unit trusts that invest in assets priced in foreign currency while denominating in the local currency.
4) Market Risk - The net value of the unit trust will fluctuate due to political, social, and economic concerns in the market.
5) Fund Management Risk - The skill and knowledge of the manager influence any unit trust's performance. Therefore, the unit trust's performance affects by poor management.
Unit Investment Trust vs Mutual Fund vs ETF
A unit trust is a closed-end fund that collects investors' money and invests it into a broad portfolio of assets. Mutual fund pools open-end funds with no termination date from numerous participants and use them to buy securities like stocks, bonds, and short-term loans. On the other hand, ETFs trade like stocks with daily price fluctuations.
| Basis | UTIs | Mutual Fund | ETF |
| Goal | Benefit the investors | Earn the Profit | Follow the market |
| Managed | Actively managed | Actively managed | Passively managed |
| Initial investment | YES | YES | NO |
| Liquidity | Less | High | High |
| Fees | Yes | Yes | No |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
No, since they are part of a long-term strategy, they are not actively managed. Instead, investors invest in successive portfolios.
An investing company or professional fund manager manages the UITs in exchange for a fee. Due diligence shown by them ensures the minimum risk and higher returns to the investors.
Unlike open-ended funds, UITs are traded directly from the investment company itself. However, they are sometimes available on the secondary market in the form of IPO.
Taxation applies to interest income from UITs. Dividend income tax is determined by whether the UIT received a special tax break from the government. If so, the investor is responsible for paying taxes on the payout. If not, there is no tax due.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Unit Investment Trust and its meaning. Here, we explain its characteristics, examples, benefits, and risks. You can learn more about it from the following articles –
