Table Of Contents
What Is The Uncertainty Principle?
The Uncertainty Principle states that participants in the financial market can precisely gauge only one of the two interdependent financial variables at a time - either the move's direction or the move's timing. If the direction of a move is predicted accurately, the timing of that move may not be apparent.
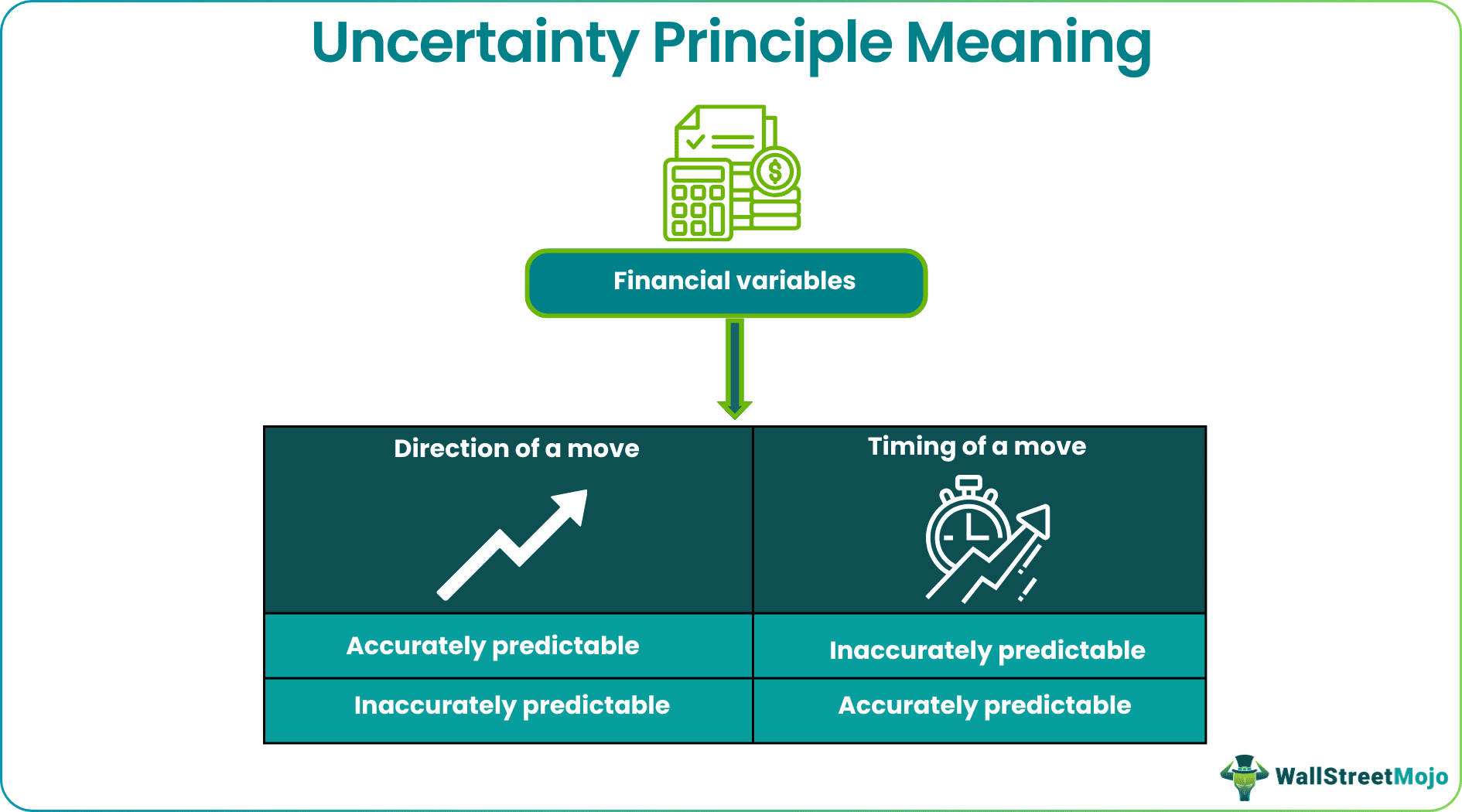
The principle is parallel with Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle in quantum mechanics. In finance, it suggests that there are limitations on the accurate interpretation of specific pairs of financial variables. Examples of variables include a financial asset's price and momentum. The more precisely market participants attempt to predict one aspect of a financial variable, the less accurate the prediction becomes for another related factor.
Table of contents
- What Is the Uncertainty Principle?
- The uncertainty principle in financial markets refers to the limitation of accurately predicting a pair of interrelated financial variables such that if one is determined correctly, the other may be ambiguous.
- While the uncertainty principle cannot be directly applied from physics to finance, it can be used as a conceptual framework to understand that it is nearly impossible to completely predict the financial markets with accuracy.
- Although conceptual similarities exist, the uncertainty principle is fundamental to quantum mechanics, whereas investing is based on economic and financial principles.
Uncertainty Principle Of Financial Markets Explained
The Uncertainty Principle in financial markets highlights the inherent unpredictability of financial markets by stating that no two variables can be predicted accurately simultaneously. Many factors, including economic conditions, geopolitical events, investor sentiment, etc., influence financial markets. This metaphorical use of the term underscores the challenge of accurately predicting market behavior due to these factors' complexity and constant change. Investors and analysts employ risk management strategies and historical data analysis to navigate the unpredictable nature of financial markets.
For instance, when trying to predict the precise future price of a stock with high precision, it becomes challenging to predict the exact timing of market movements or other associated variables like volatility. This principle underscores the inherent uncertainty and unpredictability in financial markets and emphasizes the importance of diversification and risk management in investment strategies.
Moreover, the uncertainty principle in physics and finance serves as a conceptual framework rather than a strict mathematical law. It reminds us that achieving complete predictability in financial markets is challenging due to the intricate and dynamic nature of the financial system. With the rise of quantum computing hardware, financial analysts are exploring new algorithms that embrace uncertainty rather than eliminating it. Hence, it may not directly apply the quantum physics uncertainty principle to finance but brings out the prevalence of uncertainty and the importance of risk management in financial decision-making.
One of the prominent examples of applying this principle in the financial market is the Black-Scholes model, which is used to price options that incorporate uncertainty by factoring in volatility. As uncertainty regarding the future stock price increases, option prices also tend to rise, reflecting the uncertain nature of the financial markets.
Examples
Check out these examples for a better idea:
Example #1
Suppose a market speculator gets a piece of information from a company's insider that the respective stock will upsurge from $15 to $19 due to a new merger deal. However, the speculator does not know when the price will rise. In such a case, the price move is sure; however, the time of the action is uncertain. The speculator has to look into more information to gauge the factors and make a proper decision.
Example #2
Suppose John is an investor. He is unsure of low-risk and high returns from a particular investment product. Say, if he knows that a stock X will offer high returns in five years, the risk involved in it is uncertain. Likewise, if he knows that a security Y is a minimal-risk asset, its returns are always tentative. Hence, he strikes a balanced portfolio by including both types of investments. Thus, he diversifies the investment portfolio to incorporate assets with varying risk-return profiles.
Role In Investing
Here is how the uncertainty principle influences investing:
#1 - Risk-Return Tradeoff
In finance, the principle of risk-return tradeoff suggests that higher potential returns are generally associated with higher levels of risk. Investors must balance risk tolerance and return expectations, akin to the uncertainty principle's tradeoff between measuring position and momentum.
#2 - Market Volatility
Financial markets often experience significant volatility, making it challenging to predict future price movements accurately. This unpredictability is analogous to the uncertainty principle's inherent limitation in simultaneously measuring position and momentum.
#3 - Portfolio Diversification
The strategy of diversifying a portfolio is employed to reduce risk in investing. It can be similar to the principle that if one cannot precisely know one property of a particle, they consider a range of possibilities. Similarly, diversifying across different asset classes spreads risk and aids in managing the uncertainty that is inherent in investing.
How To Benefit From It?
The uncertainty principle is a crucial concept of quantum physics; however, it can be applied to determining risk and uncertainty in financial markets. Here are some ways to make the best use of this concept:
- Diversification: Diversifying investments across different asset classes can facilitate the spread of risk and mitigate the impact of uncertainty on the overall portfolio.
- Risk Management: It is advisable to employ tools like options, futures, and other derivatives to hedge against possible losses due to market fluctuations.
- Forecasting: It helps in predicting the future returns and risks to devise suitable plans and strategies accordingly.
- Long-Term Perspective: Considering a long-term investment horizon to ride out short-term market fluctuations caused by uncertainty.
- Automation: Automating the process of tracking investments and finances to save time and resources on data collection and interpretation.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: One can spend a constant amount of money investment, despite the market status. This strategy can aid in balancing the significance of market volatility.
- Financial Reporting: Timely and accurate reporting of financial data contributes to better financial management.
- Self-Analysis: It lets one stay informed about economic and market trends to make more informed investment decisions. Conducting thorough research and analysis before making any financial moves also becomes easy.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The uncertainty principle in finance speculates that if you can measure the direction of a move, the timing cannot be accurately calculated at the same time or can only be correctly interpreted up to a certain degree.
While one of the aspects of a pair of financial variables is predictable with precision, the other aspect can be interpreted only up to a certain level, i.e., it may not be accurately predicted.
Uncertainty principle in finance has huge significance in the nature and techniques of making stock market predictions. It helps investors, traders and speculators immensely in drawing out the picture of stock market movements and make wise decisions in the future accordingly. The basic idea of applying the uncertainty principle to investing and finance is to accept that there will be a certain degree of uncertainty in every type of security. However, an investor can mitigate this risk; it cannot be eliminated.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what is Uncertainty Principle. Here, we explain it with its examples, role in investing and how to benefit from it. You may also find some useful articles here -

