Table Of Contents
What Are Types Of Business Entities?
A business entity is an entity that carries out business activities as per the country’s respective laws. It can be of various types, including private company, public company, limited and unlimited partnerships, statutory corporation, holding company, subsidiary company, and more.
The form in which an entity is established is very important as different entities are subjected to different laws and carry different features. The form an important part of any economy and their growth and expansion signify the level of prosperity of a country. These various types of entities are useful to the society in different ways.
Key Takeaways
- A business entity is an entity that engages in commercial or professional activities to generate revenue. It includes private companies, public companies, limited and unlimited partnerships, statutory corporations.
- Once the business is set up, the firm must first determine the organization's structure. Since legal and financial matters, the amount of tax the company has to pay will depend on this decision.
- Establishing the business entity is critical as different entities are entitled to various laws and have distinct characteristics.
Types Of Business Entities Explained
The types of business entity in accounting are the various forms of business organization formed which in an economy. They vary in structure, rules, laws, sizes, method of operation, etc. The growth and expansion of these entities show that an economy is progressing towards development because they create jobs, help in trading and infrastructure development, which ultimately benefits the society.
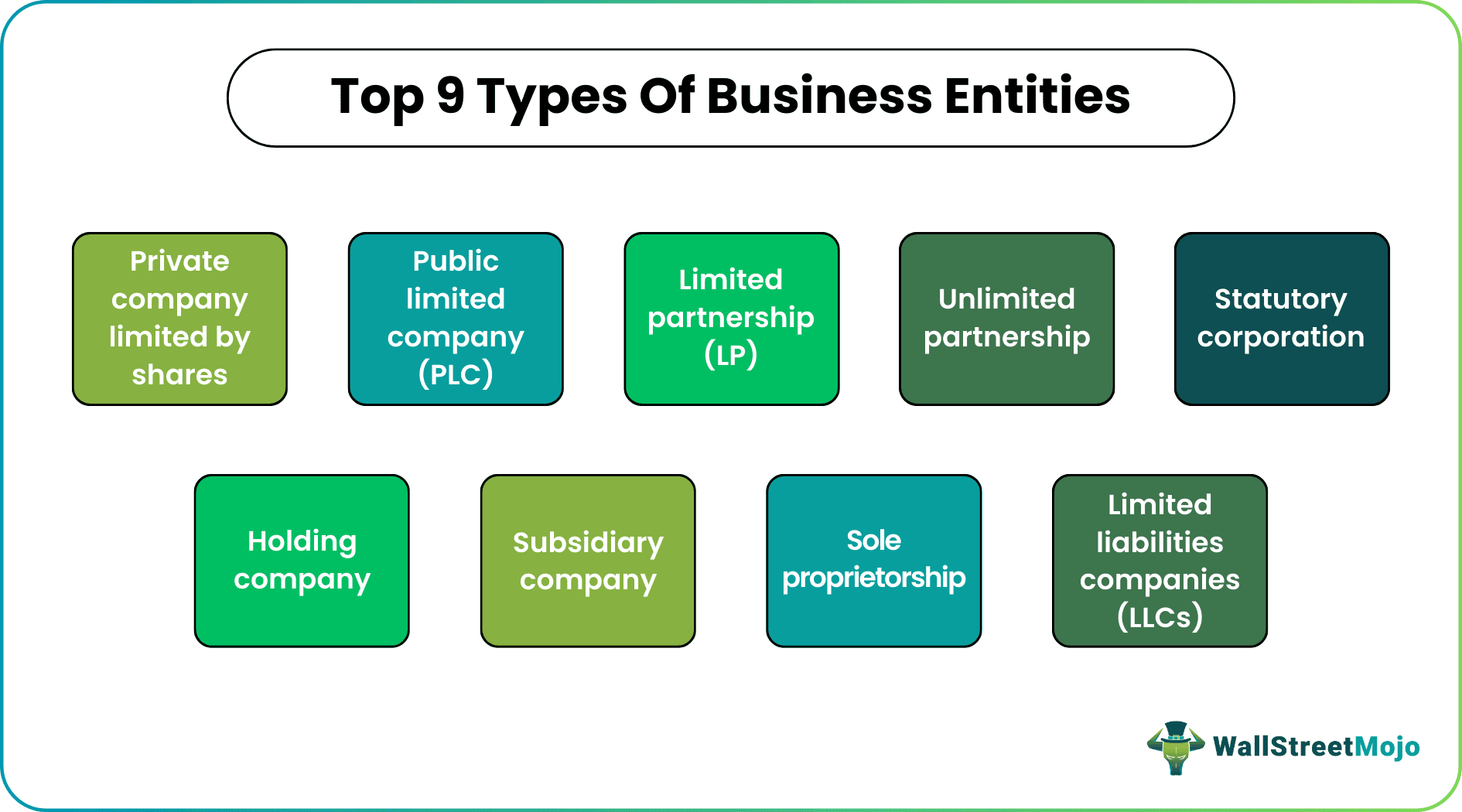
There are different types of business entities, as given below.
- Private Company Limited by Shares
- Public Limited Company (PLC)
- Limited Partnership (LP)
- Unlimited Partnership
- Statutory Corporation
- Holding Company
- Subsidiary Company
- Sole Proprietorship
- Limited Liability Companies (LLCs)
The above are the types of business entities chart. When a business entity is set up, the first thing that has to be decided is the type or structure of the organization. This is because lots of things like legal and financial matters, the amount of tax that the company has to pay, etc will depend on this decision. Even the capital structure, method of raising capital, and legal consequences in case of any unforeseen situation, type of management will depend on this decision.
Types
Given below are the different types of business entities in details.
Let us discuss each one of them in detail –
#2 - Public Limited Company (PLC)
Among other types of business entity in accounting another type of company is the one in which the liability of the shareholders is limited to the extent of share capital paid by them. There may be requirements concerning minimum share capital depending on the land law in which the company is incorporated. However, such companies are free to offer shares to the general public. That is why such companies are also known as “publicly traded companies”. They may either be listed on the stock exchange or may not be listed. In the UK, such a company must include at the end of their names the words "PLC."
#3 - Limited Partnership (LP)
A Limited Partnership is a type wherein there shall be at least one general partner and one limited partner, unlike a general partnership wherein there shall be at least two general partners. The general partners carry the same legal status as other partners in the partnership. As a result, they, along with other partners, are jointly and severally liable for the partnership's liabilities.
#4 - Unlimited Partnership
As the name suggests, it is a partnership arrangement where the partners have unlimited liability. It means that the assets of the partnership are not sufficient to meet the liabilities. Even the partners' assets can be deployed to meet such liability.
#5 - Statutory Corporation
Among the main types of business entities, another entity created by the state is called a statutory corporation. The nature of such corporations will depend on the jurisdiction under which they are made and, thus, may turn from one jurisdiction to another.
#6 - Holding Company
A Holding Company refers to a company that owns the share capital of another company. Such companies are also known as parent companies. Such companies may or may not be carrying out business activities themselves. Sometimes these companies are created to hold the intellectual property of the subsidiary company. There exists a criterion for a minimum shareholding in a company to be called the holding of such a company. A company that holds the prescribed shareholding in another company will be known as the holding company of that other company. This is also one of the main types of business entities.
#7 - Subsidiary Company
A Subsidiary Company is a company that is owned or controlled by another company (known as a parent or holding company). A subsidiary may be created either by one company holding prescribed share capital company or by way of one company exercising control over the board's composition. The company of which share capital is held or on whose board of directors the control is exercised is a subsidiary company. This is also one of the main types of business entities.
#8 - Sole Proprietorship
In the case of such an entity, there exists no separate legal entity, and as such, there is no difference between the owner and the entity. It is controlled and operated by a single person only. The liability of such sole proprietor is unlimited, and he is the sole owner of assets of the business.
#9 - Limited Liability Companies (LLCs)
LLC is a type of body corporate that is prevalent in the U.S. It is known to be a hybrid entity having features of both corporation and partnership. In the case of such an entity, pass-through taxation is followed, which means that LLC is not subjected to taxation and instead members are liable to pay tax on the income of the LLC. Also, the liability of the members is limited in the case of LLC. This is because the liability of members is limited, as in the case of a corporation, and pass-through tax structure is followed as in the case of a partnership. To learn more about forming one, formation companies, such as ZenBusiness for example, for step-by-step guidance on LLC setup and registration.
Examples
Let us take a few examples types of business entities chart to understand the topic.
Mark has set up a travel agency which caters to the needs of people who want to travel to various states of US and UK. He arranges for their travels, food and lodging as well as sightseeing. Thus, this is a perfect example of sole proprietor.
Now, if Mark takes John as his business partner to run the travel agency, then it becomes a partnership firm. However, if each partner’s liability to the business is limited to the extent of their contribution, then it is a limited partnership. But if the liability is unlimited, it is and unlimited partnership, where in case of loan default or bankruptcy, the personal assets of the partners may be confiscated.
Let us take the same example and assume that Mark and John has issued shares to the general public to raise capital and investors have subscribed. Now the company is listed in stock exchange, which makes it a public limited company. But the shareholders’ liability is limited to their contribution. In case the company is not listed in stock exchange and only the partners are the owners of the shares, it is a private limited company.
Thus, from the above examples we understand the various types of business entities.
