Table Of Contents
Alternative Investments Definition
Alternative investments refer to investments made in assets classified as non-traditional investment vehicles. It is meant for investors who wish to have a diversified portfolio with increased returns. While traditional or conventional forms for investments are open for all kinds of investors, alternative investments opportunities are confined to wealthy investors, like high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs).
These non-conventional investments involve dealing in assets other than the widely invested-in individual stocks, bonds, and commodities. With different types of options available, investors get a chance to build their portfolios by spending on securities that could help them build a better investment base.
Table of contents
- Alternative investments include types of investments made in assets that do not fall under the traditional investment category.
- Alternative investments management is more active, ensuring constant monitoring and recalibration of investment strategies given the complexities involved.
- These investments are classified into tangible (assets that could be touched) and intangible (assets that could not be touched but carry value).
- The valuation of the asset classes involved is complicated as these investments require specific knowledge and skills to be handled.
Alternative Investments Explained
Alternative investments, as a domain, are still evolving and maturing. While it is mainly considered a prerogative of the HNWI investors, some retail investors also show a keen interest in investing in these asset classes. After the financial crisis in 2008, where even the best of the diversified portfolios were swayed by extreme volatility, these non-traditional investments managed to prove their worth.
These investments differ from traditional investments in terms of complexity, liquidity, regulatory mechanism, and mode of fund management. These asset classes usually have a market correlation between -1 to 0, making them less susceptible to market-oriented or systematic risk elements.
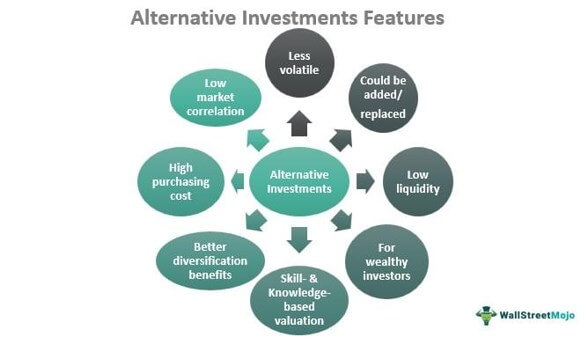
The non-traditional investments offer better diversification benefits with enhanced returns. When a stock or bond underperforms, a hedge fund or private equity firm can make up for the extent of losses over the long term. In addition, one can add or replace alternative assets based on individual investment goals and risk appetite.
These investments call for the active management of funds. The complexities involved with respect to the nature of the assets, volatility, and elevated risk level make constant monitoring and recalibration of investment strategies a must. In addition, the valuation of these non-conventional asset classes is complicated as these investments require specific knowledge and skills to be handled. Plus, the assets belonging to this category are unique, making accurate valuation difficult.
Types of Alternative Investments
Alternative investments are available in two broad categories – Tangible and Intangible.
#1 - Tangible Investments
These are the alternative investments types meant for assets having a physical existence. When an investor spends on a real asset, personal property, or hard asset, it is considered a tangible investment. Some of these assets are evaluated on their appreciation ability, while the rest are held on their ability to generate income as they depreciate. For example, collectibles have good appreciation value, and hence they are judged in accordance with that. On the other hand, equipment taken on lease is evaluated depending on their level of depreciation. Some of the examples of assets are as follows:
Precious Metals/Commodities
Not all investments are towards businesses or a pool of funds. Some of them are towards real assets like precious metals or natural resources. Investing in grains, gold, silver, or other precious metals has been preferred for ages, and they continue to be the best hedge against market movements and currency fluctuations. Investors can invest in gold either through gold coins, bullions, or indirectly through sector traded funds or exchange-traded funds.
Real estate
Real estate is yet another effective alternative investment for investors. Investing in plots, houses, and reaping rental yields or commercial assets are some of the direct ways of investing in real estate. Investors, however, can also invest in real estate indirectly through Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs). This type of investment is driven by the low co-relationship between equity markets and real estate that helps in ideal hedging against inflation.
Collectibles
Stamps, artwork, and vintage wine are normally considered mere prestigious souvenirs. However, they are highly valuable assets for investors who are aware of how profitable these collectibles are to invest in. Coins, art, and stamps are asset classes preferred for such tangible alternative investments.
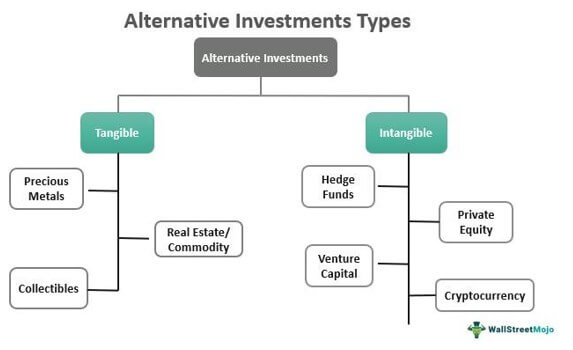
#2 - Intangible Investments
Intangible investment is made in assets that cannot be seen or checked, but the status and value of which could be monitored and assessed based on their market performance. Some of the asset classes that belong to these alternative investments types include:
Hedge funds
Hedge funds are alternative investment vehicles catering to investors with ultra-deep pockets. In the United States, hedge funds are considered accredited investors' options. As a result, they are not regulated as mutual funds and give investors leeway to invest in a broader range of securities. One thing that distinguishes hedge funds from other alternative investments is their liquidity quotient. These funds can sell off in minutes due to their increased exposure to liquid securities.
Private equity
The equities not listed on stock exchanges fall under the private equity label. These are funds that institutional investors or HNWIs directly place in private companies or use in the buyout of public companies. The firms, in turn, utilize the capital for their inorganic and organic growth while expanding their footprint, increasing marketing operations, technological advancement, and making strategic acquisitions.
Venture capital
Venture capital refers to the type of investment where investors spend on equity capital in private startups, having exceptional potential for growth. The concept might sound similar to the private equity concept, but it's not as it invests equity capital into mature companies. Venture capitalists usually invest in seed and early-stage businesses, while some invest at the expansion stage. The investment horizon is typically between 3-7 years. The expected return rate is quite high, which is a natural outcome owing to the risk quotient associated with the investment.
Cryptocurrency
The Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) consider cryptocurrency an intangible asset. These currencies are recorded at acquisition cost, which is either the price paid or the cost considered. Plus, their impairment cost is also observed and recorded after proper testing and evaluation. According to Forbes, the value of the cryptocurrency can be reduced over time while recorded in a balance sheet.
Alternative Investment Strategies
Formulating strategies to crack the best investment deals is a must. As traditional investment options are widely available, the data and information available on assets are accessible. Thus, framing effective traditional investment strategies becomes easier.
On the other hand, alternative investments, which involve only accredited investors to invest in the assets and securities, make available very limited information. Thus, the formulation of alternative investments strategies rests on the shoulders of fund managers, who remain updated and keep on studying the current and historical market trends.
While framing strategies to deal with alternative funds, there are a few things that need careful consideration:
- The United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) does not regulate these investments.
- They possess a low liquidity rate, which means they are tough to sell or convert to cash.
- They are less correlated to the market. It means the prices do not move in the same direction as the market. In short, these are less volatile investments.
Examples
Let's consider the following alternative investments examples to understand the type of them available in the market:
Example #1
HNWI Sarah began her search for an asset that would remain unaffected even if the market fluctuates. She consulted a stock advisor, Joe. He advised her not to go for traditional paper assets, like individual stocks or bonds. Rather, he suggested opting for commodities like oil, grain, gold, other metals, and natural gas less affected by the negative market movements. In addition, he told Sarah that investing in tangible commodities will mean having a shield against loss. Thus, the investor followed Joe's advice and invested at least 5% of the portfolio in tangible investments.
Example #2
The private equity industry has been out of regulatory supervision since its birth in the 1940s. However, after the 2008 financial crisis, it has been labeled under the purview of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act. In addition, there has been an increased call for transparency in recent times, and the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has started collecting data on private equity firms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Alternative investments are investments specifically meant for accredited investors who are wealthier than normal retail investors. Such investments are made in assets that do not fall under traditional asset classes, like individual stocks, bonds, etc. The lower market correlation makes these investments less volatile, and hence these turn out to be a hedge against inflation for investors.
These non-conventional investments are classified as tangible (real estate, precious metals, commodities, etc.) and intangible (private equity, hedge funds, cryptocurrency, etc.).
The exchange-traded funds or ETFs are investments that fall between alternative and traditional investments. It lets investors enjoy alternative investment opportunities while not facing any illiquidity issues. In addition, unlike other alt funds, ETFs are well-regulated and could be easily managed, sold, and converted to cash.
The differences between alternative and traditional investments are:
Recommended Articles
This has been a Guide to Alternative Investments Definition and Features. Here we discuss Alternative Investments types, strategies with real-life examples. You may also learn more about financing from the following articles –
