Table Of Contents
What Is Trust Indenture?
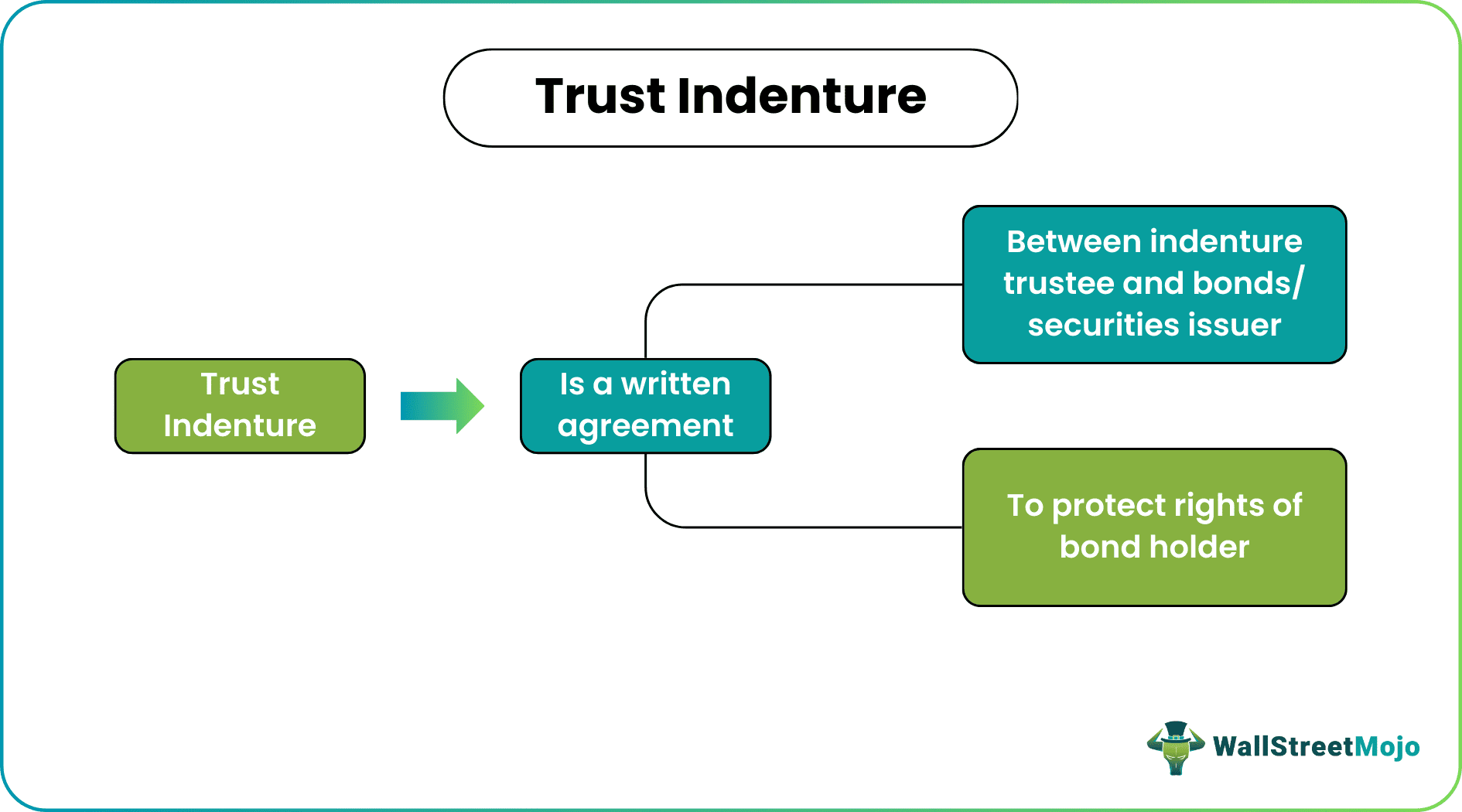
Trust Indenture is a written contract between an indenture trustee and a security issuer. The goal of a trust indenture is to reference the issuer's and bondholder's future rights and duties. It also aims to safeguard the bondholder's interests by specifying the rules and duties that each party must follow.
The trust indenture outlines the terms and conditions of the debt obligations or warrants, including the cost of borrowing, expiry, reclamation, and timing; collection methods in the event of non-payment obligations; and expiration date in the case of warrants. It also includes representations and guarantees, covenants, default causes, information on the trustee, and the like.
Key Takeaways
- A trust indenture is a document used to sign a bond contract between a bond issuer and a trustee that specifies the terms and conditions governing the trustee's conduct and the beneficiaries' rights.
- A trust indenture is a legally binding contract to protect bondholders' interests.
- The Trust Indenture Act was enacted in the United States in1939 as state legislation mandating that bond issues valued at more than $5 million be accompanied by a trust indenture endorsed by both the bond issuer and the bondholder.
Trust Indenture Explained
A trust indenture is a document during the signing of a bond contract between a bond issuer and a trustee that outlines the terms and circumstances controlling the trustee's behavior and the beneficiaries' rights. The trust deed denotes the security holder's interests as it outlines a set of rules and obligations that all parties to the arrangement comply with. It also provides instructions for the situations that may result in non-payment and the procedures in such cases.
Trust deeds are not mandatory for every bond deal. For example, trust indenture agreements are most prevalent in corporate offers. However, municipal and government-issued bonds and company issuance with a face value of less than $5 million do not require such indenture agreements.
Purpose Of Trust Indenture
Issuing bonds to lenders or investors raises funds for a corporate or government entity. Accordingly, the issuer engages a third-party trustee, often a bank or trust business, to represent investors who purchase a bond. So in this context, indenture serves the purpose of the agreement between the issuer and trustee.
A government agency or a commercial company must frequently seek more funds for various causes. Frequently, such organizations obtain funds from creditors and investors by providing them bonds via a bank or trust business that acts as a third-party trustee. Issuing bonds is governed by an agreement between the bond issuer and the trustee that is legally enforceable. This type of contract is known as a trust indenture.
It became law during 1939's enactment of the Trust Indenture Act (TIA) as state legislation. It mandates that bond offerings valued at more than $5 million have an Indenture endorsed by both the bond issuing firm and the bondholder. The TIA was enacted as an amendment to the Securities Act of 1933.
What Does Trust Indenture Include?
A trust deed contains several specifics, such as:
- Information about the trustee, including designation and phone number.
- The bond issuer, investor (or lender), and trustee must adhere to the provisions and terms throughout the bond's term.
- The trustee's responsibilities, particularly about addressing unanticipated circumstances.
- The bond details include its end of the term, face value, interest amount, payment plan, and issuance purpose.
- A detailed discussion of the situations that may result in a non-payment and the corrective measures. A trust deed incorporates an action mechanism that permits creditors and security holders to collect cash fairly; in case of evasion.
- A trust deed includes preventive or defending covenants. This involves imposing limitations on an issuer of a callable bond.
- The trust deed also stipulates the call premium or the amount the bond's issuer must pay to repurchase the bond.
Enforcement Of Trust Indenture
A trust deed is a legally enforceable contract to safeguard the interests of bondholders. During the enforcement, adhering to outlined conditions for the bond provider, bondholder, and trustee is a must. In the implementation, trustees' responsibilities are crucial since it specifies how they handle unanticipated events. In some trust deeds, for instance, the matter has to be resolved within a stipulated time.
While enforcement, one must consider the bond's conditions and features. The conditions and procedures surrounding a default are specified in one part of the deed. The indenture offers a structure for creditors or security holders to collect in an orderly way if the issuer defaults. A bondholder must be aware of taking the appropriate action in the event of a default.
Registering a copy of the trust indenture with the Securities and Exchange Commission for corporate bonds with aggregate principal issues of $5 million or more is necessary. In addition to corporate bond offerings valued at less than five million, the preceding regulation does not apply to municipal or government-issued bonds. As such, entities often opt for an indenture to reassure potential investors.
Examples
Let us look at the following trust indenture example to understand the concept better:
Example #1
Consider you are working as a paralegal team under an established lawyer. Your boss asks you for a solution for ensuring the best possible enforcement of bonds in the future. Also, the bond is valued at less than $2 million. So after looking at your client's related documents and concerns, you suggest including a bond trust indenture, even if it is not mandatory for securities below five million dollars. You explain how it is legally helpful as each condition is clear with solutions to potential disputes. So after guidance from your higher-ups, you draft a trust indenture and carefully include all the details per the enacted law.
Example #2
Bloomberg's press release describes how Gravitas Financial Inc., a financial and fintech platform acquired debentures and notes under the trust indenture.
Gravitas has entered into a debt repurchase agreement with the fiduciary acting on behalf of the beneficial holders of all of Gravitas' secured debt. As per the agreement, Gravitas will acquire variable secured debentures and notes issued under Gravitas' trust indenture held by the Debtholder on behalf of the beneficial holders.
Gravitas will pay the other holders of Notes other than the Purchased Notes any amounts due under trust indenture upon completion of the Transaction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
An issuer of bonds and a trustee are parties to a master trust indenture. The purpose of the trust deed is to safeguard the bondholder's interests by specifying the rules and duties that each party must follow.
It was enacted to regulate the sale of certain securities in interstate and foreign commerce via the mails, the trust indentures under which such securities are issued, and other purposes. In addition, ensure proper explanation of the legal responsibilities associated with certain debt instruments or bonds traded in Securities and Exchange Commission-registered transactions (SEC).
The Trust Indenture Act also exempts debt securities sold in transactions under Section 4 of the Securities Act. Thus, the Trust Indenture Act incorporates the exclusions for certain private placements, offers and sales to "accredited investors" of up to $10 million, and sales in significant dollar quantities of promissory notes backed by certain first lien real estate mortgages.
