Table Of Contents
What Is A Trading Book?
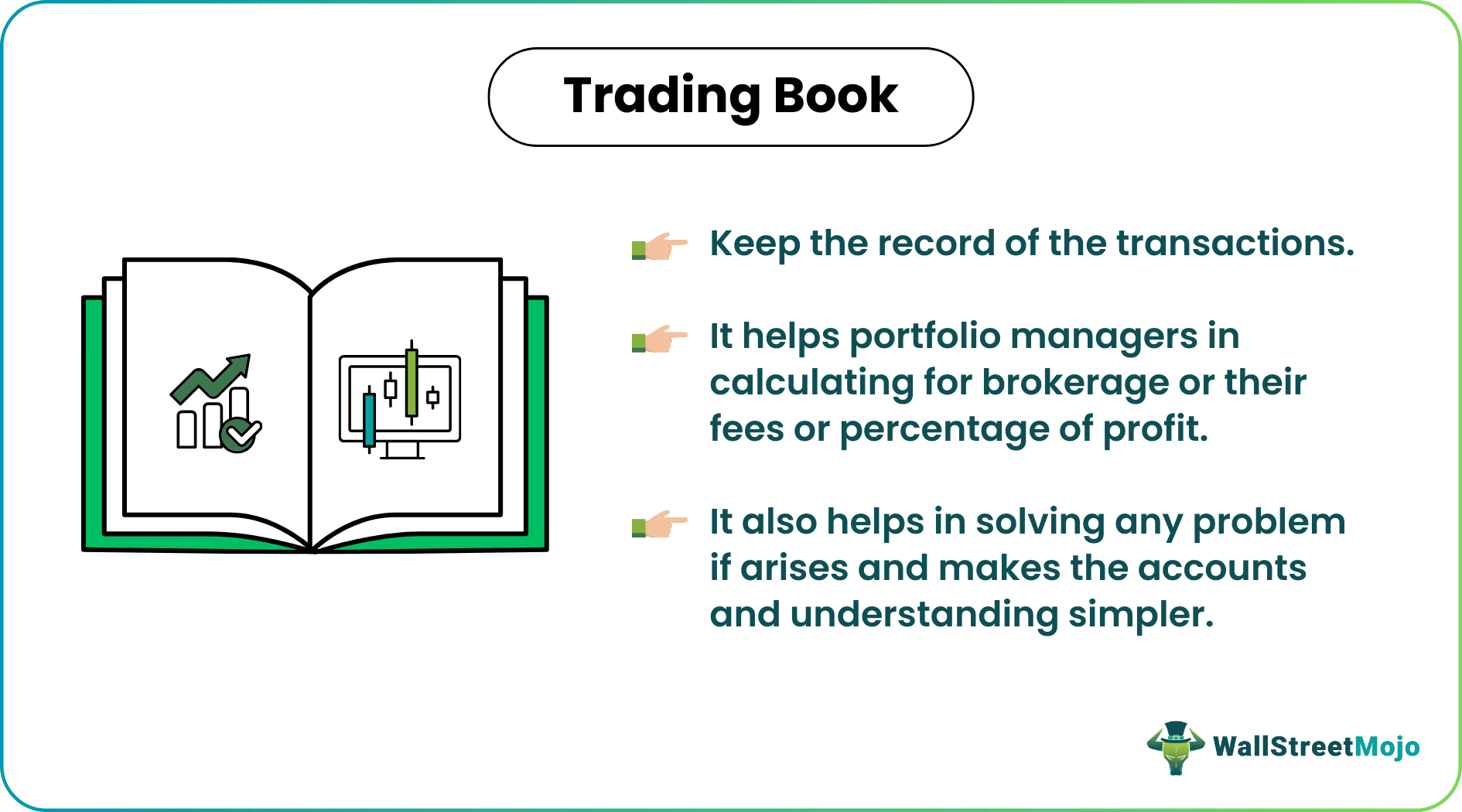
A trading book is the type of book maintained by the bank, financial institution, or stockbroker banks to record the clients' transactions who have allowed them to act as the broker or middle person for dealing in securities. This book helps portfolio managers calculate for brokerage or their fees or percentage of profit as decided between client and portfolio managers.
It acts as a ledger for accounting purposes through tracking of securities that investors hold and are frequently bought and sold in the market. History helps in keeping track of the movement and also facilitates trading actions like hedging or using price differences for profit making. These securities are the ones that are actively traded.
Table of contents
- What Is A Trading Book?
- A trading book is maintained by a bank, financial institution, or stockbroker to record the clients' transactions. It acts as the broker or middle person for dealing in securities.
- It helps portfolio managers determine the brokerage fees or profit percentage as clients and portfolio managers decide. They make two trading books: a consolidated book with all the portfolio managers' transaction records and the other is a separate book for each client.
- This book can identify and protect against fraud from the transactions nature and help to make financial plans and excellent resource utilization.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Trading Book Explained
A day trading book is a type that the portfolio managers maintain to maintain the records of the transactions entered into and the clients. Two trading books are to be prepared by the portfolio managers; one is a consolidated book containing all the records of all transactions entered into by portfolio managers.
The other is a separate book for each client. It is also a legal document and accounting ledger that can be presented as proof and accepted validly. With the help of this book, we can detect and prevent fraud from the nature of transactions. This stock trading book also helps in financial planning and the optimum utilization of resources.
The portfolio managers must maintain separate trading books for each client to help them in various compliance and maintain transparent records. These books are maintained to record the transactions so that there shouldn’t be any problem or confusion in the future between clients and portfolio managers. It also helps solve any problem if it arises and makes the accounts and understanding simpler.
Example
Let us understand the concept with the help of a trading book example. ABC Bank maintains the D-mat accounts of the clients or investors. Mr. A regularly deals in various securities. The details of various securities dealt with by Mr. A is as under:

Prepare this book, which is to be maintained by the bank, and also state how it is useful for Mr. A?
Solution:
The day trading book of Mr. A is as under:

Trading Book is useful for Mr. A in the following ways:
- It helps to view the records of the transactions done by Mr. A.
- A can access the record of transactions at any time.
- This book helps Mr. A to view profit or loss on the transactions made.
- It also helps with planning.
Thus, from the above trading book example, it is possible to understand the concept in details.
Uses
Below are some of the critical uses of this document.
- With the help of this book, the responsibility and liability of the client and investor can be fixed as the client can verify the transaction he has done, and the bank to maintain the records and to verify whether payment credited or debited as the case may be to the exchange’s account.
- They also help to verify the purpose of trading by the client. If the purpose is unlawful, the portfolio managers can warn the client and report to the authorities accordingly.
- Maintaining records is shifted from an investor to a portfolio manager with this book.
- The stock trading book can be used as legal evidence in a court of law and is recognized as a legal document.
- It is also recognized as an accounting book that contains all the financial records of the portfolio managers.
- The burden of investors is reduced as they do not have to maintain every record of the transactions. The records are maintained by the Portfolio managers, who also help calculate the tax liability.
- Past transactions can be accessible in a fraction of time, which helps both the portfolio managers and the investors smoothly conduct the transactions.
Advantages
- Trading Book helps plan the transactions to earn the maximum profits and prevent unnecessary losses.
- This order flow trading book helps to track and view the record of transactions.
- It is accepted as legal proof in a court of law and considered a legal document.
- It helps to minimize the risk by fixing the responsibility of maintaining the records and tracking the records.
- With the help of these books, fraud can be easily determined and prevented by reporting to the concerned authorities.
- Each transaction entered into by the client is maintained through this book.
- With the help of this book, the brokerage calculations become easy by the portfolio managers.
- They can also be recorded as accounting ledgers in books of accounts.
- Portfolio managers are responsible for maintaining the whole trading book of their institutions and a separate one for their clients, which helps them maintain better and more transparent records.
- With the help of this book, past activities can be viewed easily.
- It is a collection of several fiscal instruments that help in the smooth conduct of the business of portfolio managers.
- The order flow trading book helps the investor plan the investment and effectively utilize resources and investment.
Disadvantages
Let us look at some disadvantages of the trading book.
- It is important to consistently maintain the securities transaction details in the book otherwise, there will not be a detailed record of them.
- If a consistent record is not maintained, then actions like brokerage calculations, preparation of financial documents, planning investments, keeping track of past activities, etc will be difficult and there will be lots of discrepancy.
- The portfolio managers who are responsible for maintaining the book should be diligent and responsible enough to do their task on a daily basis and should have proper knowledge regarding the recording procedure of the same.
Trading Book Vs Banking Book
Let us look at the differences between the two records in details.
- The former records all assets used for trading purpose while the latter records all assets that are supposed to be held until maturity.
- The risk of the assets in the former case are measured for a shorter time frame while the risk of assets in the latter are measured for a longer time frame.
- In case of the banking book the assets in it are marked at the acquisition price or their book value whereas for the trading book, on a daily basis, the assets are marked at the current market price or fair value.
For professional-grade stock and crypto charts, we recommend TradingView – one of the most trusted platforms among traders.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Traders or trading desks generally monitor these books within the financial institution. Additionally, risk management systems are used to monitor positions and identify potential risks.
The banking book as securities in a trading book can only be held once its maturity must be suitable for active trading. In comparison, the stakes in the banking book are kept long-term. Therefore, banking books are used for long-term investments and lending activities.
The risks associated with these books include market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk.
Regulations of trading books can vary by jurisdiction, but they aim to ensure that financial institutions maintain appropriate risk management processes and have adequate capital to cover potential losses.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what is Trading Book. We explain its differences with the banking book, along with examples, uses, advantages & disadvantages. You may learn more about financing from the following articles –