Table Of Contents
Trade Secret Definition
Trade secrets are any valuable information regarding a company's processes or operations guarded and concealed from the public eye. The company actively protect them and they are available to only a limited number of people. As a result, they possess the potential to be licensed or sold for profit.
The technical or commercial information contained in trade secrets is often a result of years of internal research that can give its keepers a competitive advantage in the market. Therefore, unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of the data is unfair and includes commercial or industrial espionage, breach of contract, and confidence.
Key Takeaways
- Trade secrets are confidential business information and are a type of intellectual property.
- Therefore, an entity can either license it or sell it for profit. These include knowledge about a company's processes, designs, client information, etc. and the company keeps it a secret, out of the public eye.
- The knowledge must be financially valuable, and the general public shall not be aware of it, except for a limited number of persons who have the authorization to know about it.
- They are different from patents, exclusive rights granted for an invention or an innovative solution. They are complementary to patents, trademarks, and Copyright Protection.
- Uniform Trade Secrets Act (1985) in the U.S. overlooks information infringement and other issues.
Trade Secret Explained
Trade secrets form part of intellectual property rights on confidential information posted by companies. These include knowledge about the process or procedures of the company, research and development data, etc. The theft of trade secrets is part of unfair practices since there is general protection for confidential information and against unfair competition. The law can determine the question of trade secret protection violations only after studying the circumstances of individual cases.
For a piece of information to be qualified as a trade secret, it must possess the following:
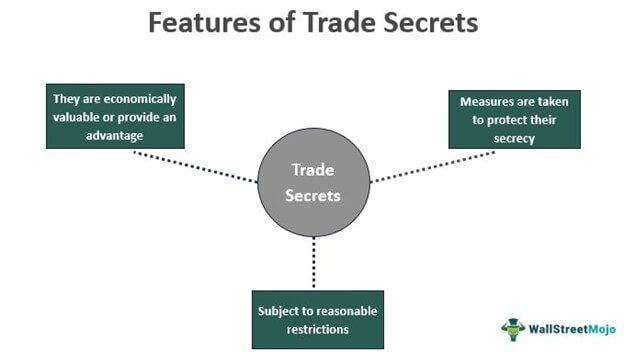
- It should be valuable commercially, and people outside the business are unaware of it.
- Only a limited group of people have the authorization to know about it.
- The respective authority takes reasonable steps to conceal the information by using non-disclosure agreements and other confidentiality agreements for business partners and employees.
Companies and businesses adopt various methods to protect crucial information that others can exploit if leaked out of the organization. Companies asking employees to sign non-disclosure agreements(NDA) is an example of this.
Types of Trade Secret
A trade secret contains both technical and commercial information. Technical information includes knowledge of the processes used in manufacturing a product, the results of pharmaceutical sector tests, drawings, designs, prototypes, formulas, necessary details about computer programs, etc. Commercial information secrets involve knowledge about distribution methods, Business management information and techniques, lists of suppliers, crucial clients, and other advertising strategies. Not limited to the categories mentioned above, data can include protected financial information, formulas, recipes in the food industry, and source codes in the software industry.
Trade Secret Examples
Example #1
Suppose there is a big restaurant with fried shrimps as its specialty called "BFS-Best Fried Shrimps."They have been in the business for over a century and have a global chain of eateries. Samantha visited one of its less busy eateries for taking away. When the food order took so long to deliver, she went inside to enquire. She saw certain ingredients that were part of the secret recipe of the fried shrimps. Excited, Samantha decided to phone her friend and share the information with her. Unfortunately for Samantha, it is an information infringement as the eatery, or the company did not impart it to her for her knowledge. She did not possess the authority to share it with another person. Yet she did it. Therefore, the organization can initiate a lawsuit against her for violation of the organization's secrets.
Example #2
Google has a page rank feature. It developed the feature as a link analysis algorithm to attribute numerical weighting for hyperlinked documents. This feature measures the document's relative importance. Google trademarks this particular feature, and the company alone knows the process of ranking, including influencing the tools to decide on it exclusively. Therefore, attempting to decode the process, procedures, or any information relating to the page rank can result in an infringement lawsuit from Google.
Trade Secret Law
Uniformly, the TRIPS (Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights) of WTO (World Trade Organization) offers Trade secret protection to all members against unfair competition. Apart from that, in the U.S., trade secrets receive protection under state laws. As per the laws, every state protects against trade secret theft even though the statutes and degrees vary from state to state. Uniform Trade Secrets Act (1985) is one such act that offers uniformity across. All states have adopted the act with the exception being Massachusetts, Texas, and New York. The act provides definitions for trade secrets, misappropriation, and remedies (injunctive relief, damage relief, and attorney's fee in some cases).
According to the act, a trade secret possesses the following characteristics:
- Independent economic value and others can obtain the same economic value on their use or disclosure.
- Generally not known to the public and incapable of being readily ascertainable by proper means.
Specifications in a Nutshell:
Uniform Trade Secrets Act of 1985, Section 1(4), states that for liability to exist under this act, the simple action of duplicating an unpatented item is not punishable. Either the secret's acquisition, its disclosure to others, or the use of the secret must be improper under Section 1(4) (2). According to the act, when multiple people are entitled to protection for the same knowledge or information, only the one who was misappropriated is eligible for a legal remedy. The act also recognizes reasonable efforts to maintain secrecy and prevent infringement.
Trade Secret vs. Patent
A patent is an exclusive right awarded or granted for an invention, a product, or a technique that offers a new and innovative technical solution to a problem or provides a new way of doing something in general.
Points that distinguish a trade secret from a patent are:
- Filing a patent requires disclosure of information regarding the invention. This disclosure helps the general public derive use from the invention.
- The patent and Trademark Office (PTO) usually grants patents following statutory requirements. Trade secrets have components such as client and customer lists exclusive to the business and do not come under the extent of patents.
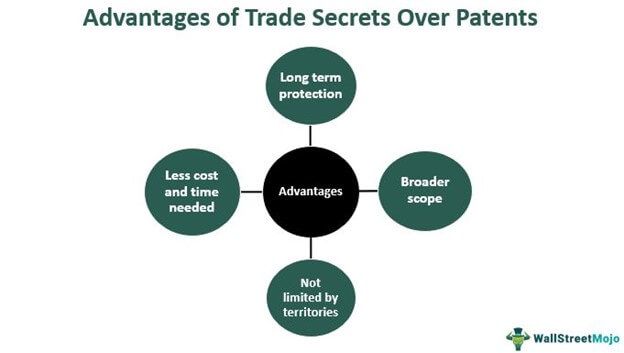
- The company can protect trade secrets without much hassle, whereas patent protection requires filing and adhering to the standard norms in the industry. Moreover, the mere application of patents does not guarantee protection.
- Patents are not universal and have a limited scope, and they are subjected to territorial protection only; for a limited period. On the other hand, secrets do not have an expiry date (unless specific exemptions are present).
- A patent application is costly and time-consuming.