Table Of Contents
What Is Timberland Investment?
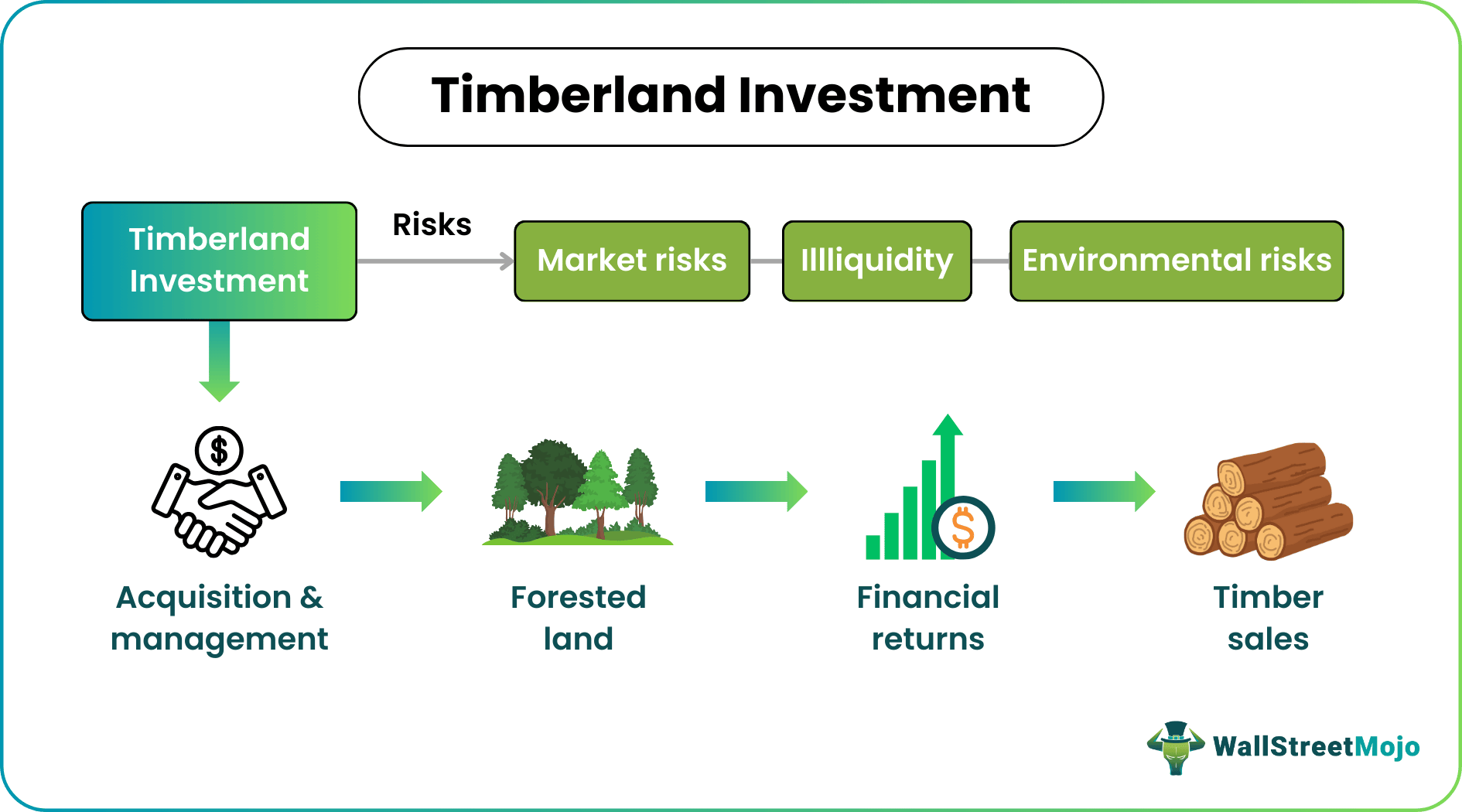
Timberland investment refers to the acquisition and management of forested land to generate financial returns through the sustainable harvesting and sale of timber. The purpose of timberland investment is to capitalize on the long-term growth potential and income generation offered by timber resources.
Individuals or institutions can benefit from the increasing demand for wood products by investing in timberland while contributing to sustainable forestry practices. This is an important concept as it offers diversification to an investment portfolio, as timberland tends to have a low correlation with other asset classes, such as stocks and bonds.
Table of contents
- What Is Timberland Investment?
- Timberland investment involves acquiring and managing forested land for financial gain, primarily through the production and sale of timber or other forest products.
- It offers potential benefits such as a renewable resource, diversification within a portfolio, and the ability to generate income from non-timber sources.
- It requires long-term commitment and expertise in areas such as land acquisition, forest management, market dynamics, and environmental regulations.
- Professional timberland investment managers often oversee operations to ensure effective management of forest assets.
Timberland Investment Explained
Timberland investment involves acquiring and managing forested land to generate financial returns through sustainable timber harvesting and sales. It is a long-term investment strategy that capitalizes on the growth and value of timber resources over time.
Timberland investment typically starts with identifying suitable forested properties for purchase. Factors such as timber quality, location, accessibility, and potential for future growth are considered during the selection process. Once the land is acquired, it is managed to optimize timber growth, ensure sustainable practices, and maintain the health and productivity of the forest ecosystem.
Timber harvesting is a key component of timberland investment. Trees are selectively harvested based on their maturity and market demand to maximize the value of the timber while maintaining the long-term sustainability of the forest. The harvested timber is then processed and sold to various industries, including construction, furniture, and paper. It provides an opportunity to invest in a tangible and renewable resource. Forests are vital in carbon sequestration, biodiversity conservation, and ecosystem services.
Timberland investments have historically shown competitive returns and the potential for capital appreciation, making them an attractive option for investors seeking long-term growth and income.
Types
There are different types of timberland investments, each with its characteristics and considerations. Here are three common types:
- Direct Ownership: This type involves purchasing and directly owning forested land. Investors acquire the land and manage the timber resources, including harvesting and sales. Direct ownership gives investors full control over the management and decision-making process but requires forestry management and operations expertise.
- Timberland Investment Management Organizations (TIMOs): TIMOs are specialized investment firms that manage timberland investments on behalf of institutional investors. They acquire and manage large portfolios of forested properties, providing professional expertise in forest management, timber sales, and operational efficiencies. Investors can participate in timberland investment through funds or partnerships managed by TIMOs.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): Timber REITs are publicly traded companies that own and manage timberland properties. Investors can buy shares of these REITs, providing them with exposure to timberland investments without the direct ownership of forested land. Timber REITs typically focus on acquiring and managing large-scale timberland assets and often distribute a portion of their earnings to shareholders as dividends.
How To Diversify?
Let us look at some strategies to consider for diversifying timberland investments:
- Geographic Diversification: Invest in timberland properties located in different geographic regions. Different regions may have varying timber species, growth rates, market demand, and regulatory environments. By diversifying across regions, one can mitigate risks associated with localized factors such as weather events, pests, or regional market fluctuations.
- Timber Species Diversification: Consider investing in timberland with a mix of different tree species. Different species have varying growth rates, market values, and uses. Diversifying across timber species, one can hedge against risks associated with changes in market demand for specific species or susceptibility to diseases or pests.
- Property Size and Type: Diversify timberland investments by considering properties of different sizes and types. Hence, this can include larger-scale commercial timberland, smaller private tracts, or even timberland investments within conservation easements. Each property type offers unique characteristics, risk profiles, and potential returns.
- Harvesting and Timber Management Strategies: Implement different harvesting and timber management strategies across timberland investments. For example, one might have investments focusing on long-term growth and sustainable harvesting, while others may involve shorter rotation cycles for more frequent harvesting. Thus, this diversification can balance steady income generation and potential long-term appreciation.
Examples
Let us look at the examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Suppose John, an investor, purchases a 200-acre forested property with a mix of hardwood and softwood trees. He manages the timberland sustainably, ensuring proper care and growth of the trees. After a few years, when the trees reach maturity, John selectively harvests and sells the timber to local buyers. The income generated from the timber sales provides a steady source of returns for John while the value of the land appreciates over time. John benefits from income generation and potential capital gains through his timberland investment, all while contributing to sustainable forestry practices.
Example #2
As per an article by Acretrader, AcreTrader and Gridline have partnered to make high-quality alternative assets more accessible. AcreTrader was impressed by Gridline’s expertise in providing investors with diversified portfolio exposure to historically exclusive and prohibitively expensive private market opportunities.
AcreTrader provides valuable diligence insights that will inform Gridline's portfolio construction via Acres, its industry-leading technology, and its dedicated team that has directly purchased and managed hundreds of millions of dollars worth of farm and timberland. Together, they aim to expand access to farm and timberland investment opportunities.
How Does It Generate Returns?
Timberland investments generate returns through various mechanisms:
- Timber Sales: One primary source of returns from timberland investments is the sale of harvested timber. Thus, as the trees on the timberland reach maturity, they can be selectively harvested and sold to sawmills, wood product manufacturers, or other buyers. Hence, the revenue generated from timber sales can provide a significant portion of the investment returns. Species, quality, market demand, and prevailing market prices influence timber's value.
- Timber Growth and Appreciation: It offers long-term growth and appreciation potential. Hence, as the trees continue to grow, the volume and value of the timber increase over time. Investors can benefit from appreciating the timber asset by practicing sustainable forest management and allowing the timber to mature. This can result in capital gains when the timberland is sold.
- Land Appreciation: In addition to timber growth, the underlying land value of these investments can appreciate over time. Factors such as location, accessibility, development potential, and market dynamics can influence the value of the timberland property. Thus, if the timberland is located in areas experiencing population growth, urban expansion, or increased demand for recreational land, the land value can appreciate, contributing to investment returns.
Risks
Let us look at some key risks associated with timberland investments:
- Market Risk: Timberland investments are subject to market risk, including fluctuations in timber prices. Also, demand and pricing for timber products can be influenced by economic conditions, construction activity, global trade, and changes in consumer preferences. Timber prices can vary over time, impacting the profitability of timberland investments.
- Environmental Risks: Timberland investments are exposed to environmental risks such as wildfires, pests, diseases, and natural disasters. These events can damage or destroy timber resources, impacting the value and productivity of the land. Climate change-related risks, including shifts in precipitation patterns and increased frequency of extreme weather events, can further exacerbate environmental risks.
- Regulatory and Legal Risks: Timberland investments are subject to regulatory and legal risks associated with land use regulations, zoning restrictions, environmental regulations, and permits. Compliance with forestry practices, conservation requirements, and logging regulations can impact operations and profitability. Changes in government policies or regulations can also affect timberland investments.
- Illiquidity: Timberland investments are typically illiquid, which means they cannot be easily bought or sold compared to more liquid assets like stocks or bonds. Selling timberland properties may require a longer time frame, limiting the ability to quickly convert investments into cash. Illiquidity can pose challenges if there is a need for immediate liquidity or if market conditions are unfavorable for selling.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The bulk of timberland returns has fallen between 2% and 6% per quarter, with an occasional return above this range and a few below. A timberland investment has annual return distributions that are peaked and positively skewed, even across major historical market movements.
Timberland investments are typically made by institutional investors like pension funds and endowments, as well as timber investment management organizations (TIMOs), although private individuals and companies can also participate.
Investing in timberland can provide several benefits, including diversification, inflation protection, and the potential for long-term returns. Timberland investments have historically provided returns that are comparable to those of other asset classes, such as stocks and bonds.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what is Timberland Investment. Here, we explain its types, examples, risks, how to diversify it, and how it generates returns. You may also find some useful articles here -
