Although testnet and Devnet are closely correlated with their functions, they differ. Let us look at their differences:
Table of Contents
Testnet Meaning
Testnet, in blockchain, is a testing phase where the features of the original blockchain are tested on the alternative chain (or network). It is like a backstage process, where the sole purpose is to test the proposed features and detect bugs within the blockchain before its launch.
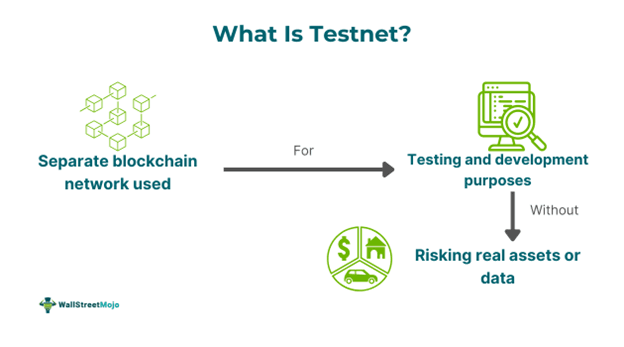
The testnet phase usually occurs before the mainnet event. Thus, any upgrades required on the original blockchain undergo testing. They are then launched on the network. However, this phase only creates a sandbox environment. Therefore, the tokens released hold no value in reality.
Key Takeaways
- A testnet is an environment where developers can test new features and upgrades separately from the leading network. It creates a simulated atmosphere to detect bugs and errors.
- In a testnet, nodes validate transactions, add them to blocks, and form a separate chain. The genesis block created is independent of the mainnet.
- Users can obtain crypto tokens at no cost via online faucets and transact with these coins. However, they hold no real market value.
- A testnet differs from a devnet, as the latter focuses on development rather than testing features.
How Does Testnet Work?
The testnet refers to the testing event where the developers create a duplicate or akin blockchain network to testify to the features before launching it on the leading network. If a set of features works perfectly on the sidechain, a similar chance of success is also possible on the mainnet. As a result, the chances of errors or glitches in code and protocol are reduced. Also, the potential for network vulnerabilities vanishes.
The core testnet mechanism almost replicates the original blockchain protocol. The only difference is that it is independent of the mainnet. Any feature tested on the sidechain is not reflected in the latter. Instead, developers use the same technology and mechanism to test its functionality. Like the original blockchain, a group of nodes work to verify transactions and add blocks. In addition, the incentivized test participants also receive coins that have no worth. They are available only for testing purposes.
The network also distributes these tokens for free via online faucets. They only aim to test the functionality of the cryptocurrency in a real market without losing any money. Once the users receive them, they can make transactions in the testnet wallet and use them. These tokens are also valuable for decentralized applications. However, they are not intended for real-time transactions. Likewise, any bug registered will alert the developers to the extra testing. If not, it can be installed on the leading network through a group consensus of nodes.
Both the testnet and mainnet have different genesis blocks. Also, the blocks added to the sidechain are slightly marked differently from those on the original blockchain. Thus, transferring crypto coins from the core testnet to the leading network is impossible.
Examples
After understanding the mechanism of incentivized testnet, let us look at some examples to comprehend it better:
Example #1
Suppose ABC is a cryptocurrency that works on the Ethereum blockchain. The entire team and developers built the token infrastructure. However, testing the features before launching them on the network was crucial. Therefore, Alfred and his team created a sandbox environment, or testnet, where the same features could be applied. Here, a team of miners started verifying the transactions and adding them to blocks. These blocks were then attached to the Genesis block, creating a sidechain.
With this setup, ABC tokens were available free of cost on online faucets. Crypto users could use them to trade assets and store them in testnet wallets. During this process, a glitch was discovered in the transaction process. When coins were sent to another wallet, the user received fewer coins than expected. Alfred noticed this issue and rectified it during the testing phase. After a month, when the main net was released, it received immense user support for its robust infrastructure and security.
Had the same error occurred after the main net launch, it would have caused significant damage to the coin's image and goodwill. Thus, testing the network saved millions and ensured a smoother launch.
Example #2
According to recent crypto news, as of July 2023, the decentralized ZK-Rollup ecosystem Taiko launched its fourth testnet, Eldfell L3. The Eldfell L3 testnet introduces the concept of Inception Layers and a new staking-based prover design. This staking mechanism assigns a block to a designated prover, who must provide valid proof within a specified time. Failure to do so results in the slashing of their stake. The Inception Layers concept allows for the potential deployment of additional layers, such as Layer 3 (L3) and Layer 4 (L4), making the Taiko network more scalable and efficient.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Testnet provides various benefits to the network, yet this simulation has certain limitations. Let us look at them:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| It helps to detect any errors or bugs within the network. | Chances of scams and malicious actors may sell these coins disguised as original tokens. |
| Developers can testify to the new features of the token in a separate environment. | These coins have no value in the crypto market. Thus, using them to purchase goods and services is not feasible. |
| It provides constructive feedback on the proposed updates. | A risk of mixing these tokens with original tokens exists. |
| They create a simulation for users to trade the crypto coin. | |
| There is no crypto expenditure, even if an error occurred. Developers have to pay nothing to deploy smart contracts. |
Testnet vs Devnet
| Basis | Testnet | Devnet |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Meaning | A simulation phase to test the new features of the blockchain in a separate environment. | Devnet is also a testing phase, allowing developers to perform live testing on the active or mainnet. |
| 2. Purpose | To test the upgrades proposed by the network participants. | It enables development of the features. |
| 3. Type of Environment | It operates in an independent chain and a separate environment. | It is conducted live on the original blockchain. |
| 4. Network Size | Compared to the latter, it is decentralized and can be applied on the blockchain. | Devnet is less crowded and not suitable for real-time use. |
| 5. Access | The access to this network is available to testers and beta-testers. | Here, developers can access devnet. |
