Table Of Contents
Technical Bankruptcy Meaning
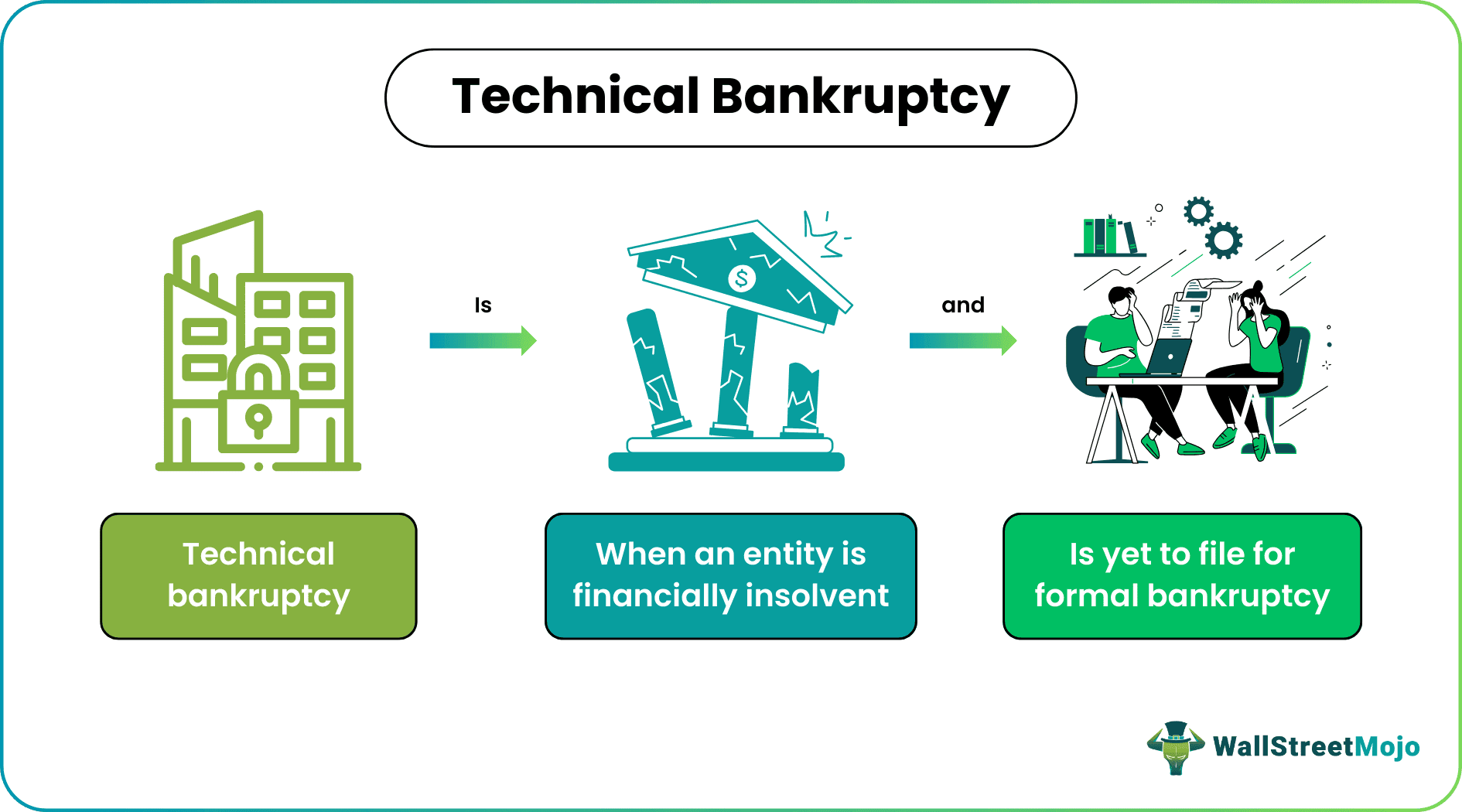
Technical bankruptcy occurs when a firm or an individual turns insolvent, but its owners and creditors are yet to file for bankruptcy officially. This bankruptcy type aims to protect the debtors from suffering the adverse consequences that a formal bankruptcy causes, which include having negative credit information or a low credit rating.
When individuals or firms declare technical bankruptcy, the creditor might be willing to discuss and settle for more agreeable solutions to this financial problem. They may renegotiate the terms of the existing loans and help the entity restructure its debt plans. This step might help the entity recover from its insolvency.
Key Takeaways
- Technical bankruptcy is when an individual or a company has declared itself insolvent, but neither they nor their creditors are willing to file for bankruptcy officially. Instead, they try to find more acceptable ways to solve this financial crisis.
- Even though filing for bankruptcy offers security to the insolvent entity against harrowing lenders and potential eviction, it is an expensive process and harms the debtor's credit reports. Thus, the debtors and creditors may be hesitant about filing for bankruptcy.
- This bankruptcy could also apply to an entirely different concept. It could mean a situation where a company uses outdated software programs that negatively impact its operation, so the entire IT system must be replaced.
Technical Bankruptcy Explained
Technical bankruptcy is a financial condition when an individual or a company declares insolvency, yet the owners and the creditors are unwilling to officially file for bankruptcy. Instead, they are eager to offer more acceptable solutions to the problem. Formally filing for bankruptcy protects the insolvent entity against eviction proceedings and pestering from the lenders.
However, it also has significant negative consequences. The entity may suffer from a negative credit rating, making it difficult for them to obtain credit in the future. Furthermore, filing for bankruptcy can be expensive, adding further financial burden on the debtor. As a result, the creditors may prefer helping the entity recover from insolvency when they declare technical bankruptcy by making specific changes to the loan offers and debt strategies.
Another technical bankruptcy is used in an entirely different context. It could imply a scenario where a company uses severely outdated software programs, and the whole system requires replacement. In addition, the entire IT system must be upgraded as the ancient system causes significant problems in the company's business operations.
Causes
Technical bankruptcy occurs when a company or an individual turns insolvent, but neither they nor their creditors are willing to file for bankruptcy officially. They are generally hesitant about bankruptcy and prefer looking for a more sustainable solution to the problem. Formally filing for bankruptcy safeguards the debtors from harassment by creditors and eviction activities. However, it also comes with significant drawbacks. It will negatively impact the borrower's credit score.
Additionally, individuals with little to no assets cannot meet the outstanding loans, and filing for bankruptcy may be another extra expense. As a result, companies prefer to look for other solutions to their financial problems. Renegotiating the existing loan terms and restructuring the loan strategies could help the business sustain itself. They are also considered a less expensive alternative than filing for bankruptcy.
Types
The technical bankruptcy types are as follows:
#1 - Balance Sheet Bankruptcy
This bankruptcy occurs when a company or an individual does not possess enough assets to cover the liabilities amount. It implies that the debtors cannot repay their debts by selling their assets. Therefore, it is considered a more severe bankruptcy type. However, creditors may allow the borrowers to restructure their debt plans and recover from the bad debts.
#2 - Cash-Flow Bankruptcy
This technical bankruptcy type occurs when a business or an individual does not have enough cash to pay off their current payments. This is a less threatening bankruptcy type as the entity may have enough assets to repay the creditors. This bankruptcy results from liquidity problems and may be temporary.
Examples
Let us understand technical bankruptcy with the following examples:
Example #1
Suppose Mrs. Rose owns a company named Beauty Boutique that sells designer clothes. Beauty Boutique has turned insolvent and does not have enough assets to cover its liabilities. However, it did not formally file for bankruptcy. Instead, the creditors allowed Mrs. Rose to negotiate on the existing loan terms and restructure her debt strategies. This is an example of technical bankruptcy.
Example #2
On January 2023, Bloomberg News reported that Genesis Global Capital, a giant crypto company, was preparing to file for bankruptcy. After the downfall of FTX, a significant crypto exchange, the company froze customer redemptions on November 16, 2023. The market anticipated Genesis Global Capital's bankruptcy for weeks following this event. Genesis and its parent company, Digital Currency Group, and the creditors have discussed several proposals. This is an example of technical bankruptcy.
Consequences
The technical bankruptcy consequences are as follows:
#1 - Loss Of Property
It might lead to the loss of property where an individual or a business might require to give away their belongings to repay the creditors. These possessions may include jewelry, antique furniture, automobiles, and real estate.
#2 - Impact Others Financially
It can impact other people who are related to the individual financially. For example, if an individual makes his spouse a guarantor for his loan, the spouse will be liable to meet his obligations to some extent.
#3 - Impact On The Credit
This situation causes impairment on an individual's credit. Bankruptcies lead to damaging particulars on the credit report, which might affect how future creditors perceive the individual. Lenders might refuse to extend any loan to the individual, charge higher interest rate, and offer less beneficial terms if they decide to provide loans.
How To Avoid?
Technical bankruptcy can be avoided in the following ways:
#1 - Prioritizing Debt Repayments
Most bankruptcies come from unpaid business loans, so companies should pay back the loans on a priority basis. First, they must look into how much they owe to whom and sort the bills according to the order of their importance. Then the businesses must repay the important ones first.
#2 - Cutting Down All The Unnecessary Expenses
The management must study the business expenses and filter out any unnecessary costs. Cost-cutting would be required to help a business secure its financial position.
#3 - Selling Unessential Business Assets
The management must scrutinize the business asset. They can go for selling away any assets that the company no longer uses. However, there may also be certain assets that are not worth the upkeep. Such assets must be eliminated to lower the business expenses.
#4 - Discussing Repayment Plans
The management can rediscuss the repayment plan with their creditors. Creditors might be willing to slash the repayment amount or increase the repayment period. Renegotiating the loan's terms can save a business from defaulting on its loans entirely.
#5 - Increasing The Revenue Streams
A business must navigate ways in which it can increase its revenue streams. Likewise, an individual can look for ways in which they can get some extra income. Additional income from various sources can help minimize ongoing losses.
#6 - Formulating New Business Strategies
The business must analyze its strategies and plan how to increase its revenue. The management must make the company stand out from its competitors, which would require rebranding or new marketing and sales strategies. They might also plan a new budget to help the business increase its profit margin.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Technical bankruptcy occurs when a company's liabilities amount exceeds its assets amount. However, it can continue its operations as it has enough cash flow to meet its operational and financial requirements. Financial bankruptcy occurs when a company cannot repay its debts and must formally file for bankruptcy protection. A company can be technically bankrupt and financially solvent at the same time.
Technical bankruptcy can impact investors adversely as it could lead to a significant fall in the company's security prices. Additionally, it may lead to an enormous reduction in the worth of their investments. Furthermore, if the company's financial standing continues to decline, it may eventually have to officially file for financial bankruptcy, which could lead to massive losses for the investors.
Creditors can protect themselves against technical bankruptcy by periodically tracking the company's financial performance. Additionally, they may set up suitable credit terms and limits while constantly monitoring the firm's creditworthiness. Furthermore, they may establish requirements for the company to offer appropriate guarantees or collateral to secure their debts.
