Table Of Contents
What Is A Taxable Allowance?
A taxable allowance can be defined as those components of an individual's salary that are subject to taxation under the Income Tax Act of 1961. These allowances are given to employees for expenses incurred over the basic salary. They are taxed since they have access to financial benefits offered by the employer.
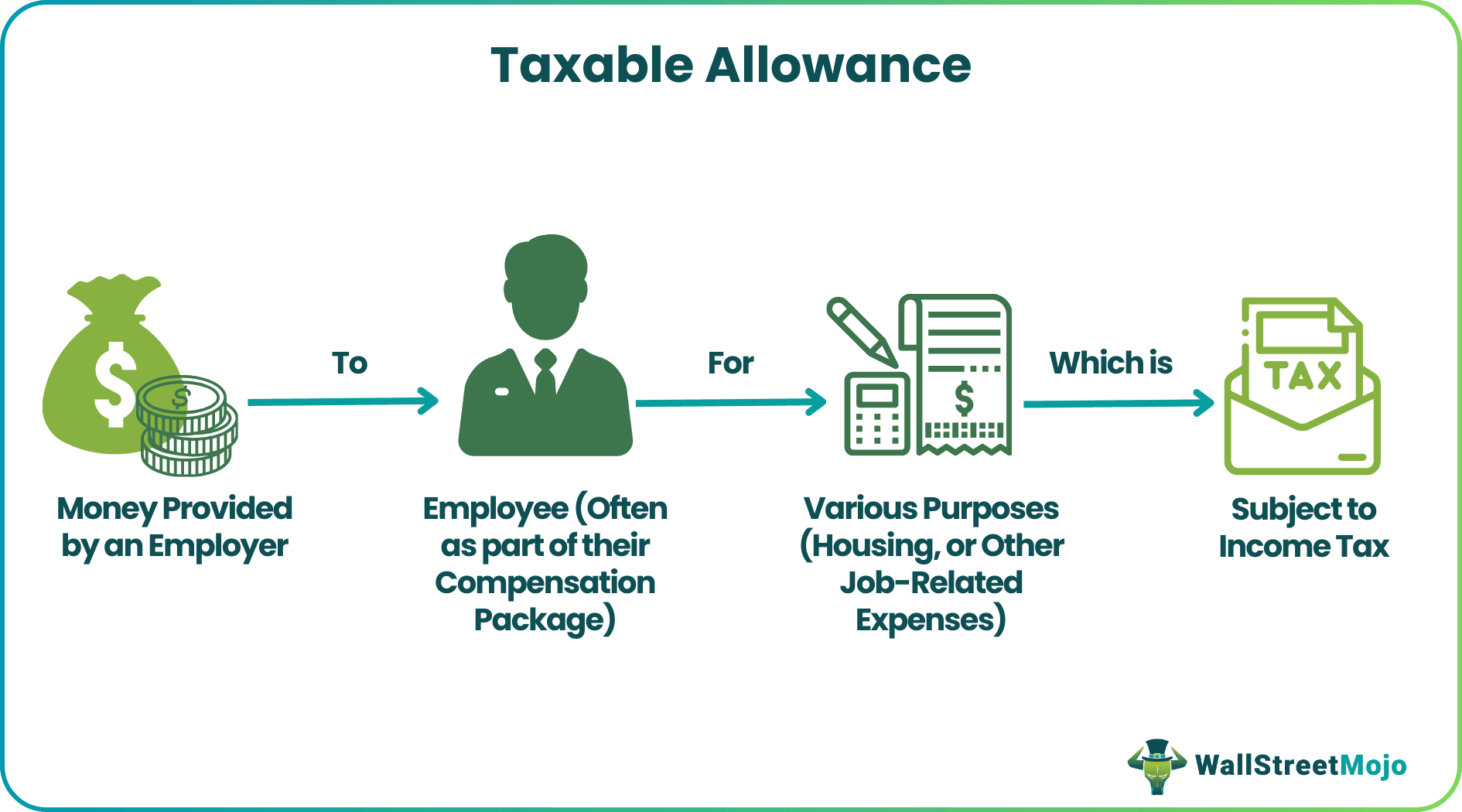
The Income Tax Act specifies three types of salary allowances – fully taxable, partly taxable, and non-taxable. The Indian government follows this type of taxation system for allowances. Some examples of taxable allowances in salary include medical allowance, transport allowance, house rent allowance (HRA), and leave travel allowance (LTA).
Key Takeaways
- Taxable allowances in salary refer to additional remuneration paid to an employee on which income tax is levied.
- Allowances are paid over the employee's basic salary due to extra work or expenses incurred.
- These allowances can be wholly or partly taxable, depending on the nature of the allowance. There is also a distinction in the tax computation of these allowances. There are also other allowances exempt from taxation.
- While some allowances are taxable in India, similar rules exist in countries such as Canada, the Philippines, etc.
Taxable Allowance Explained
A taxable allowance is an essential component of income tax. Often, employees receive a few allowances and benefits from their employer. It can be due to extra expenditure or additional work the employee does. For instance, overtime allowance paid to the employee is an example. It can also be due to the employer's work culture, which incentivizes employees, such as leave travel allowance.
But these allowances can be recurring, say, monthly or yearly, and thus form a portion of the employee's salary. Therefore, the government collects tax from the individual's income. While some allowances are fully taxable, some are partially taxable. Let us see how this works.
Fully taxable allowances are taxed along with the individual's income at the standard rate of the slab to which they belong. The employee's salary includes these allowances, and the tax rate is applied directly. Examples of these allowances include dearness allowance, medical allowance, overtime allowance, entertainment allowance, meals allowance, transport allowance, etc.
Partly taxable allowances are exempt from taxation to a certain extent (often, a predetermined limit), and the appropriate tax rate is applied to the remaining amount. Examples include house rent allowance, transport allowance, children's education allowance, leave travel allowance, etc.
Consider the case of house rent allowance in India. The amount of allowance exempted from income tax calculation is taken as the minimum of the following cases:
- Actual house rent allowance received from the employer.
- 40% of salary (basic amount and dearness allowance); 50% of salary in Chennai, Delhi, Kolkata, and Mumbai.
- Rent paid – 10% salary (basic amount + dearness allowance)
The minimum of the above three is deducted from taxable income, and the tax rate is applied to the balance amount.
Note that HRA is available only for central government employees.
Examples
Study the following examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
John is a government employee posted in the United Kingdom on official duty. In February 2023, he earned a total salary of ₹90,000, including an allowance of ₹10,000. His income is ₹90,000. From this, the allowance will be deducted. Therefore, only ₹80,000 will be taxed.
Example #2
Shirley is an Indian government employee working in Delhi. The following information is given. Let us find the taxable house rent allowance.
Basic salary = Rs 90,000
Dearness allowance = Rs 6300
House rent allowance received = Rs 10,000
Rent paid = Rs 25,000
From the information in the previous section, let us calculate the minimum of the three instances.
Case 1: Actual house rent allowance received from employer = Rs 10,000
Case 2: 50% of salary = 50% (96,300) = Rs 48,150
Case 3: Rent paid – 10% of salary = 25,000 – 10% (96,300) = Rs 15,370
The minimum of these three cases is case 1 – Rs 10,000
Thus, Shirley can deduct Rs 10,000 from her monthly taxable income.
Example #3
The Department of Expenditure under the Ministry of Finance recently outlined the conditions under which individuals are ineligible to claim house rent allowance (HRA), which is a taxable allowance. HRA is exclusively available to central government employees who live in rented accommodations. These regulations are in place to prevent employees from evading income tax by inappropriately seeking HRA deductions.
Additionally, suppose a government employee shares accommodation allocated to another government employee or resides with a family member (spouse, children, or parents) to whom the government (state, central, public-sector undertaking, or semi-government organizations) has assigned accommodation. In that case, they cannot claim HRA as a tax deduction.
Taxable And Non Taxable Allowance
Allowances provided to employees can be categorized into two main types: taxable and non-taxable allowances. Both types serve to cover additional expenses incurred by the employee. Let us understand the differences between them.
| Basis | Taxable Allowances | Non-Taxable Allowances |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allowances are subject to income tax. | Allowances exempt from income tax. |
| Taxation Method | Fully taxable or partially taxable. | Exempt from income tax. |
| Deduction from Taxable Income | Deducted before tax calculation. | Not deducted; no tax applied. |
| Purpose | Provided to cover additional expenses. | It also provided for specific reasons. |
| Tax Calculation | Tax calculated after deduction (if any). | No tax calculation is required. |
Let us see a few examples of these allowances to understand the difference better.
| TAXABLE | NON-TAXABLE |
|---|---|
| Medical allowance | Uniform allowance |
| Transport allowance | Allowances paid to government employees abroad |
| Leave travel allowance | Allowances paid to United Nations employees |
| House rent allowance | Sumptuary allowance |
