Table Of Contents
Tax Planning Meaning
Tax planning or analysis is a lawful method to reduce tax liabilities over a calendar year by capitalizing on tax deductions, benefits, and exemptions. It assists the taxpayers in obtaining commercial security and retirement savings with the decreased fiscal burden. Nevertheless, tax planning for individuals does not include tax avoidance or tax evasion.
This certainly aids in the proper usage of full benefit via all favorable tax law provisions. Moreover, it has three types, i.e., purposive, permissive, and short and long-range tax analysis.
Key Takeaways
- Tax planning is a legal approach to lowering the tax burden through tax benefits, deductions, and exemptions. It has three types, i.e., permissive, purposive, and short and long-range.
- It assists the taxpayers in obtaining tax efficiency by adequately planning their expenses and accumulating retirement savings.
- The tax analysis strategies incorporate broadening the outlook, making annual affordable commitments, and evaluating post-tax returns.
- The objectives of tax analysis are decreased litigation, financial stability, economic expansion, lesser total tax burden, and profitable investment.
Tax Planning Explained
TTax planning implies evaluating the taxpayer’s financial condition and conceiving approaches to surge tax efficiency ethically, both in corporate and non-commercial industries. This certainly helps them plan their capital budget and expenditures better.
It is completely legitimate if tax planning for retirement is executed according to the regulatory framework and also helps save one’s inheritance. Nonetheless, utilizing questionable strategies like tax evasion is strongly discouraged and is liable to litigation. It has two major categories, namely, Corporate and Inheritance tax analysis.
Here, corporate tax planning refers to the cutback of the tax burden on a registered firm through employee health insurance, business transport, retirement planning, office expenses, etc. Contrastingly, Inheritance tax planning implicates the procedure of passing on the earnings of an estate to the selected beneficiary.
Corporate tax planning aids in decreasing direct and indirect tax liabilities during inflation. Conversely, inheritance tax planning lets the individuals draft a tax-efficient will so that the heirs can live a stress-free life.
Simply put, adequate corporate or uncommercial tax planning for individuals is an outcome of:
- Attentiveness concerning court judgments and relevant tax laws
- Reporting of accurate details to pertinent IT divisions
- Flexible analysis to include potential forthcoming changes
- Incorporation of legalized tactics and not tax avoidance or evasion.
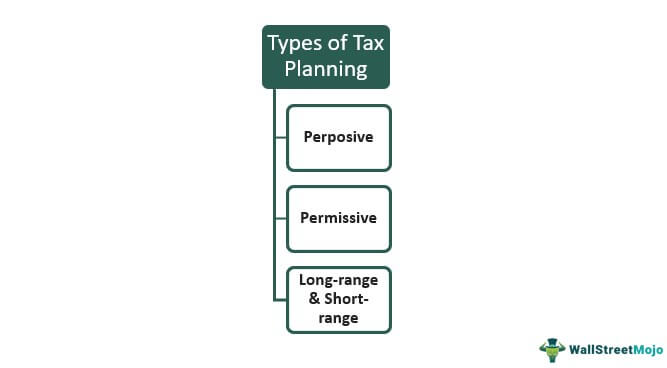
Types Of Tax Planning
To clarify, there are three types of tax planning for individuals:
- Purposive: It indicates the planning of taxes with a specific aim.
- Permissive: This type of tax analysis is performed as per the regulations of the nation’s taxation laws.
- Long-Range And Short-Range: Here, long and short-range tax planning for retirement is conceptualized at the beginning and end of a financial year, respectively.
Tax Planning Strategies
Now, let’s explore a few smart tax analysis strategies:
#1 - Make Inexpensive Yearly Commitments
As lucrative as it may sound, every insurance scheme is not worth the investment. Hence, taxpayers must only put their finances into a product or service that is both cheap and profitable in the long run. They must check their available funds to examine their affordability to retain the investment.
#2 - Analyze Post Tax Returns
While evaluating the tax returns, taxpayers must not let the profitable-yet-suspicious policies distract them. Please note that comprehending tax implications is of paramount importance. Rather, they must check out products with tax-free profits like Public Provident Fund (PPF) and Mutual funds.
#3 - Broaden The Outlook
Taxpayers must channel their annual returns into policies with long-term benefits. For instance, investing in long-term debt instruments assists them in leveraging the offered withdrawal alternatives. Then, they may reinvest the collected maximum tax-free capital amount in a financial vehicle like Equity Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS).
Examples
For better understanding, here are some examples.
Example #1
Davina is the owner of a multinational toy manufacturing firm. First, she assesses the taxable aspects of her annual income ($20000) and computes the payable tax amount. Then, she invests in financial instruments with maximum tax benefits.
She invests in PPFs, mutual funds, ELSS, and many other debt funds. Consequently, these investments lower her taxable pay amount by 40% ($8000). So, her tax liability over a fiscal year is now worth $12000.
Example #2
Proactive tax analysis certainly assists small enterprise owners in decreasing their tax liabilities. So here lies a few tax deductions to save the maximum amount of money.
- Health insurance premiums
- Retirement plan contributions
- Professional and legal services
- Business marketing
- Insurance premiums related to the business
- Business-related automobile expenditures
- Home office discounts
- Taxes and licensing for the business
- Office supplies
- Self-employment tax
- Cell phone
Tax Planning Objectives
Generally, the primary goals of tax analysis are:
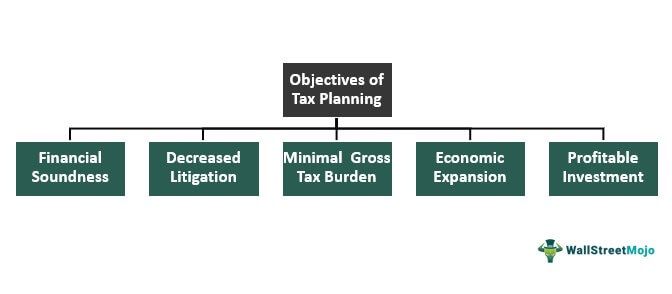
#1 - Financial Soundness
Please note that the superior tax analysis of an entity is the ultimate testament to its monetary stability and accounting profits.
#2 - Decreased Litigation
Appropriate tax analysis certainly assists avoid the usual disagreement between the taxpayers and tax collectors.
#3 - Minimal Gross Tax Burden
Tax analysis undoubtedly lets the taxpayers exploit the available tax benefits, exemptions, and deductions. In addition, it helps arrange the taxpayers’ commercial operations as per their tax decisions. As a result, it saves the maximum capital amount from being included in the tax liabilities.
#4 - Economic Expansion
The growth of a nation is directly related to the development of its citizens. As tax analysis facilitates the flow of white money, it certainly boosts the country’s fiscal standing.
#5 - Profitable Investment
The more the taxpayers save on their tax liabilities, the more they can devote it to a profitable channel. That is to say, an entity with quality tax analysis can direct its earnings into productive investments or dividends. Consequently, this assists in smart investments with optimum utilization of the available resources.
