Table Of Contents
Tax Haven Meaning
Tax Haven is a place or countries where there is a very low or nil rate of income tax for the business or individuals or foreign investors and also provide an attractive macroeconomic environment like financial and economic stability as well as financial secrecy from tax authorities.
In simple words, it means a country that offers meager taxation rates along with financial secrecy for foreign individuals and corporate entities. Tax haven rather accepts a nominal charge against the services they offer.
Tax Haven Explained
Tax haven countries play a very prominent role in the financial system of the world. Introduced to support and develop the broken economy of countries after World War II, now have become a vital tool for big corporations and wealthy individuals worldwide to evade taxes.
It constitutes the single largest drain on the economies of the countries globally.
A report by Citizen for Tax Justice during 2016 says that more than 370 companies out of Fortune 500 operate subsidiaries in such countries.
Incorporating companies in tax haven countries, transferring money, property titles, and investments for saving taxes are technically legal. But practices to conceal financial transactions, evasion of taxes, money laundering, etc. are not permissible and not legal.
Example
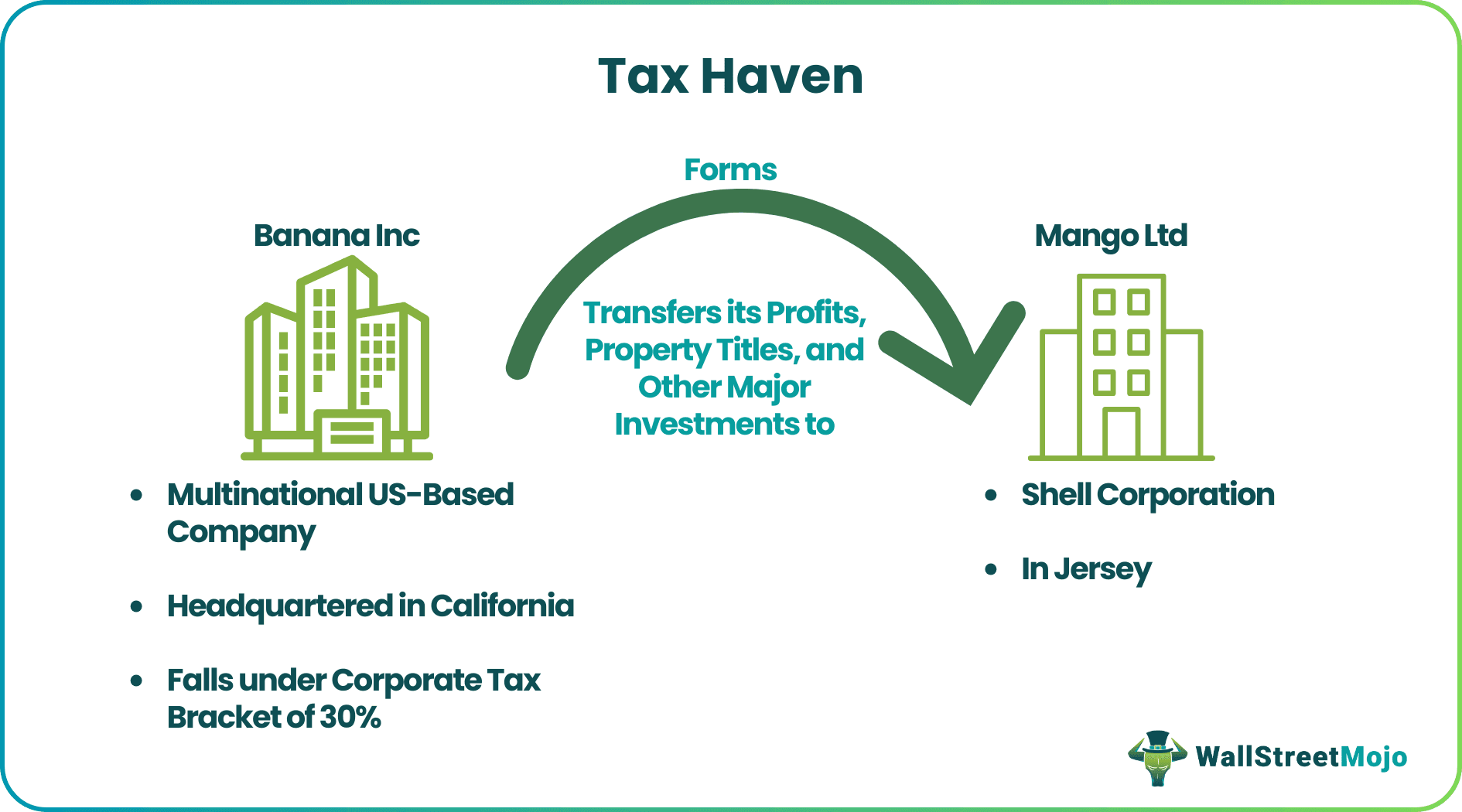
The working can be better understood with a hypothetical case study. Say Banana Inc, a giant multinational US-based company headquartered in California, creates extraordinary income worldwide and falls under the corporate tax bracket of 30% as per US tax codes.
- Now Banana, in order to pay fewer taxes, forms Mango Ltd, a shell corporation in Jersey popular tax haven destination for US corporations, including Apple Inc that does not carry any operations related to trade or commerce and does not own any significant asset.
- Banana transfers its profits, property titles, and other major investments to Mango Ltd and thus makes its profits earned in the USA to be taxable under Jersey’s Tax Jurisdiction. Jersey typically does not tax corporate income.
- So Banana Inc has successfully saved itself a 30% tax.
Remember, taxes are the single source of revenue for the governments and also their legal right. Practices of Banana Inc is a loophole under US tax laws that is violating the legitimate right of the US government.
Tax Haven Explained in Video
Features
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) provides various features to identify tax haven states or countries :-
#1 - Extremely Low Tax Rates
It offers or imposes negligible taxes for earnings made under their jurisdiction; this may vary with different countries. However, a nominal charge is levied against the services they offer.
#2 - Secrecy of Information
The other most important feature of tax haven places is that they protect the personal and financial information of their clients with high credibility. Without the client’s consent, no information is shared with foreign tax authorities.
#3 - Lack of Transparency
The biggest problem with offshore financial centers is their system is entirely opaque. Financial information is not even disclosed to the national governments. The system is thus manipulated for tax evasion practices and other illegal activities, including money laundering.
#4 - No Substantial Activities Required
Tax haven states do not require outside entities to produce goods or services within their jurisdiction. Entities can bypass their earnings and wealth created in tax-paying countries to be taxable under its jurisdiction by just opening the company’s head offices in such havens or transferring significant financial transactions of the company to subsidiaries or shell companies located in tax haven places. E.g., we can commence the trade practices in London and be liable to pay taxes under the jurisdiction of the Cayman Islands
The Panama Papers
The Panama Papers refers to a leak of very confidential documents related to the world’s fourth-largest offshore law firm based in Panama, Mossack Fonseca.
The documents released in 2016 exposed the network of more than 2,14,000 shell companies incorporated in various tax havens and revealed the identities and financial information about a number of wealthy individuals and entities from 200 different nations.
The leak involves various famous individuals, including world leaders, politicians, celebrities, and business peoples. The leak revealed how the rich could exploit offshore tax regimes.
Shell companies or business entities in tax havens are not illegal in general, and the leak also did not show inappropriate or unlawful operations by such entities, excluding a few. However, offshore-companies in the majority were established to conceal the identities of the true company owners.
Advantages
Let us analyse the tax haven benefits.
- Offer zero tax incentives to those who transfer their profits and jobs in such countries.
- Identify and minimize loopholes in offshore taxation policies.
- The world forums should force tax haven authorities to increase financial transparency and share confidential information in case of illegal practices.
- Penalize and/ or punish heavily who practice trade and finance inappropriately or illegally.
Disadvantages
Apart from the tax haven benefits, the limitations are as follows:
- The biggest disadvantage is the fact that low or middle-income families and individuals struggle to meet their tax obligations. In contrast, big corporations and rich individuals evade taxes using offshore financial centers.
- Companies in the USA, yearly, avoid payments of taxes of more than $90 billion. General Electric somehow managed to pay $0 as taxes during 2010.
- Tax evasion can be drastic for the country's economy as taxes are the only source of revenue for the government.
