Table Of Contents
Tax Fraud Meaning
Tax fraud is the deliberate use of wrong information in filing tax returns. It is an illegal act where an entity willfully tries to evade tax liability. Defaulters take advantage of the tax system and violate laws.
This unlawful act causes significant loss to the governments' income. The US reports a $1 trillion loss owing to tax frauds every year. Most defaulters are either huge business entities or affluent individuals. Unlike tax evasion, there are legitimate ways of minimizing the tax burden within the law. This is referred to as tax avoidance.
Key Takeaways
- Tax fraud is an illicit practice. Individuals and corporations evade tax obligations by hiding their actual income or financial records from the tax authorities.
- Alternatively, they deliberately claim incorrect exemptions and deductions.
- If a tax preparer willingly deceives or misleads the tax authorities by submitting false statements and returns of their client, they are considered a tax defaulter.
- It is a punishable offense in many countries; however, the intensity of punishment relies upon the category of misconduct.
- The severity of the crime varies between civil and criminal frauds. Therefore, the penalty for the crime also ranges from hefty fines to imprisonment.
How Does Tax Fraud Work?
Tax fraud is the deliberate supply of misinformation by the taxpayer. Defaulters commit this crime to dodge their tax liabilities. Thus, it can be defined as any false representation of the income or wealth with the intention to cheat on the tax sum owed. However, there is a legitimate way of minimizing the tax burden within the law. This is referred to as tax avoidance. Here, a tax consultant can suggest acceptable tax planning methods and income allocation to lessen the taxable income.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) treats such frauds in two different ways. For civil frauds, the tax liability is reassessed, and civil penalties are imposed on the defaulter along with the due tax amount. In contrast, for criminal frauds along with the monetary fines, the defaulter also faces prosecution. This could potentially lead to imprisonment.
Intentional non-disclosure, manipulation of income-related financial records, false claims, false deductions, incorrect exemption, and asset concealment are all considered tax frauds. People are usually involved in this misconduct to save taxes and pay as little as possible. Defaulting on taxes is considered a punishable offense in most countries. Similar to Internal Revenue Service (IRS), governments set up regulations and take various measures to control tax evasion by strengthening the system.
Types of Tax Fraud
Following are the different kinds of unethical tax practices:
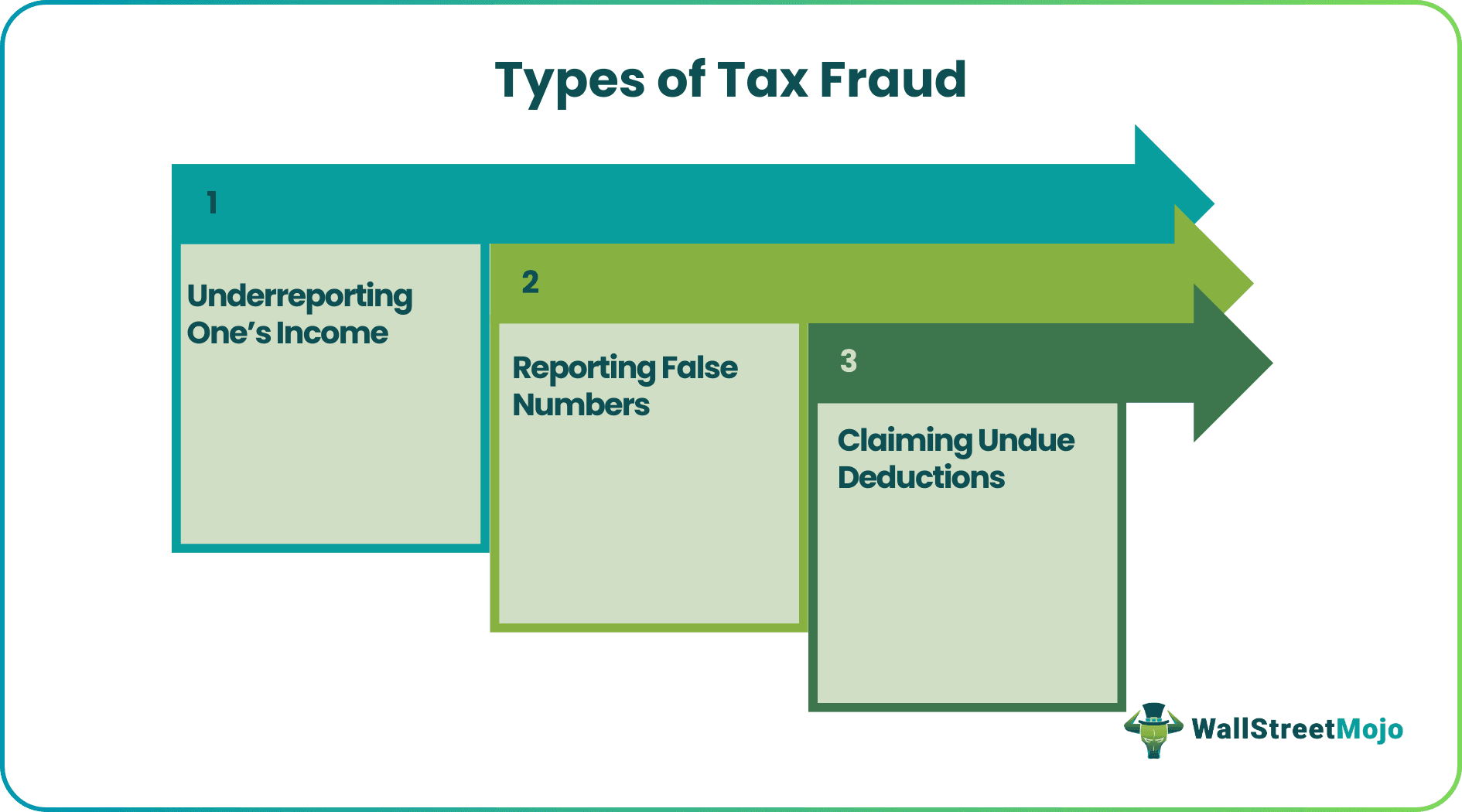
- Tax Evasion: In this form of criminal tax fraud, an individual knowingly presents false income information to the tax authorities. Alternatively, some report an income lower than the actual income while filing for tax.
- Claiming Unqualified Credit and Deductions: Many defaulters apply for deductions or credit that they are not eligible for.
- Wilful Non-filing of Tax Return: If an individual premeditatedly fails to file tax returns, it is seen as an act of civil tax fraud.
- Intentional Non-payment of Tax: When taxpayers deliberately evade tax obligations or hide evidence pertaining to their income, it is seen as an act of criminal tax fraud.
- Stating Wrong Numbers or Presenting Fake Documents: The taxpayers who furnish false documents or provide incorrect statements pertaining to their income are also considered defaulters.
- Tax Evasion by Tax Preparer: Tax preparers who aid their clients by facilitating any or multiple types of offenses mentioned above are also prosecuted for tax evasion. These accountants give their clients an unfair advantage.
Tax Fraud Examples
Consider the following examples for better understanding tax frauds.
Example #1
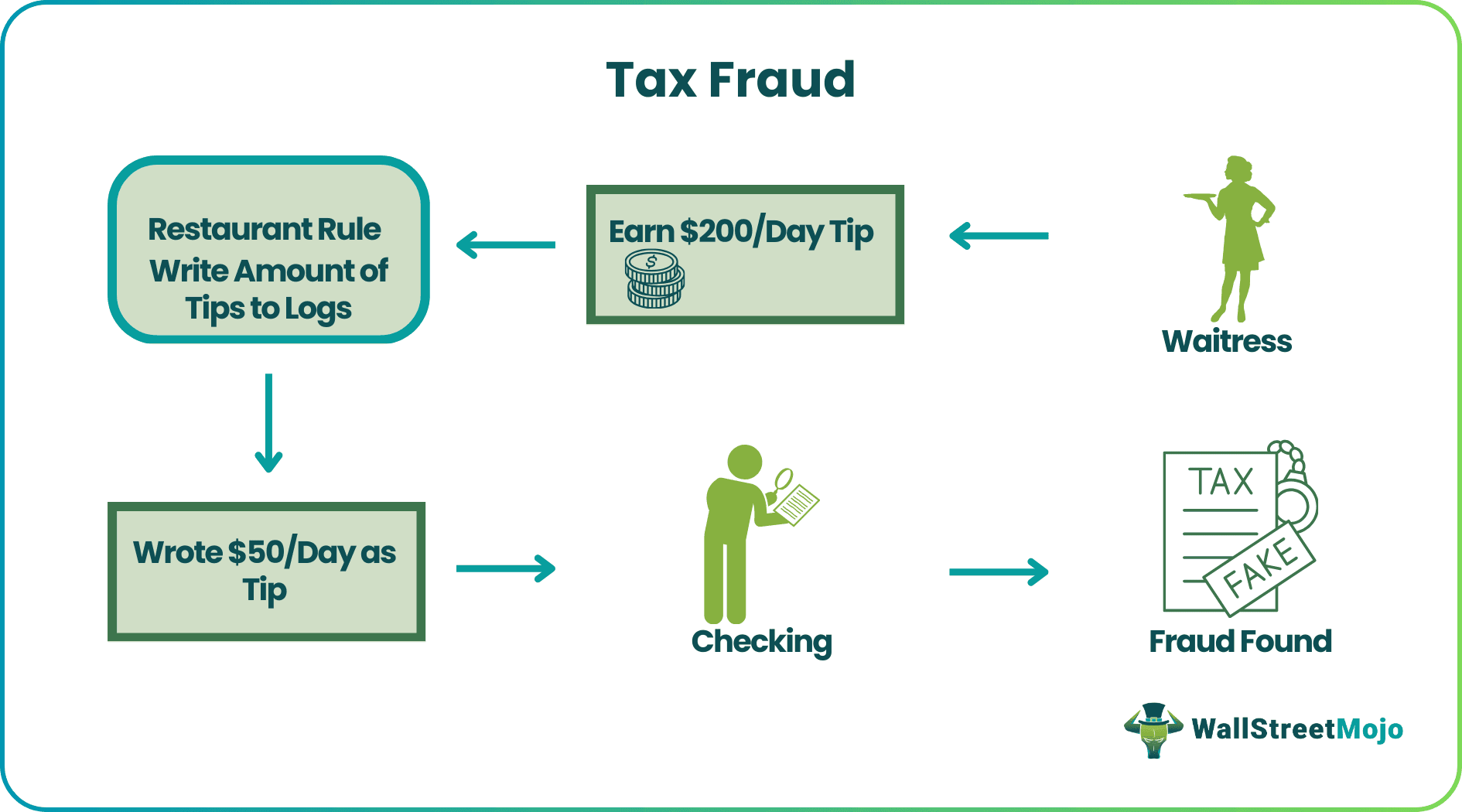
Lisa is a waitress in a restaurant. She is tipped around $200 every day. The rule of the restaurant requires the waitress to write down the exact amount received. To avoid taxes, Lisa reports only $50/day in her logs. After an internal audit, Lisa was found guilty of tax fraud and liable for a hefty penalty. In extreme cases, defaulters can face imprisonment.
Example #2
On August 27, 2021, Cisco's Global Supply Manager, Prithviraj "Roger" Bhikha, was condemned to three-year imprisonment. He was found guilty of wire fraud and tax fraud. This was reported by the US Department of Justice. Bhika was the head of Cisco's "Project New York" in 2013. This project aimed to retain Cisco's third-party vendors. Bhika allegedly created Lucena Ltd. in Singapore to serve as a supplier for Cisco, violating the corporate laws. He reportedly took kickbacks of $1.15 million from Cisco's vendors and continued to associate with Lucena from 2014 to 2017. In 2017, Bhikha was expelled from the company as his fraud got discovered.
Moreover, Bhikha agreed that he and his wife had repatriated with an account balance exceeding $9 million under a business entity named Lucena Ltd. The couple confessed their tax evasion as they did not disclose income earned via Lucena from 2014 to 2017. They evaded the income tax amounting to more than $2.5 million. As a result, the Federal court ordered Bhikha to pay $2.5 million as compensation to the IRS. This was in addition to the $1.15 million reimbursements paid back to Cisco Systems Inc.
Tax Fraud Punishment
The penalty for civil fraud is mostly limited to fines. For instance, the deliberate non-filing of tax returns bears a 15% penalty of the due monthly tax amount not exceeding five months. The maximum fine is up to 75% of the unpaid tax amount. Further, on filing a misleading tax return, the defaulter is liable to pay a fine of 75% of the underpaid tax amount.
In the US, the IRS has set up criminal tax fraud regulations under Section 7201 of the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) for intentional falsification of tax assessment and payment. It has a provision of penalty and incarceration if a person is found guilty of a felony. The monetary fine imposed on an individual offender can be as high as $250000. The penalty for a business entity can go up to $500000. In addition, the period of imprisonment for such defaulters is stated as up to 5 years accompanied with or without the fine. Also, the prosecution charges are to be borne by the defaulter. For example, if a defaulter deliberately fails tax filing or maintenance of records, the individual is charged a maximum of $25000, and such an entity is fined up to $100000 and/or imprisonment up to one year.
Case Study
In July 2020, a tax preparer in Las Vegas named Martha L. Williams was found guilty of filing clients' false tax returns. She is the owner of a tax preparation firm, MJW, and Associates and allegedly accepted to file 750 fake tax returns. The IRS stated a loss of $5,29,782 caused by Martha's offense. She was sentenced to two years imprisonment by the US District Judge. Additionally, Martha was made to pay a compensation of $5,29,782 compensation to the IRS.
How to Avoid Committing Tax Fraud?
Instead of breaking the law, Individuals or companies can use the legal means of tax avoidance to reduce their tax obligations. The advisory firms and tax preparers can suggest various lawful methods of claiming tax deductions.
One of the most common ways to refrain from fraudulent tax practices is to set a robust tax planning structure. In addition, firms should inform their employees about the tax procedures, tax evasion regulations, and compliance. Firms can monitor and flag defaulters regularly. Moreover, businesses should not associate with any suppliers or customers who are on trial for defaulting.
It is equally important to choose an ethical business for tax preparation. Furthermore, even the tax preparers should follow the code of conduct and avoid any illegal means to provide undue advantage to their clients. Lastly, if a company suspects any incidence of tax evasion, they must immediately report the crime.
