Table Of Contents
Tax Exempt Meaning
Tax exempt refers to earnings excluded (partly or wholly) from tax collection at the federal, state, or local level. It helps ease off the tax liability and improve organizational transparency. For example, the government provides the tax exempt certificate to eligible entities for specific professional advancement or for encouraging charitable foundations.
Tax exempt income is subtracted from the total earnings to calculate the taxable income. Moreover, maximum taxpayers are subject to definite exemptions for taxable salary cutback. At the same time, some individuals and companies relish total income tax exemption.
Key Takeaways
- Tax exempt denotes the wholly or partially non-taxable income at the local, state, or federal level. Moreover, a common tax exempt example is the interest earned through municipal or US Federal bonds.
- Tax Exemption, Tax Deduction, and Tax Credit are three different terms and must not be confused with each other.
- The IRS exempts the tax of public welfare firms. It comprises charitable institutions, churches and religious groups, private foundations, political entities, and nonprofits.
- Its merits are decreased tax burden, socio-economic advantages, and increased transparency. On the other hand, the demerits include increased cost of compliance and reduced tax collection.
Tax Exempt Explained
Tax exempt or immunity signifies that a portion of or the total revenue of an entity is not liable to tax. Moreover, the tax exempt certificate allows the association or individual to make a tax-free purchase. For example, interest income on municipal bonds and US Federal bonds are tax-free.
If the married exempted taxpayer reports a joint federal tax return to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), both partners collect the tax exempt income. Also, it permits the taxpayers to acquire additional exemptions for each claimed dependent.
Please note that income tax exemption, tax deduction, and tax credit are three distinct concepts.
- Tax exemption represents wages that are partially or wholly non-liable to tax.
- Tax deduction depicts particular incurred payments and holdings qualified to decrease the taxable compensation.
- The tax credit is the capital amount subtracted from the overdue income taxes.
Examples
Let us go through the following tax-exempt examples to understand the concept better:
Example #1
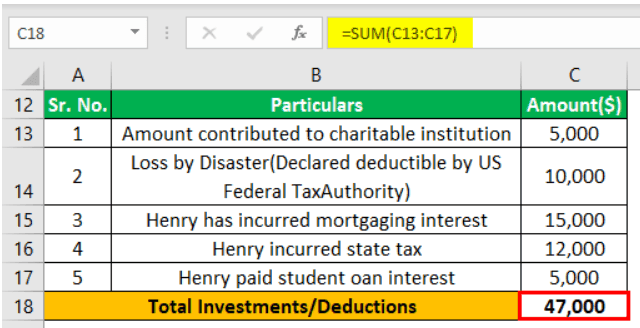
Let us compute the taxable salary and payable tax amount of businessman Henry. Please note that the applicable tax rate is 24%.
Furthermore, the details of his gains, expenditures, and assets are as follows:

Here are the losses, donated amount, interest, and taxes paid:

So, the taxable salary and payable tax amount will be:

Example #2
Let’s determine the taxable income and tax liability for another businessman named Jacob. Please note that the applicable tax rate in this situation is 22%. Moreover, here lie the complete details and the required calculation.

Example #3
On 8 March 2021, Thailand announced the relaxation of investment tax rules in digital assets. The move will assist develop and facilitate the industry. In addition, it will allow traders to counterbalance the yearly losses against profits for taxes overdue on cryptocurrency investments.
Also, it has exempted a 7% Value Added Tax (VAT) for cryptocurrency trading performed on the authorized exchanges. The exemption will be effective during April 2022-December 2023. Furthermore, it incorporates the central bank-issued commercial central bank digital currency trading.
Tax Exempt Organizations
Tax-free organizations are mostly IRS-accredited associations committed to the public good. Moreover, it assists them in encouraging public prosperity efficiently. This relies upon the pursuits, revenue sources, and motives of the non-profits. Although exempt, they must typically lodge annual profits and bill returns with the IRS.

1. Churches and Religious Bodies
Eligible churches (entailing unified auxiliaries and treaties or alliances) are automatically untaxed. Therefore, they don’t have to fill out the IRS tax-exempt forms.
2. Charitable Institutions
It incorporates solely structured establishments and is utilized for charitable, scientific, religious testing for literary, educational, public safety, or further stated objectives.
3. Political Entities
A committee, party, fund, association, or other agency (incorporated or not) is essentially regulated and employed for directly or indirectly spending and/or receiving donations for an exempted activity.
4. Private Foundations
Generally, they have one crucial financing source (grants from a single company or family). They don’t directly conduct charitable trusts. Instead, most of them make grants to other humanitarian organizations and entities and receive a considerable tax benefit.
5. Other Non-profits
The civic leagues, social welfare institutions, labor organizations, business leagues, and social clubs must fill out the tax-exempt form.
Advantages & Disadvantages Of Tax Exempt
Availing tax immunity or exemption may have pros and cons for any individual or entity. So let us look at them:
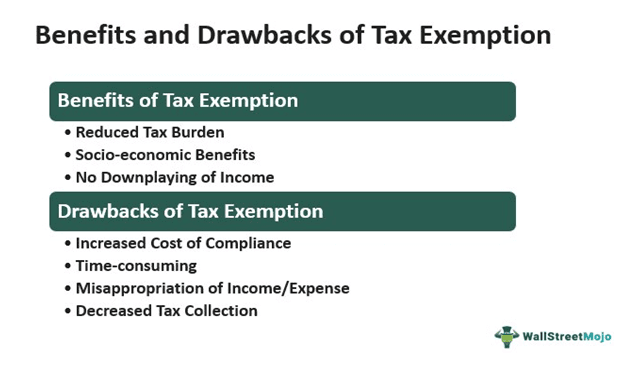
1. Benefits
Reduced Tax Burden
It helps diminish the tax pressure on an individual or firm.
Socio-economic Benefits
Providing tax benefits to the public welfare programs refines their business structure and offers numerous socio-economic advantages.
No Downplaying Of Income
Filing tax exempt forms on specified investments (for example, US federal bonds) reduces the odds of reporting incorrect financial statements. Needlessly, this brings more accountability and enhances transparency.
2. Drawbacks
Increased Cost Of Compliance
Filling the tax-exempt forms mandates the amenability to many formalities. Subsequently, this keeps adding to the cost of the organization.
Time-Consuming
The entire legal procedure may be quite time-consuming, with tons and tons of paperwork. So, the entity must be well-prepared for the same and be patient throughout the process.
Misappropriation of Income/Expense
Sometimes, individuals or firms use fraudulent activities to hamper their actual income statement. As a result, they tend to weigh the expenditures way higher than the profits.
Decreased Tax Collection
The government typically ends up with a much-reduced tax collection. Also, this reduces the net tax liability amount.