Table Of Contents
What Is A Tax Deduction?
A tax deduction is a provision that allows taxpayers to subtract items from their taxable income. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) will enable taxpayers opting the standard deduction method of filing with double the number of items. However, they can choose itemized deductions on Schedule A to file their returns, depending on their type of income.
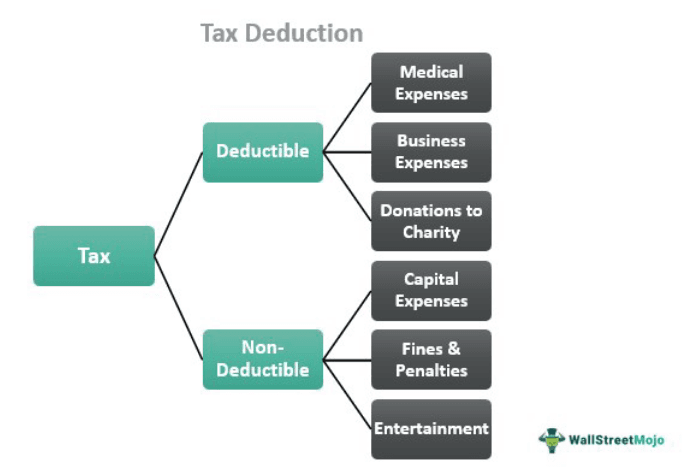
Mortgage interest payments, local and state tax, life insurance, and medical expenses are among the items that are tax deductible. To claim such deductions, the individual or the company has to file the tax returns on time and be aware of each deduction's limits. For example, there are certain limits on an Individual Retirement Account (IRA) deduction for every year.
Key Takeaways
- Tax deduction refers to the provision that allows taxpayers to reduce their taxable income and, thereby, their tax liability.
- These deductions have two variations, namely, standard deductions and itemized deductions.
- Taxpayers are free to choose from both categories. Generally, individuals with relatively low income opt for standard deductions to avail of the maximum benefit,
- and people with high income opt for itemized deductions to avail of similar benefits.
- Since these deductions reduce the overall tax liability year on year, it motivates citizens to save and invest the amount. Such investments are subject to deductions as well.
Tax Deduction Explained
Tax deductions are a portion of items not subject to tax and reduce the overall tax liability of taxpayers. These deductions come in four categories: pre-tax, post-tax, mandatory, and voluntary.
The two primary modes by which taxpayers can opt for deductions are-
#1 - Standard Deductions
It is a specific amount that reduces the taxable income of the taxpayer. The standard deduction for single filers is $12,950, $25,900 for joint filers, and $19,400.
#2 - Itemized Deductions
Itemized deductions are provisions based on eligible expenses such as real estate taxes, mortgage interest, sales taxes, SALT, charity donations, and more.
Depending on the individual or organization’s income level, it might be a good idea to choose one of the two options. For example, if an individual from a low-income group wants to file their taxes, it might be better to opt for the standard deduction as IRS would waive off a lump sum amount from their liability. However, itemized deductions might be a better approach if their income is high.
These deductions help taxpayers mitigate a particular sum from their income and save hundreds or even thousands in tax annually. In addition, this provision allows citizens to develop a habit of saving and investing as the tax on income is reduced.
Types
Apart from the primary division of standard and itemized deductions, individuals and couples filing jointly can avail of the deductions from the list of eligible items, a few of which are as below:
#1 - Education Deductions
The fees paid toward a child’s education at a school, college, or any other educational institution is eligible for deduction up to $2,000. This provision includes the fees for tuition, books, and other supplies for the course. Additionally, 25% of the $2,000 can be deducted, totaling up to $2,500.
#2 - Healthcare Deductions
The internal revenue system allows all taxpayers to deduct 7.5% of all unreimbursed medical expenses that exceed their gross income after adjustments. Therefore, it is vital to be aware that it is essential to opt for an itemized form of deduction and declare the same on Schedule A.
#3 - Investment Deductions
It refers to the income from investments such as interest, rental income, qualified dividends, and royalty incomes. According to IRS norms, individuals contributing to their own IRA or their spousal IRA can avail of deductions on such investments. Therefore, it is essential to declare items such as rental income to avail of a rental tax deduction.
#4 - Mortgage Interest Deductions
The tax paid on the monthly installments toward the mortgage can be tax deductible. Apart from availing of mortgage interest tax deductions, taxpayers can avail of deductions for refinancing points, and property taxes are also deductible.
#5 - Self-Employment Related Deductions
Work-from-home and home businesses are gaining popularity among the self-employed section of society. The increase in popularity has increased the expense relating to such companies. Hence, individuals can claim deductions on expenses such as office supplies, internet costs, travel, and advertising.
#6 - Donation/Charity
Individuals donating a part of their income to charity can claim a deduction. To do so, they must file a Schedule A along with their tax form to avail of the donation tax deduction.
Examples
Let us understand the application of these deductions with the help of the examples below:
Example #1
Michael’s 14-year-old son Clarke's school tuition and other related fees are his highest yearly expenses. As a result, he needs help to accommodate the additional education costs, such as the course materials and other charges. The previous year, he spent around $1,500 on course materials alone.
After sharing this with his friend Steve, he learned about the deductions he could make from the taxes he paid for such expenses.
While filing for returns this year, Michael declared these expenses on Schedule A and deducted the tax he owed on the whole of $1,500 as a part of his income tax deduction.
Example #2
Capital gains are considered according to two-time frames- short-term and long-term.
If an individual holds an asset for more than one year before selling it, its profits are considered a long-term capital gain.
However, if a taxpayer’s capital losses exceed their capital gains, they can claim deductions up to $1,500 if filing individually or $3,00 if filing jointly. In addition, if the net loss exceeds even the limit, it can be carried forward to later years.
Benefits
Let us understand the benefits of deductions for taxpayers through the points below:
- Deductions reduce the annual tax liability to Federal and State Governments.
- Promotes investments by providing deductions for most instruments such as shares, bonds, rental income, etc.
- Retirement investments such as IRA or employer-sponsored 401(k) retirement plans are deductible, allowing taxpayers to plan their retirement well in advance.
- Education is one of the most critical and costly expenses taxpayers annually incur. To make it easy on them, the IRS allows deductions of such expenses.
Tax Deduction vs Tax Credit vs Exemption
The IRS provides tax benefits such as deductions, credits, and exemptions for citizens filing annual tax returns. Regardless of these provisions reducing the tax liability, the application and eligibility of each are different. Let us understand them through the table below:
| Basis | Tax Deduction | Tax Credit | Exemption |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Function | Reduces taxable income | Reduces the tax amount directly | Usually arises in situations with pre-tax payments. |
| Example | Interest on a mortgage payment | Child tax credit | Health insurance payment program by an employer. |
| Application | It is applied after arriving at the gross income figure. | It is applied to the sum after all calculations relating to filing tax returns. | Incomes excluded or exempted from tax returns do not reflect on the tax return. |
