Table Of Contents
What Is Tax Base?
Tax base refers to the total income (including salary, income from investments, assets, etc.) that can be taxed by a taxing authority and is thus used to calculate tax liabilities owed by the individual or the corporation. It serves as a total base on which the tax can be charged.
It is an important source of reliable information to gauge the total income earned by a country's government through taxation. It stands as a reliable accounting source to generate statistics in this regard. It becomes imperative for the government to properly determine the base to have efficient taxation, thereby ensuring people are neither overtaxed nor undertaxed.
Tax Base Explained
The term tax base explains the value of goods and services, transactions, income or property on which the government of the country can impose tax. This concept not only identifies the areas on which tax is to be charged, but also identifies the total minimum, amount which may become taxable based on tax base rate.
This amount becomes the one on which tax will be calculated and will prove to be a source of revenue for the government that will supply funds for development and maintenance of infrastructure of the country. This leads to an all round development of its citizens and therefore all individuals and corporates should correctly disclose its tax base to the government.
The government, usually in its budgetary session, will decide on the tax slabs or tax base rate and the various sources of income it would like to tax or, rather, not tax. It becomes important that one stays updated in this regard to understand what comes under the total taxable income basket of the government to determine the base.
It is thus a very crucial aspect of the entire taxation structure of the country and thus, it is subject to different and stringent rules and regulations imposed by policymakers. This ensures the tax base calculation with accuracy and transparency so as to help the government attain its objective. Any discrepancy will lead to serious implications that affect both the government and also the taxpayers.
Formula
The tax liability is determined by multiplying the tax base by the tax rate. Therefore, it would thus be the tax liability divided by the tax rate.
Tax Base Formula = Tax Liability / Tax Rate
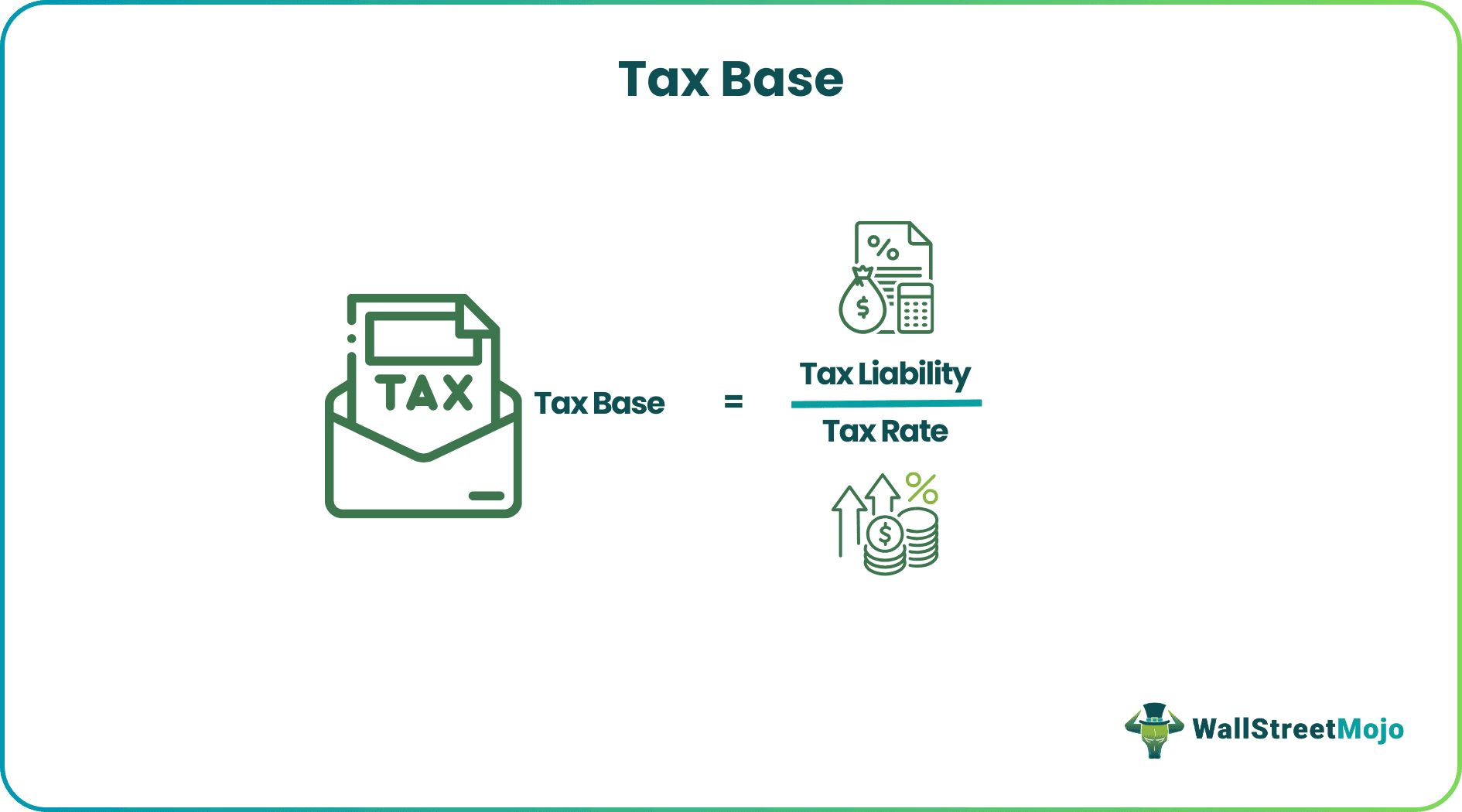
In the above formula of income tax base, we see that the numerator represents that tax liability which is the amount to be paid as the tax to the tax authority. The tax rate is decided by the policymakers based on the type of income of transaction on which tax will be paid.
Example
Let us try to understand the concept of income tax base with the help of an example.
Mrs. Lucia, a businesswoman, happened to earn $20000 last year. Out of this amount, $15000 was subject to tax.
Let us now consider the tax liability assuming a tax rate of 10%.
Tax Liability = Tax Base * Tax Rate

The details are listed as follows.

Hence we can back-calculate to arrive at the tax base as tax liability/tax rate, which would now be 15000 (1500/0.1)
Features

#1 - Simplicity
It is simple to arrive at. All one would ever have to do is consider the net total of all the assets or revenues that are subject to tax. This will thus help the government ascertain the total number of taxpayers and then consider the income subject to tax. It would help one understand the total tax that the government will tend to earn through this simple method.
#2 - Gauge of Taxable Income
The official statistics collected from numerous sources help the government assess the total revenue from the asset tax base it tends to gain, usually from taxable income, by looking at the economy's tax base as a whole. This helps the country's government to ascertain the total income that it can thus generate for the previous assessment year.
#3 - Wide Base Increases Revenue
When a government goes to tax various other items on an indirect basis, such as VAT, Central duty, excise duty, imports, tariffs, etc., its base would now widen. The enhanced base would be a source of further revenue for the government. The government can now channel this towards productive purposes such as developing infrastructure projects, social and welfare spending, etc. Such activities would further the development of the nation.
#4 - Acts as an Accountable Source
When a government goes on to establish its tax base, this would now serve as an accountable source of revenue. This information can now be fed into statistical data combined by various agencies. Thus this data serves as a reliable source to gauge the amount of taxes a country collects to enable it to compare with various other countries to ascertain the total amount collected from taxes.
Limitations
#1 - Does not Consider the Shadow Economy
There are many in the illicit business, such as drugs. These are usually unreported, and thus there is no tax on them, yet the mediators tend to make a fortune. It tends to miss out on such income and is not inclusive of the shadow economy.
#2 - Narrow Base may Impede Growth
If a country tends to stick to taxing only one source, such as income tax, and does not go on to consider the taxation of other indirect sources such as VAT, the asset tax base now narrows. This narrowing is a loss of revenue for the government. Because of the loss of such revenue, the income of the government will be reduced, and it may not be able to undertake developmental activities for the welfare of the economy, and this will impede Growth
#3 - Excludes Exemptions and Tax Relief
The government may give certain incentives for certain sectors, which relieve the ones relying on such occupations and, exempt from paying any taxes. Furthermore, various incentives and exemptions introduced by the government help the public save or invest in those avenues to take advantage of tax exemptions. However, this seems to be a disadvantage for the government as it will have the tax base reduced to such an extent, which further reduces the revenue to the government.
Tax Base Vs Carrying Amount
Both the above concepts have different meaning but are commonly used in the financial world related to taxation and valuation of assets. Let us find out the basic differences between them.
- The tax base amount is used to calculate the tax liability, but the latter is used in case of financial reporting of asset or liability value of the business.
- The former is fixed or decided by policymakers as per the tax laws, but the latter is decided based on accounting principles and rules of recording transactions relate dto depreciation, amortization, historical cost, etc.
- Both may change over a period of time but the former may change due to tax laws, but the latter may vary due to accounting laws.
- The carrying amount is the historical cost or the fair value but the differences between the tax base and carrying amount will give rise to deferred tax asset or liability.
- The former explain at which point of time the taxable income will be recognized but the former explains the determination of income or expenses for financial reporting purpose.
Thus, the above are some important differences between the two concepts.
