Table Of Contents
What Is Tax-Advantage?
Tax Advantage is the investment or saving plan that provides tax exemption, deferred tax, and other tax benefits. Examples include Government bonds, Annuities, Retirement Plans, and other investment plans authorized by the country's Tax Department that provide benefits in terms of taxes.
Tax advantage plans benefit all categories of individuals from various income groups. Individuals make decisions based on future financial goals, family requirements, health expenses, educational expenses for children, and wealth creation over a period. Utilizing both types of tax-advantaged strategies will provide flexibility and benefits.
Tax-Advantage Explained
The concept of tax advantage deals with various types of financial accounts, investments, and different savings plans that can either offer some kind of tax benefit, or they have the option for tax exemption. They can also be tax-deferred. It gives financial benefit to the investors or account holders.
In such cases, the income earned before tax is charged, is typically used for investment purpose and the tax can be paid later as per the applicable rates. This facility is availed by a huge number of employees of various financial institution or individual investors. For tax payers who have a very high income can opt for tax-free municipal bonds.
Investments that offer the tax-exempt status or deferred facility are very commonly used because they help the taxpayers minimise the amount that flow out for tax purpose, thus, allowing them the facility to save money for other investment purpose. The accounts set up for tax benefits are extremely useful because they provide benefit in the future during withdrawal of funds for retirement.
However, all the above proves that be it a tax exempt account, where tax payment is done immediately or deferred account, where tax is given at a future date, both are beneficial and advantageous for investors.
Types
The following are the different types of accounts that are commonly used for investments.
- Pre-Tax Investment Accounts (Deferred Tax): These investments delay your taxes for a later date in the future until the investment provides gains and funds are withdrawn from investments.
- After-Tax Investment Accounts: The tax you already paid contributes to this account. Gains/earnings from these accounts will not have any taxes applicable up to a certain limit.
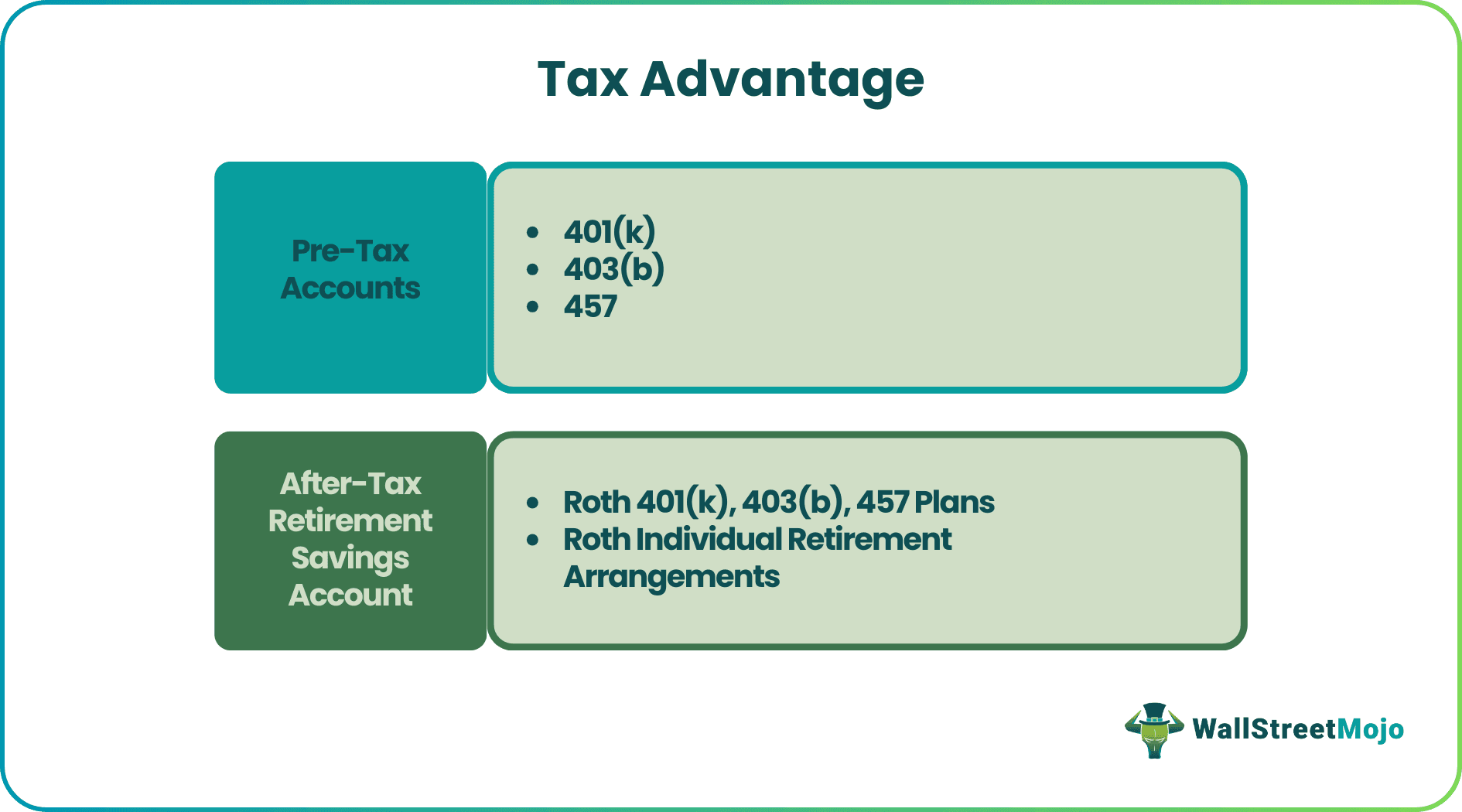
#1 - Pre-Tax Accounts
In the U.S Traditional 401(k), 403(b), and 457(b) are mostly used employer-sponsored saving plans; most of these plans are funded by an employee, while certain employers provide a matching contribution in these accounts.
#1 - 401(k):
- Most business organizations offer this plan. The employee selects their contribution up to certain limits with various investment options, mainly based on the tax-deferred principle. Some employers also contribute a matching amount to this fund. Yearly employees can contribute up to $19,000 to this account, while employees above 50 can contribute an additional $6,000.
- The amount of employees invested in this account is safe even if the employee leaves an organization; upon new employment, the employee will have the option of switching or staying with the old plan. Up to the age of 70, an individual can eventually invest and keep their money in these accounts after they need to withdraw and pay taxes on their earnings as regular income.
#2 - 403(b):
Especially for employees from non-profit organizations, universities, schools, religious organizations, hospitals, etc.; Tax rules and contributions remain the same as the 401(k) plan.
#3 - 457:
Local and state government employees can invest in a 457 plan, similar to 401(k) for contribution limits and tax rules. Still, they do provide some additional tax benefits.
- Double contribution in case employers offer 403(b) when you don't have more than three years for your retirement age;
- If the employer offers all three mentioned plans, then your investment contribution in this tax-deferred account can be doubled, i.e., $38000 or $50000 (for individuals above 50 years).
- Early withdrawals before age 59.5 are subject to taxes, but the penalty is not applicable to this investment account.
Traditional Individual Retirement Arrangement: Under this account, the contribution from an individual's income is deductible. In case the employer of an individual offers an employer-sponsored plan and the income of an individual crosses the limit of modified adjusted gross income, contribution in this plan may not be allowed for tax deductions.
All the above plans are considered with a point of view that when an individual retires and withdraws their investments, they will be in the lower-income group compared to the time they were in employment, which gives them tax benefits at a future date when they retire.
#2 - After-Tax Retirement Savings Account
An account funded with income after tax is a Roth account. Select this option for people who expect higher tax at retirement compared to the time of employment.
- Roth 401(k), 403(b), 457 Plans: Same as a tax-deferred option, an employer might also provide an after-tax investment option. According to these options, individuals will not benefit from contributing to these plans. Still, they will receive a tax-free distribution on withdrawal after five years or after the age 0f 59.5. Employer contribution will come under traditional plans, and a minimum distribution will be required for an individual over age 70.
- Roth Individual Retirement Arrangements: Roth IRA does not provide tax deductions, but qualified tax-free distributions are available.
Other Tax Advantage Saving Plans
College/education saving plans
- 529 plan: Withdrawals are tax-free, but contributions can be decided by the individual, whether tax-deferred or after-tax.
- Coverdell education saving account: contribution can be made depending on a tax-deferred or after-tax basis; available withdrawals are tax-free but should be used before the child of an individual turns 30.
Example
Let us take the example of AB Ltd, which employs around 1000 people. The company gives the employees the option of investment in retirement account, where each employee contributes a part of their monthly salary. In this way, each employee is able to reduce the monthly taxable income and pay less tax. On the other hand, a part of their salary is invested safely in the retirement account.
Importance
Some importance that can be attributed to this kind of financial benefit are given below. Let us study the same in details.
- Promotes Investments: Proper investment using tax-advantaged funds will not just provide benefits in terms of taxes but also promote investment strategies for individuals.
- Multiple Strategies: There are multiple strategies for tax advantage accounts available, depending on the individual's goals and financial condition. They can decide which is more suitable for them.
- Future Planning: Individual plans their investment for a future time like retirement, family, child education, healthcare, wealth planning, etc. Such accounts provide an overview and help to decide which strategy every individual should adopt.
- Reduce Tax Burden: These investments help reduce the tax burden with various strategies, from tax-deferred to after-tax investments. E.g., Government bonds.
- Good option for companies- The companies or businesses can offer different retirement plans that will allow its employees to contribute their pre-tax income. In this way valuable and useful talent is attracted and retained by companies.
- Beneficiary benefits – Beneficiaries who inherit property can continue to get tax benefit, thus, minimizing the burden of tax upon them when they inherit the funds.
- Fast growth – The money accumulated in investments into tax-advantaged accounts grow very fast since there is no deduction of taxes from the accounts, allowing the money to multiply very fast. Sometimes their contribution limits are also higher as compared to some regular investment accounts. This allows better savings.
- Diversification – The process allows diversification of the burden of tax and gives the investor better flexibility in fund management and during retirement.
Thus, the above are some benefits of the concept.
Tax-Advantaged Vs Tax-Deferred
Both the above are types of investment options using the benefits of tax savings. However, there are some differences between them as follows:
| Sr.No | Tax-Advantage | Tax-Deferred |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The tax advantage is a type of investment that will benefit an individual in terms of taxation through various investment options. | Tax-deferred is a type of investment, that will delay the taxation on your income for the future at the time of withdrawal. |
| 2 | There are two tax advantages: 1) Tax-deferred and 2) After-tax. | Tax-deferred focuses on various investment options, which delays taxation. |
| 3 | After-tax plans will provide tax-free withdrawal on a plan. | Eventually, the individual has to pay taxes on their income on withdrawal after a certain time limit. |
| 4 | Beneficial for All types of individuals, whether High-income groups or lower-income groups. | Beneficial for the High-income group by selecting the tax-deferred plan, the tax might be less on income compared to current earnings in case of retirement. |
- Tax planning is an important part of an investment since part of your income you pay to the government as taxes. Whether to choose from tax-deferred or after-tax investment depends completely on individuals' decision to pay taxes at the time of earning or at the time of withdrawals; However, tax-saving today is better, and the benefits of receiving tax-free withdrawals in the future at cost after-tax investment are very high because of investment size.
