Table Of Contents
What Is Tax Accounting?
Tax accounting refers to the methods and policies used for the preparation of tax returns and other statements needed for tax compliance and therefore, it provides frameworks and guidelines for arriving at a taxable profit.
Also, tax policies in each country differ with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles on various items. This variation leads to the generation of Deferred Tax assets and liabilities. Also, there are separate guidelines for VAT (Value Added Tax) accounting, transfer pricing, and cross border transactions, which all fall under tax accounting.
Tax Accounting Explained
Tax accounting is pivotal to any business or individual as it provides a framework to declare the correct income and pay appropriate taxes. In case of ambiguity, a tax professional should be consulted to avoid any miss in tax compliance as there are fines and penalties for tax defaulters. It also works for tax avoidance by selecting which method works best for each type of business or individual.
In this concept the main focus of the accounting system is on taxation rather than financial statements. Thus, it is the process of recording of transactions related to accounting for tax. The rules, policies and procedures followed in tax accounting course are stated in the Internal Revenue Code, which the companies should adhere to while preparing the returns.
Every individual and corporate should follow them, even though they may be exempted from tax payment. The process focusses on revenue earned, deductions, donations, gain or loss from investment, etc. It is a complex process, even though there may be usage of tax accounting software, where thorough analysis is done regarding when and where the fund is spent and whether it is taxable or not.
Types
The reason for doing Income Tax accounting is arriving at taxable profit and tax payable by making adjustments in the book profit arrived by accounting principles. All these working and adjustments form part of the Tax return, and these statements are kept for Tax audits. There are various components of accounting for taxation, some of which are discussed below –
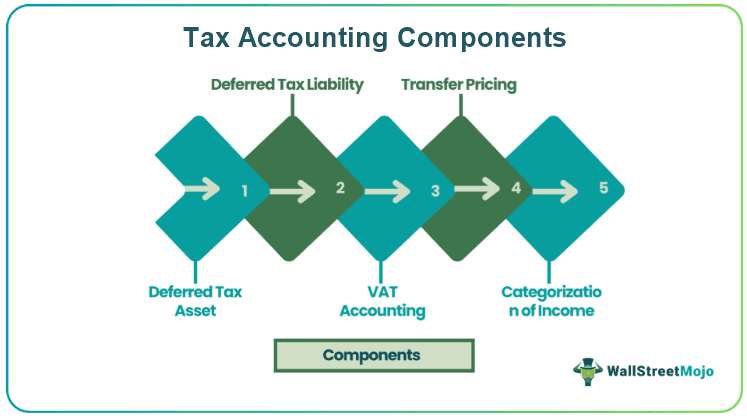
#1 - Deferred Tax asset
Is generated when there is a difference in book profit, and taxable profit arises due to a timing issue. There are expenses like provision for doubtful debts, which are considered for deduction in accounting in the current year. However, these are allowed for a deduction for taxation only when the amount is declared as bad debt, which can happen in the coming years.
In this case, the taxable profit will be higher compared to accounting profit, and the person or organization will pay more taxes this year, which. The extra amount paid as tax on incremental profit due to rejection of provision amount for deduction is considered as deferred tax, which will be realized in the coming years.
#2 - Deferred Tax liability
Deferred Tax Liability is generated when the person or organization has to pay fewer taxes in the current year due to the timing difference. For example – let's consider that an asset of $10,000 is being depreciated in accounting books under (SLM) straight-line method for 8 years – the depreciation each year will be $1,250 ($10,000/8).
However, if the tax rules state that assets have to be depreciated @20% (WDV) written down value method. The depreciation for taxation purpose in second year will be $1,600 (($10,000 – 2000 i.e. 20% for first-year) = $8,000*20% = $1,600)).
Here the organization will get an extra deduction of $350 ($1,600-$1,250) for taxation purposes. If we consider the tax rate to be 30%, the deferred tax liability here is $105 ($350*30%).
#3 - VAT Accounting
Most of the countries a Good & Service Tax (GST) or VAT (value-added tax), which forms part of almost all the invoices issued. Now, this should not be considered as expenses directly because the organizations get an Input Tax credit on the amount already paid. To claim those inputs, the tax authorities lay certain conditions regarding the format of invoice, name, and registration of the company, details of the second part, etc. and all these conditions have to be met by tax accounting team before claiming VAT/GST input credit.
#4 - Transfer Pricing
In today's world of globalization, many companies open their branches in various parts of the world. A policy monitors transfer pricing called an Arm's Length transaction Pricing, which advocates the fair-trade policy across the globe. In simple words, it says that a related part or person should not avail good or services at a lower cost than the price at which it has been sold to an unrelated third party.
Also, if an organization has set up an only offshore office where people are working, and no other business is being done in that country. As per the Transfer pricing policy, the organization has to pay a certain percentage (8-15%) of tax on the expenses incurred in operating the offshore office. Transfer pricing is one of the fast-paced and challenging components in today's world.
#5 - Categorisation of Income
Accounting considers all the receipts and payments for calculating the accounting profit. However, not all receipts are related to business, and the rate of tax differs depending on the type of receipt it is.
Job Description
The professionals completing the tax accounting course in this field is responsible for providing help and guidance to both individuals and corporates while filing their tax returns, with strict adherence to legal rules. They are required to collect forms from the clients and look for any credits that can be used to set off the expenses like funding for education and business. Some of the common responsibilities that they need to take are given below:
- Preparation of tax payments.
- Tracking of tax returns and also estimation of the same.
- Preparation of tax reports on a regular basis, be it quarterly or yearly.
- Continuous updated knowledge regarding the changes in any tax related rules and laws within the jurisdiction.
- They should be able to manage their time effectively and efficiently because of multiple tasks they need to handle.
- The are required to be very particular about meeting deadlines.
- These professionals should be able to organize and maintain records and reports related to tax payment of their clients and recommend procedures to manage tax payments efficiently.
Apart from the above, they should possess skills like computer literacy, knowledge regarding various accounting and taxation related tax accounting software that are commonly sued in the market, number crunching skills and attention to detail. A BSc degree in finance, accounts, taxation or related field is desirable. A certification as Certified Management Accountant (CMA) or Certified Public Accountant (CPA) will add to their demand.
Example
Let's consider below example of tax accounting for small business-
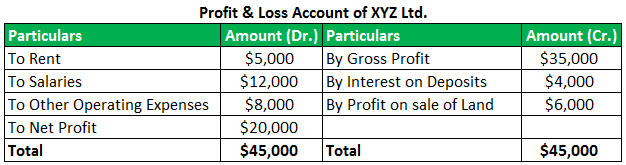
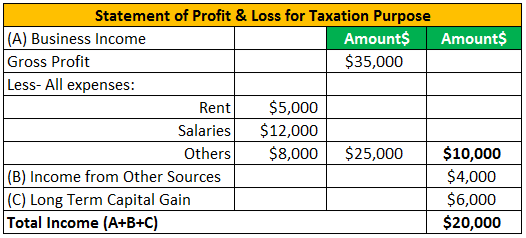
In table 1, the extract from accounting books is shown, and in the second table shows how tax accounting has to categorize the type of income as the Income-tax rates differ on types of income.
Career Path
In the field of tax accounting, the candidate can explore various opportunities.
They can plan to become Senior Tax Auditors who are deemed to be experts in the field of tax law. They have the ability to assess the financial records of the client to ensur that the rules are properly followed. They ensure there is no fraud or misstatement in the financial reports. They are required to possess a CPA certification or they may also have the certification related to Certified Internal Auditor(CIA) or Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA). They earn lucrative salaries based on their level of job.
These professionals can also become Forensic Accountants, who point out illegal activities like fraud, embezzlement of funds, etc. They primarily deal with tax payments and check every financial details of the business thoroughly. They need to provide legal testimony on public records. Along with Bachelor’s and Master’s degree in accounting and taxation,they are CPAs, and along with that they may also be Certified Forensic Accountants(CFA) or Certified in Financial Forensics (CFF). They earn quite a lucrative salary.
Advantages
Some common advantages of the concept of tax accounting for small business or big business are given below:
- Categorization of Income for application of correct tax rate;
- Statutory compliance adherence.
- Losses of current and previous years can be set off in future periods by filing Tax returns.
- Tax audit facilitation.
- Self-assessment and tax payments in a timely manner;
Disadvantages
Given below are some disadvantages of the process of corporate tax accounting.
- Needs extra time and resources for the work;
- Tax professionals charge dearly to organizations.
- There are changes in tax policies almost every year.
Important Points to Note
Every time there is a change in policies, tax rates, etc. the rganizations/individual must keep themselves updated, and accounting software should be amended accordingly.
Tax Accounting Vs Auditing
Both the fields are related to thorough verification and clarity in the accounting process. But there are some differences between them, as follows:
- The corporate tax accounting ensures that the process of tax filing and planning is correct, as per the rules and properly accounted for. But the latter deals with the process of verifying whether the accounting methods, entries and procedures followed are correct, transparent and ethical.
- The former makes the decision tax management, cash flow, reporting of taxable earnings, etc. But the latter looks into the books of accounts after the above work is done, to clarify whether they are free or any errors, discrepancies and loopholes or not.
- The former deals with recording and maintaining details of taxation process, but the latter deals with uncovering any intentional or unintentional mistakes that may affect the business negatively in future.
Thus, the above are some important differences between the two concepts.
