Table Of Contents
What Are T-Shaped Skills?
T-Shaped Skills refer to a symbolical framework describing an individual's in-depth skill set shaped as T. It aims at cultivating individuals possessing deep expertise related to a chosen field while allowing and maintaining a good grasp over interrelated domains.
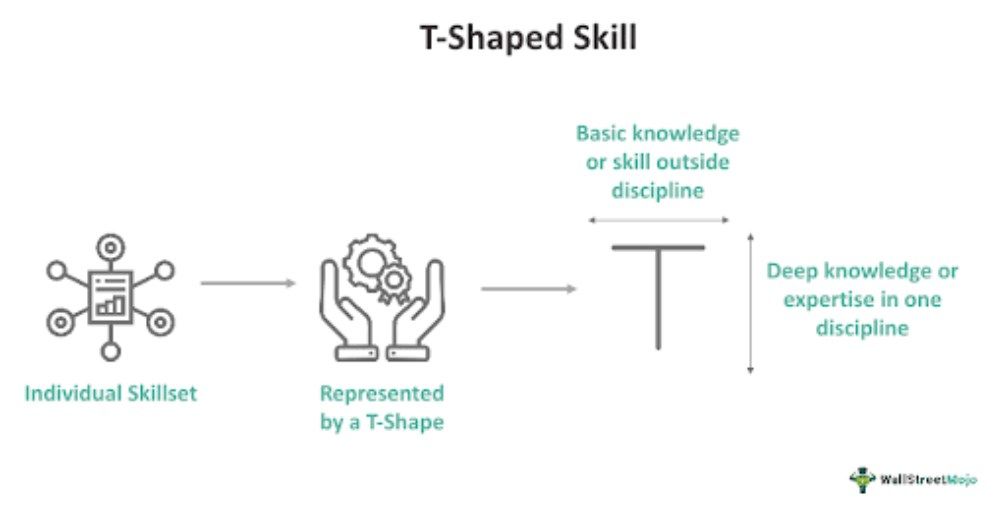
The vertical bar of T represents the deep skill set in one field, and its horizontal bar represents the less in-depth understanding of broad, diverse sectors. The balanced mix of skill sets in vertical and horizontal bars promotes adaptability, teamwork, and innovation. This concept emphasizes the importance of specialized knowledge and a diverse skill set.
Key Takeaways
- T-shaped skills encompass a metaphorical structure representing an individual's profound expertise shaped
- like a "T," aiming to nurture those with specialized depth in a chosen domain while fostering a solid understanding of interconnected fields.
- It can be developed by cross-training for breadth, exploring interests, deepening knowledge, involving managers, and cross-training in expertise-related sectors.
- Moreover, it combines profound expertise and broader comprehension; I-Shaped skills focus on specific sectors, and V-Shaped skills have moderate width.
- These have benefits like- improving communication, collaboration, flexibility, problem-solving, autonomy, fast learning, innovation, leadership, and a customer-centric approach.
T-Shaped Skills Explained
T-shaped skills refer to a combination of broad general knowledge (the horizontal bar of the "T") and deep expertise in a specific field (the vertical bar of the "T"). The concept was first introduced by the CEO of the design firm IDEO, Tim Brown, in 1991. Since then, it has spread across every spectrum of industry for innovation and collaboration. Therefore, the idea behind T-shaped skills is to encourage professionals to excel in their specialized fields and possess a certain level of familiarity with other areas.
It enables individuals to contribute significantly in their selected field. However, they are also made to collaborate with other departments and individuals from different areas during that period. As a result, the individual develops more profound knowledge in one field, making them experts (vertical bar of T). Plus, they also gain a good understanding of other departments in a broader sense to collaborate with them (horizontal bar of T) effectively.
They have been used in various fields needing leadership, interdisciplinary teamwork, communication, project management, and collaboration. These include healthcare, technology, education, and business.
Besides, the concept of T-shaped skills, often referred to as the T-shaped skills model, has gained significant traction in various industries. Moreover, versatility and adaptability align well with today's professional landscape's t-shaped skills and agile nature. Furthermore, the T-shaped skills assessment is a tool advocated by McKinsey and other organizations.
Hence, it plays a crucial role in evaluating an individual's proficiency in both specialized depth and cross-disciplinary breadth. Therefore, integrating T-shaped skills enhances collaborative efforts and fosters innovation and problem-solving across diverse domains.
In summary, these skills and talents make people versatile, successful, and effective in various disciplines by combining specialization in one area with a comprehensive understanding.
How To Develop?
Developing T-shaped skills requires a planned approach to improve both one's interdisciplinary skills and vertical expertise. Hence, the following steps are needed to create T-shaped skills:
- Cross-training for breadth: One must acquire skills in related processes by cross-training. It will help in skill set broadening outside of one's core expertise.
- Explore interests: One has to actively participate in sports meetups or hobbies exploration to discover newer fields of interest. It helps one to develop a broader range of skill sets.
- Deepen knowledge: An individual must put more effort into delving deeper into the skills required in the primary job. It enhances one's expertise in achieving T-shaped skills.
- Managerial involvement: Try to involve more with managers to imbibe the necessary skills as per the development plan of such specialized skills.
- Adjacent cross-training: A person must try to cross-train in sectors related to and closer to their expertise. As a result, their versatility grows at an individual level.
- Engineering career growth: Many engineers can quickly develop T-shaped skills. It will help them in their post-graduation career.
- Ethical skills and leadership: One should concentrate on learning and developing ethical culture, leadership, articulation of the firm's vision, and governance for cultivating the T-shaped skills.
Examples
Let us use a few examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
An international association of investment specialists, CFA Institute, has published market research that finds an innovative organizational approach for assisting financial institutions in creating and effectively implementing big data and artificial intelligence plans.
The article stated draws on significant CFA Institute field research to show how investment firms can place themselves on a path to effective AI and big data implementation. The study provides examples of this concept's success in transforming entire organizations by combining technology (data science) and investment activities to enhance investment procedures and results.
The article covers case studies from UOB Asset Management, NN Investment Partners, and Man Group asset managers. It provides a how-to menu for investment organizations looking to create their T-shaped teams.
Example #2
Imagine Alex, a software engineer with T-shaped skills. His vertical expertise lies in front-end web development. He's highly proficient in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, and he can easily create stunning and interactive user interfaces.
However, Alex's skills continue. The horizontal bar of his T-shaped skill model demonstrates his ability to collaborate across different domains. Moreover, he has a basic understanding of back-end development using technologies like Node.js and databases like MongoDB. While he may not be an expert in these areas, his familiarity allows him to communicate effectively with back-end developers, ensuring a smoother integration of front-end and back-end components.
Furthermore, Alex has developed excellent problem-solving skills. Therefore, this ability makes him a valuable team member during troubleshooting sessions, where his insights often lead to quicker problem resolution.
Alex's communication skills also shine through his willingness to participate in cross-functional discussions. He can converse with designers, product managers, and even marketing teams, understanding their perspectives and contributing his insights effectively.
Thus, Alex's T-shaped skill set showcases his depth of expertise in front-end development while highlighting his ability to collaborate, problem-solve, and communicate across different areas of software development. Hence, this multidimensional skill set makes him a well-rounded and adaptable contributor to his development team.
Benefits
It has become more and more crucial in the workplace for numerous reasons. Hence, the following are some benefits associated with having T-shaped talents in the workplace:
- Improves communication and collaboration: It helps individuals have broader knowledge about different fields. Moreover, it allows effective communication with people from diverse work backgrounds. As a result, the collaboration among these people increases tremendously.
- Increases flexibility: T-shaped talent increases the adaptability of individuals to dynamic circumstances. It leads them to take on different roles per the firm's needs and become versatile at the office.
- Improves problem-solving: It helps people to solve problems effectively and creatively.
- Removes overdependence between teams: It leads to the development of autonomy in teams leading to hassle-free coordination between various groups.
- Fast learning: It teaches the ability to learn anything faster. Hence, such individuals become valuable assets for fast-evolving industries.
- Increases innovation: Individuals having such skill sets develop a tendency for innovation and a cross-functional attitude. Thus, individuals put forth a variety of perspectives and ideas in the workplace.
- Leadership: It promotes leadership quality in such individuals ’t-shaped talents. Thus decision making enhances, and knowledge transfer also rapidly improves.
- Reduced Bottlenecks: It also eliminates most of the sources of bottlenecks through cross-disciplinary input. Thus, project flow increases and smoothens.
- Customer-Centric Approach: It directly impacts customer service through in-depth knowledge of all domains, including customer service.
T-Shaped Skills vs I-Shaped Skills vs V-Shaped Skills
Let us use the table below to etch out their difference:
| T-Shaped Skills | I-Shaped Skills | V-Shaped Skills |
|---|---|---|
| It comprises a mixture of in-depth expertise and a broader understanding. | Such a skill focuses on in-depth expertise for a single sector. | V-Shaped skill mixes strong vertical specialization having moderate width in attached areas. |
| These require vertical specialization blended with interdisciplinary collaboration. | Moreover, this skill requires an extreme skill level in a particular field. | Hence, it tries to reach a balance between cross-disciplinary knowledge and depth. |
| They teach teamwork and innovation across different fields. | Besides, this skill has limited ability to add to the specialized area from outside. | Wherein they need effective teamwork among specialists.. |
| However, it results in effective collaboration between different departments. | I-Shaped skill adapts lesser to roles needing diverse skills. | Such skill contains little versatility and has depth also. |
| This skill has problem-solving versatility. | Here, the model fits roles needing in-depth expertise in a single area. | Hence, it requires a higher potential to contribute across numerous domains. |
