While synthetic and forex trading can be two different strategies used by traders and investors in the financial markets, the significant distinctions between the two are outlined below:
Table Of Contents
What Is Synthetic Trading?
Synthetic trading refers to a method in which traders trade on synthetic financial instruments. These instruments are created by combining traditional financial instruments, such as options, futures, or swaps, in specific ways to replicate the performance of the underlying financial assets.
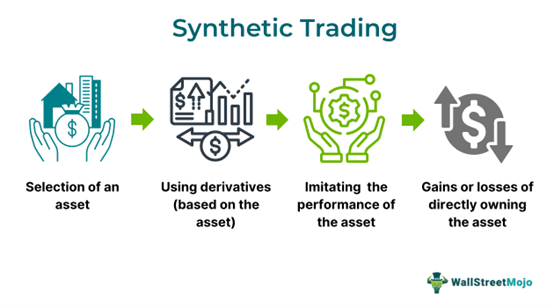
Synthetic financial instruments usage to derive returns similar to those of a particular asset without making a hefty capital investment is an effective trading strategy. Moreover, just like options trading, it successfully helps to mitigate risk. Hence, trading on synthetic assets is a more convenient alternative to traditional call-and-put options.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Key Takeaways
- Synthetic trading is buying and selling synthetic financial instruments that imitate the performance of the underlying financial assets.
- Synthetic instruments come with features that are modified more than those of the underlying assets, tailored to the particular strategic objectives of the traders, like a different duration, cash flow pattern, and risk profile.
- It helps the investors benefit from the financial assets without investing a hefty capital in them. Further, it ensures risk mitigation and offers greater flexibility, liquidity, and ease of trading.
Synthetic Trading In Futures And Options Explained
Synthetic trading in futures and options is a financial strategy to mitigate risk and maximize profits from buying and selling financial instruments that track the performance of the underlying financial assets. It doesn't require investors to invest in, buy, or sell the assets directly but ensures that the returns so made are equivalent to those offered by these assets. Such synthetic assets can mold their characteristics for risk-taking, duration, maturity, or cash flow patterns to suit the specific needs of the traders or investors.
In synthetic futures trading, the trader may choose a synthetic long futures position by using a combination of buying the call option and selling the put option, with the same strike price and the date to expiration or can create a synthetic short futures position by selling a call option and buying a put option. Synthetic trading in options allows traders to follow the performance of underlying assets or futures contracts. This is also done by combining call and put options to create synthetic positions that mimic owning or shorting the asset without trading it.
Examples
Synthetic trading is a win-win strategy for professional traders; let us understand its significance for investors through the following examples:
Example #1
Alex is an investor with a significant stock portfolio. He uses synthetic trading strategies to hedge against a potential drop in stock prices. Alex created a synthetic short position by buying put options on his stock holdings and selling call options with the same strike price and expiration date. This strategy imitates the profit potential of shorting the stock, helping protect against declines in stock value.
In this method, Alex safeguards his portfolio against possible losses without selling his stocks. This strategy provides an effective way to manage risk and balance the investment value in a declining market.
Example #2
Umoja, a protocol focused on smart money investments, joined hands with Merlin Chain, a prominent Bitcoin Layer-2 network, to introduce USDb, the first high-yield synthetic dollar based on Bitcoin. Unlike traditional stablecoins that rely on collateral or algorithms to maintain a U.S. dollar peg, USDb uses transparent, on-chain trading strategies to maintain its value, offering a self-sustaining mechanism.
This collaboration would improve the accessibility of sophisticated financial tools by combining Umoja's innovative Synths with Merlin Chain's infrastructure. Umoja's Synths enable retail investors to engage in advanced trading strategies especially reserved for financial institutions, further aiding them in wealth creation.
Umoja's Founder, Robby Greenfield, mentioned that partnering with Merlin Chain is a strategic decision signifying the latter's decentralized nature and ability to attract a vibrant community. He believes that the most adopted form of money will be decentralized, accessible, low-risk, and high-yielding, qualities that align with Bitcoin's principles. Hence, this partnership aims to collaborate Bitcoin's security with DeFi's innovative potential to transform the financial scenario.
For professional-grade stock and crypto charts, we recommend TradingView – one of the most trusted platforms among traders.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Advantages
- Synthetic trading facilitates traders' reaping similar returns to those of their target assets.
- Also, these instruments are packaged with enhanced characteristics like duration, maturity, risk-taking, or cash flow patterns. Thus, these assets offer greater flexibility to investors.
- Moreover, synthetics require low capital investment. Hence, traders don't need to worry about the huge funds required to buy the financial assets that these synthetics mimic.
- Further, it allows for a tailored approach, where synthetic assets are available in the form of options, swaps, futures, and other derivatives designed to cater to the specific trading purpose and strategy of the investors.
- These instruments ensure risk management and mitigation in a volatile market scenario, just like any other derivatives, options, or futures contract.
- It is a more convenient and effective strategy than call-and-put options trading.
- It facilitates retail investors' benefit from indirect investing or trading in markets that are otherwise restricted to institutional investors or other prominent traders.
- Further, these assets have greater liquidity than the other financial instruments due to the ability to switch positions without any significant loss.
Disadvantages
- This trading strategy is vulnerable to the rules and regulations of different jurisdictions, necessitating greater legal and compliance knowledge.
- Although serving as a risk mitigation strategy, synthetics are also exposed to market risk up to a certain level, such as price change in case of sudden market fluctuation.
- Trading such assets involves margin requirements and leverage buying, which increases the risk of overexposure.
- The synthetic long position comprises an extreme loss or profit potential, making it a risky affair for traders.
- Synthetic trading is not suggested for beginners and novice traders since it requires a complete understanding of the complex options and futures strategies.
- However, some of these assets, like synthetic options, need more liquidity.
- However, this strategy may turn out to be more expensive than normal asset trading.
- Another critical challenge is the selection of a reliable synthetic trading broker since not every broker is licensed.
Synthetic Trading vs Forex Trading
| Basis | Synthetic Trading | Forex Trading |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Definition | It is a trading strategy that allows investors to exchange financial instruments that track the returns of other assets but offer modified characteristics in terms of cash flow pattern, risk, and maturity. | It is an approach where traders engage in trading currency pairs to book profits on exchange rate differences in the foreign exchange market. |
| 2. Underlying Asset | Indices and other financial instruments. | Currency pairs in the foreign exchange market. |
| 3. Transparency | Less | More |
| 4. Regulatory Risk | Regulatory Risk Holds higher regulatory risk since synthetic trading brokers are usually not regulated. | It involves less regulatory risk due to the need for licensing and regulatory compliance of the forex brokers by regulatory authorities like the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). |
| 5. Market Hours | Market Hours Markets for synthetic indices trading are usually open 24x7 | The forex market is open from Monday to Friday during specific trading hours. |
| 6. Instrument’s Volatility | Instrument's Volatility The volatility of these instruments depends upon their structure. | Forex assets are more volatile and vulnerable to international market fluctuations. |
| 7. Suitable For | Retail investors | Both retail and institutional investors |