Table of Contents
What Are Sustainability-Linked Bonds (SLBs)?
Sustainability-linked bonds, or SLBs, are versatile financial instruments that can provide support to the overall sustainability strategy of the issuers. These bonds incentivize issuers’ achievement of externally verified and predetermined environmental, social, and governance (ESG) objectives via sustainability performance targets (SPTs) and key performance indicators (KPIs).
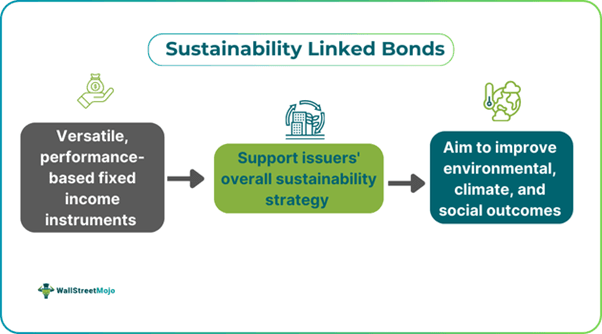
SLBs enable a wider range of companies to take part in sustainable debt markets, as organizations can issue such securities even if they fail to identify adequate, sustainable, eligible assets. Although these bonds emerged via private-sector issuance in 2019, now their use is common in both public and private sectors. Their key objective is to enhance environmental and climate outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Sustainability-linked bonds are debt instruments with structural characteristics that are subject to adjustment based on the predetermined sustainability goals’ fulfilment.
- It incentivizes issuers’ fulfillment of prespecified ESG goals.
- A key difference between green bonds and SLBs is that the companies cannot utilize the funds acquired by issuing the latter for financing general corporate activities.
- There are multiple advantages of SLBs. For instance, they can help in funding any type of corporate activity.
- Moreover, they help organizations from even less green nations to establish ESG credentials.
- A disadvantage of SLBs is that they are susceptible to greenwashing.
Sustainability-Linked Bonds Explained
Sustainability-linked bonds refer to debt securities that have structural and financial features linked with predetermined ESG or sustainability goals. They aim to improve further the vital role that debt markets have the potential to play in encouraging and funding organizations contributing to sustainability. These bonds can be especially helpful to the industry in which sustainability is difficult, for example, the shipping industry.
These bonds offer issuers successfully implementing ESG or sustainability principles lower interest rates. However, if issuers fail to meet their sustainability goals, they have to pay a penalty in the form of higher interest to the investors. Thus, these performance-based financial instruments allow the issuing companies to commit to future enhancements concerning sustainability outcomes explicitly while taking advantage of a discounted rate of interest.
Instead of allowing issuers to utilize the bond proceeds for a particular initiative, SLBs incentivize the issuers to improve their ESG standards across the business. The companies set KPIs that help in measuring the performance toward the objectives. Moreover, almost all the SLBs provision a possible coupon step-up in case the fulfillment of the objectives does not happen.
Nevertheless, since the companies are the ones determining the key performance indicators, ensuring ambitious and consistent results can be difficult, and the step-ups might not happen even in case the company seemingly failed to achieve the ESG targets.
Examples
Let us look at a few sustainability-linked bonds examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Suppose ABC is a development bank in the United States. The company issued sustainability-linked bonds to raise funds to fulfill KPI targets related to ESG. It allocated the major portion of the process from the issuance to funding multiple renewable energy and affordable housing projects.
Moreover, it funded woman-led projects and offered different financial products to individuals belonging to the low-income group. It utilized the remaining amount to meet the expenses related to different corporate activities.
Example #2
Per a report published on September 24, 2024, the International Finance Corporation or IFC, announced that it would invest in a sustainability-linked bond issued by one of Thailand’s leading retail property developers, the Central Pattana Public Company. The purpose of the investment is to give the green transition a boost in Thailand. The World Bank Group member disclosed that its investment would be worth roughly $100 million.
The property developer would utilize the money raised to fund initiatives concerning the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and fulfill its set green building targets.
Benefits
The benefits offered by sustainability-linked bonds are as follows:
- The funds raised by companies through the issuance of SLBs can help finance any kind of corporate activity.
- These bonds are more diverse and inclusive than social or green bonds as they enable organizations to establish their ESG credentials from less green countries or sectors.
- These bonds make issuers’ commitment measurable to the investors.
- SLBs help issuers express their near-term and medium-term priorities concerning sustainability.
Drawbacks
The drawbacks associated with sustainability-linked bonds are as follows:
- Failure to meet the predetermined KPIs can damage the issuers’ reputation. Moreover, companies fail to get the benefits of achieving the target and end up incurring higher interest costs. Note that failure to meet the targets can also negatively impact an issuer’s share price.
- Compared to the majority of the ESG-labeled bonds, SLBs require more close monitoring for possible greenwashing. Note that greenwashing is a practice that involves issuers misleading investors regarding their commitments toward environmental improvement.
Sustainability-Linked Bonds vs. Green Bonds
Individuals new to finance often find the concepts of SLBs and green bonds confusing. They can eliminate their doubts and develop a clear understanding by knowing the following key differences between the financial instruments.
| Sustainability-Linked Bonds | Green Bonds |
|---|---|
| Issuers can use the funds raised from issuing SLBs to meet the expenses related to any corporate activity. | The proceeds from the issuance of green bonds are for sustainable purposes, like environment-friendly projects only. |
| There is no mandate related to green expenditure allocations. | Green bonds mandate significant green expenditure allocations. |
| These bonds are accessible to more issuers than green bonds. | Such financial instruments are less accessible. |
