Table Of Contents
What Is Supply Chain Transparency?
Supply chain transparency refers to a holistic approach of having complete knowledge of the suppliers at every stage of its logistics process, from raw material acquisition to the manufacturing and distribution of finished products. It even involves making such real-time information available to all external and internal stakeholders.
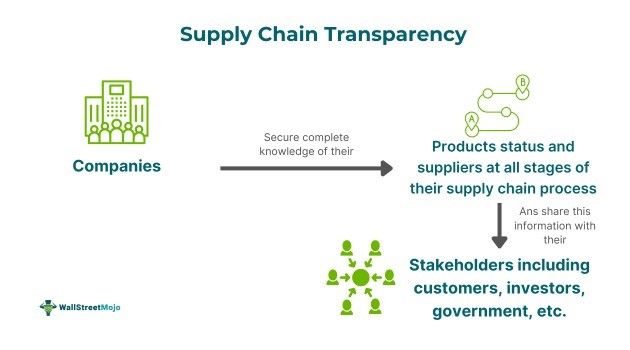
A transparent supply chain is essential for keeping the trust of the customers, investors, and government. Such a practice helps the company adhere to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) compliance regulations. Also, it aids businesses in managing or mitigating risk at every level of their supply chain process.
Key Takeaways
- l Supply chain transparency is the practice of possessing and disclosing (to the stakeholders) holistic information on the product status and suppliers involved at every step of the logistics process.
- l It starts from purchasing or extracting raw materials to distributing or selling finished goods.
- l With the rise in globalization and the need for sustainable business practices, external stakeholders like investors, business associates, government, and customers demand greater supply chain transparency.
- l Therefore, firms use advanced technology like blockchain, big analytics data, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Supply Chain Transparency Explained
Supply chain transparency refers to the scope to which a company discloses the suppliers' information at every step of the logistics process. The need to maintain a transparent supply chain has become a priority for business entities due to globalization and the increasing demand of stakeholders to maintain honesty and trust in all their processes. Sometimes, the blind spots or hidden facts make the customers, investors, associates, workers, and other stakeholders suspicious of the company's actions. At the same time, some suppliers in the value chain may indulge in unethical practices like harming the environment, ecosystem, planet, or human rights.
For instance, the California Supply Chain Transparency Act is an initiative to discourage inhuman practices like human trafficking and slavery in the state. As noticed, companies indirectly support such crimes by associating with the supply partners who engage in these malpractices to procure labor for their businesses. Therefore, the California Supply Chain Transparency Act mandates that retailers and manufacturers, disclose their efforts to discourage these practices from their supply chain.
However, achieving openness in the supply chain system is a formidable mission due to various reasons. Since the supply chain is an extensive process involving different aspects, it is difficult to decide where to start. It is not enough for a company to solely adopt the best practices for maintaining integrity and transparency in its supply chains; it is equally essential to convince the logistic partners, like suppliers, vendors, and distributors, to maintain the same level of honesty. Further, since the benefits of ensuring transparency in the logistics system are not materially evident immediately, it is quite strenuous to get the approval of the senior management, board of directors, and other top-level executives to contribute financial and human resources, time and efforts towards such practices.
How to Achieve?
The transparency of the supply chain is only possible through the tracing and monitoring of real-time data for accurate visibility. Given below are some relevant steps towards maintaining a transparent supply chain:
- l Mapping the Supply Chain: The foremost step is to document, record, and have a close look at the flow of material, finished goods, money, and information from the procurement of raw materials to the distribution of goods.
- l Collaborating With Supply Partners: Transparency can only be achieved by having complete information from the suppliers. Thus, it is essential to collaborate and coordinate with these business partners for a constant flow of information.
- l Life Cycle Assessments (LCAs): Businesses should adopt the LCAs to quantify the environmental impact of their actions, such as using natural resources and energy, and the extent of harm caused to the environment during the overall supply chain process.
- l Conducting Due Diligence: It is necessary to gauge the impact of business practices and supply chain processes on human rights, the environment, and nature to mitigate the risk of unethical or irresponsible corporate behavior.
- l Complying With Standards: The companies also need to standardize their custody mechanism right from the raw material purchase to the sales of finished goods to ensure transparency with the government regulatory bodies. It involves acquiring certificates from recognized certified organizations like REDcert2 and ISCC PLUS.
- l Leveraging Advanced Technology: Businesses can use software and tools like blockchain to ensure utmost transparency in their procurement and distribution process.
- l Training and Encouraging Suppliers and Workers: A company's supply chain is made up of its supply partners and employees who require proper training and motivation to maintain transparency in all their endeavors.
Examples
A transparent supply chain is an integral part of any business, as evident through the following instances:
Example #1
Suppose PQR Co. Ltd. is an essential oils manufacturing and export company. While the company labels itself 100% sustainable and eco-friendly in front of its external stakeholders, it needs to disclose the proper information about the packaging material it procures from the suppliers. Notably, 60% of its products are packaged in recyclable glass bottles, and the company proudly discloses the relevant suppliers' list in this context to its stakeholders, 40% of the packaging material authenticity is still suspicious since the company does not disclose its suppliers. Thus, the customers and investors raise their voices against such practices and question the company's compliance with supply chain transparency.
Example #2
The investors are compelling Inditex, Zara's parent company, to compete with the transparency levels of competitors like H&M and Primark by disclosing its complete suppliers' list. While Inditex reports the number of suppliers in 12 prominent countries annually, it hides specific factory details, unlike other leading brands. This lack of transparency has led to the company's criticism, with Dutch asset manager MN and other investors demanding a comprehensive suppliers list to improve due diligence and confirm ethical practices.
Although Inditex has associated with IndustriALL for internal disclosures, there are demands for broader public transparency. Further, Inditex asserts that its traceability system upholds high standards but has not agreed to publish detailed supplier information. However, the investors emphasize that greater disclosure is essential for evaluating supply chain resilience and adherence to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria.
Source - https://www.japantimes.co.jp/business/2024/03/12/companies/investors-zara-inditex-supply-chain/
Importance
Companies strive to ensure a transparent supply chain with the increasing demand of stakeholders to make them familiar with all information. Some of the reasons for which this process is significant to the businesses are:
- l Regulatory Compliance: Companies have to follow government regulations to protect the planet, human rights, the environment, and workers.
- l Time and Cost Saving: When the real-time supply chain data flows and is shared at every level with the stakeholders, it limits the supply chain wastage and ensures operational efficiency.
- l Competitive Advantage: Such a practice helps companies stand out from their competitors who miss out on the transparency aspect of the supply chain process.
- l Increased Brand Reputation, Loyalty, and Trust: Moreover, companies that have an honest supply chain can build trust, loyalty, and reputation among their customers, investors, and other stakeholders.
- l Better Risk Management: It ensures that the company effectively mitigates risk by efficiently identifying and rectifying the bottlenecks and disruptions in the supply chain.
- l Establishes Accountability: Such a practice helps firms make their suppliers accountable for their actions due to broader supply chain visibility.
- l Industry-Wide Best Practices: Such a process helps the business to develop best practices that the whole industry can adopt.
- l Strengthens Vendor Relations: The companies can improve their vendor relationships by maintaining an environment of open communication.
Supply Chain Transparency vs Supply Chain Visibility vs Supply Chain Traceability
Supply chain transparency and traceability are critical approaches to achieving visibility. However, these three processes differ in the following ways:
| Basis | Supply Chain Transparency | Supply Chain Visibility | Supply Chain Traceability | |||
| Definition | It emphasizes the complete disclosure of information about various logistics stages and the involved parties with all stakeholders, such as consumers, investors, regulators, and business associates. | It is a company's efficiency to accurately trace, disclose, and map the suppliers, products, processes, and materials at every supply chain step. | The business can collect data, identify risks, and monitor the status of the products or services at each stage of the logistics process. | |||
| Purpose | Making all the suppliers' information available to the stakeholders (both internal and external) | Ensuring operational efficiency during the movement of goods from supplier to manufacturer to distributor to customers | Monitoring product quality, safety protocols, and authenticity at every stage of its supply chain process. | |||
| Objective | Comply with regulatory standards, adopt ethical practices, and secure stakeholders' trust | Observing and mapping the flow of goods or services across the overall supply chain journey | Using various software and tools to keep a close look on the flow of goods right from its origin to final destination. | |||
| Driven By | Stakeholders' demand for using ethical and sustainable products and the government's requirements for complying with the ESG and CSR regulations | Need for maintaining and tracking real-time information about the product's condition and status | Quality and safety requirements in the supply chain process. | |||
| Interdependence | It facilitates attaining visibility in the supply chain. | Traceability, transparency, and mapping are vital components of supply chain visibility. | It is crucial for ensuring transparency and visibility in the supply chain. | |||
| Example | An FMCG company discloses its procurement details, including the list of suppliers that provide raw materials for manufacturing cereals and snacks. | An automobile company closely follows the procurement of the auto parts, their assembly process, quality check status, warehousing, and distribution process. | A light bulb manufacturing company discovers a defective batch. It traces it in reverse order to find out the reasons for the defect by reviewing the process and the quality of the filament and other raw materials procured from the suppliers. |
