Table Of Contents
What Is Strategic Business Unit (SBU)?
A strategic business unit is a fully functional, independently operational setup of a particular business. These units are active and have their vision, growth, and direction. The main objective of such a unit is to maximize profits and mainly focus on offering a particular product targeting a market segment.
They are typically small business entities within a large organization that deals with multiple products and services. Therefore the units operate like profit centers with separate business divisions with a set product line or specific goods for a particular location or target audience.
Key Takeaways
- Strategic business units (SBUs) are small independent divisions of a main business dealing in a particular product with its independent objectives, profit, and customer base.
- These are often observed among global conglomerates with multiple layered business models and various product lines and services worldwide.
- There are four types of SBUs - cash cows, dogs, stars, and question marks- each categorized depending on growth, performance, and market share.
- Each SBU doesn't need to perform well, and sometimes setting up an SBU in the wrong industry can backfire with losses.
Strategic Business Unit Explained
Strategic business units (SBU) are separate divisions of a parent company that operates in different industries and market sectors, offering several product lines or services. SBUs are formed within enterprises that usually have huge businesses worldwide providing different goods and services.
A strategic business unit operates on three levels - the headquarter or the parent company always remains at the top, and the SBUs in the middle and below are clustered accordingly. An SBU is supposed to submit its business's performance, results, growth, and revenue from time to time to the parent company.
A strategic business unit plan is essential here because it separates the product lines of a common parent company. In this way, each SBU is known individually, creating more market capitalization than a company with no business units. When a company decides to launch a new product in a different market, the SBU helps in market analysis, research and development, pricing, and creating market awareness and recognition.
The cash flow investment requirement and major decision-making may get sanctioned from the top level. Besides that, each SBU operates freely in the market with its competitors, offers, business strategies, mission, and objectives. Each SBU operates freely in the market with its competitors. In sectors like healthcare, many organizations use Healthcare BPO Solutions to support these independent operations and improve efficiency. Each strategic business unit level has its challenges. It is a complex process for any enterprise to set up an SBU successfully with long-term survival and growth prospects. One effective approach to align efforts and measure progress within each unit is setting OKRs (Objectives and Key Results), which helps ensure clarity and strategic focus across the organization.
Characteristics
The characteristics of a strategic business unit are -
- It is designed to target a specific customer base present in the market.
- Since these business units are independently regulated and operational, they have their market competitors present.
- The SBUs mostly have their shares listed on the stock exchange, separate from their parent companies.
- The customer may or may not know the parent company of an SBU and identify it as a separate entity.
- The SBUs have a manager responsible for all the unit's planning, profitability, and performance.
- A company can establish many SBUs, each with its own planning. Additionally, they shall report the overall performance to the parent company.
Types
There are four types of strategic business units –
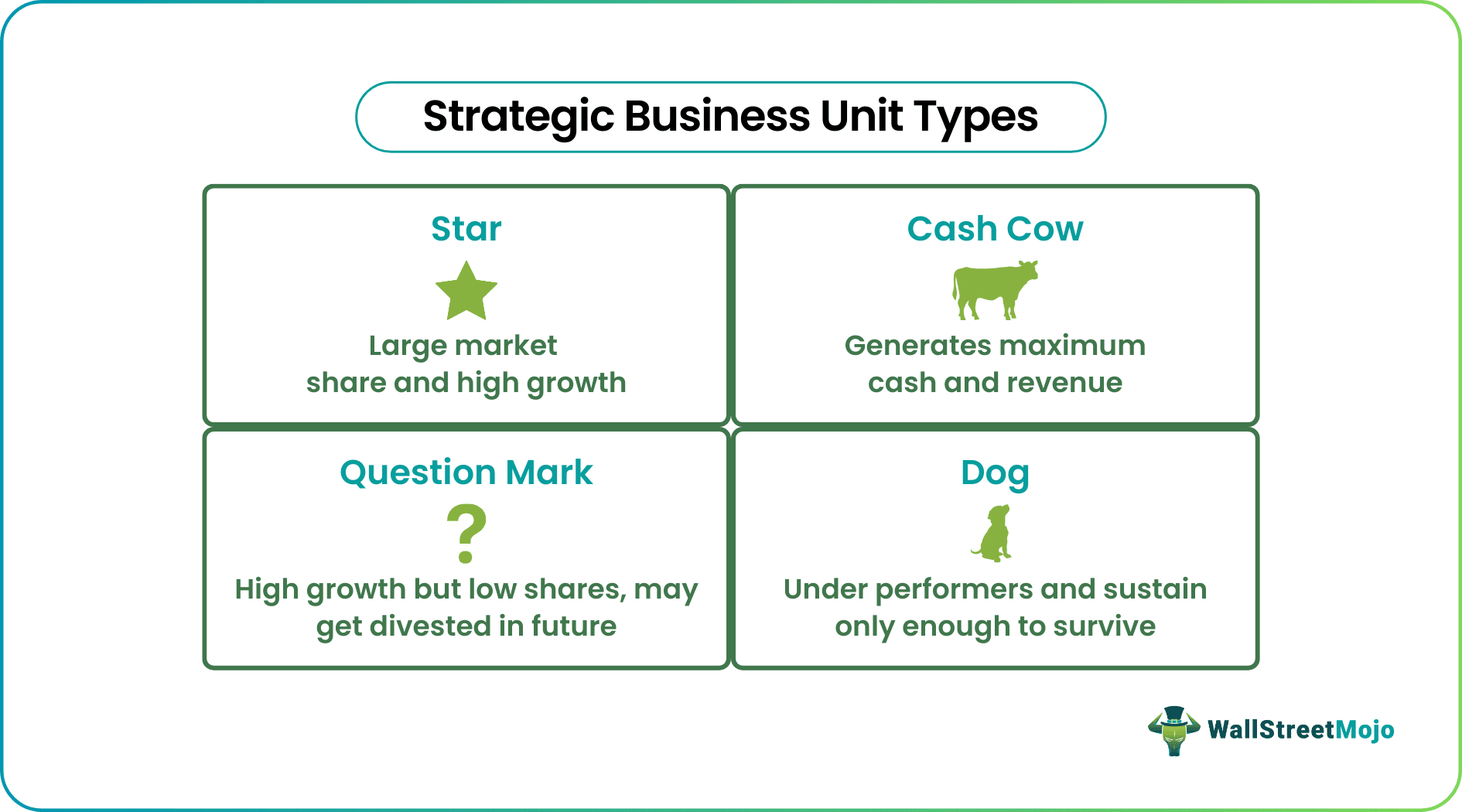
#1 - Star
Star SBUs represent business divisions that reap high growth and market share of the business in its particular sector. Star SBUs are units with a monopoly over a market or big industry giants. They demand high monetary investment and constant cash flow maintain the strategic business unit structure.
#2 - Cash Cows
A cash cow is the SBU that generates the maximum cash or revenue for the business, dominates the market, yet has slow growth. Sometimes, one type of SBU turns into another type of SBU. So if a high-growth market settles down, the star SBU becomes a cash cow.
#3 - Question Marks
The market experts define some units as question marks when a quintessential question arises with such SBUs that are high growth functioning with low shares. Such units demand high monetary investment that is diverted from cash cows. Therefore, corporations always need help understanding whether to invest in or remove such units.
#4 - Dogs
Dogs are the SBUs that businesses have very low hope of growing in the future, and they can never become star SBU. They are underachievers with low market shares and diminishing growth. Such business units only generate enough cash to survive and keep themselves afloat. As a result, these units receive less attention from corporations.
Examples
Check out these examples to get a better idea:
Example #1
Martin owns a tech company that manufactures laptops and smartphones. He built the business from scratch and has been running it for nine years. Martin's company has a good history on the stock exchange. Now Martin, looking at the market, has come up with an idea in the automobile industry, manufacturing cars. He invested much money and set up a completely independent strategic business unit. Now both companies are listed on the stock market.
From his SBU, Martin was able to manufacture affordable cars for people with low or mid-level households. This SBU will report to Martin's parent company and the tech company. Now both are SBUs, but in this way, he connected with people needing an affordable car and simultaneously has another business set up in the tech industry.
Thus, he expanded his business and reaped more profits and revenue. In the future, even if the tech market is problematic and people are more interested in investing in the automobile sector, they can buy Martin's motor company shares or vice versa. For Martin, each company operates in a different sector with its product and has its market competitors. Still, in the real world, it is a much more complex and time-consuming process and structure demanding critical planning and execution.
Example #2
Another very good strategic business unit example is the case of Disney. The entertainment company has five SBUs with businesses like studio entertainment, the media network, consumer products, parks and resorts, and the interactive media business. Among all five, the parks, resorts, and consumer products contribute with a unique design and manufacturing structure contributing to the value chain.
The cost-sharing of all five business units is closely linked and takes help from each other for innovation, publicity, and work operations. For example, Walt Disney incorporated Marvel in their theme parks, offering a novelty to its customers.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Here are the main advantages and disadvantages of SBUs:
Advantages
- The profitability is more likely to increase as an SBU directly targets a separate market section and customer base.
- Creating SBUs helps companies stay, survive and succeed in the market for a long.
- It simplifies the bookkeeping process for big corporations.
- Decision-making becomes easy as not every permission goes to the central authority, and each unit operates independently.
- Offers exhaustive research and development for targeted markets.
Disadvantages
- Setting up SBUs is a complex process as it separately demands its vision, goals, messaging, promotion, and every other aspect.
- With SBUs, a high level of competition sometimes backfires on the parent company.
- The whole process of strategic business units is expensive and increases the total operational cost for the corporations with staff, hiring, office setups, and a complete hierarchy.
- Most corporations with SBUs need more communication induced by divisional workplaces and head offices.
- There are different types of SBUs, and therefore an unrealized competition among SBUs of the same parent company gets sparked with dirty politics and irrelevant comparison.

