Table Of Contents
Stockbroker Meaning
A stockbroker is an individual or company qualified enough to trade securities in the financial markets on behalf of financial institutions, individual and institutional investors, and organizations. They can work either independently as a professional trader or broker-dealer or associate with a brokerage firm.
Trading of stocks and securities in stock exchanges is full of risks. Furthermore, these marketplaces do not allow investors to trade directly. With their expertise and knowledge of financial markets, stockbrokers advise investors on making the right investment decisions. They implement investors' stock-related decisions for purchasing or selling securities. In return, they receive a commission or fee from their clients that could be a flat figure or a percentage of the securities sale or purchase price.
Table of contents
- Stockbroker Meaning
- Stockbrokers are independent professional traders or brokerage firms buying or selling securities on behalf of investors. In return, they receive a flat fee or percentage of the asset sale or purchase price as commission.
- Being a registered representative is a provision under the Security and Exchange Commission (SEC) guidelines or the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA).
- Aspiring candidates must be finance or business administration graduates. In addition, they must pass the Series 7 and the SIE examinations to gain a license to work as general securities representatives.
- There are three categories of broker-dealers based on investors' trading requirements – full-service, discount service, and no advice.
Responsibility Of Stockbroker Job
Even though investors can purchase shares directly from their issuer, they cannot buy or sell securities directly in a stock exchange. Hence, they need to connect with individual brokers or broker-dealers, or stockbroker companies to trade stocks on their behalf. In addition to executing trades, they are responsible for providing investment management and financial advisory services. However, being a member of a stock exchange or stockbroking firm makes one eligible to trade directly on exchanges.
Being a broker-dealer is a provision under the U.S. Security and Exchange Commission (SEC) guidelines or the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA). Besides in-person or as a firm, there are now online brokers that can handle securities trading automatically on behalf of retail investors and institutional investors and charge much lower fees.
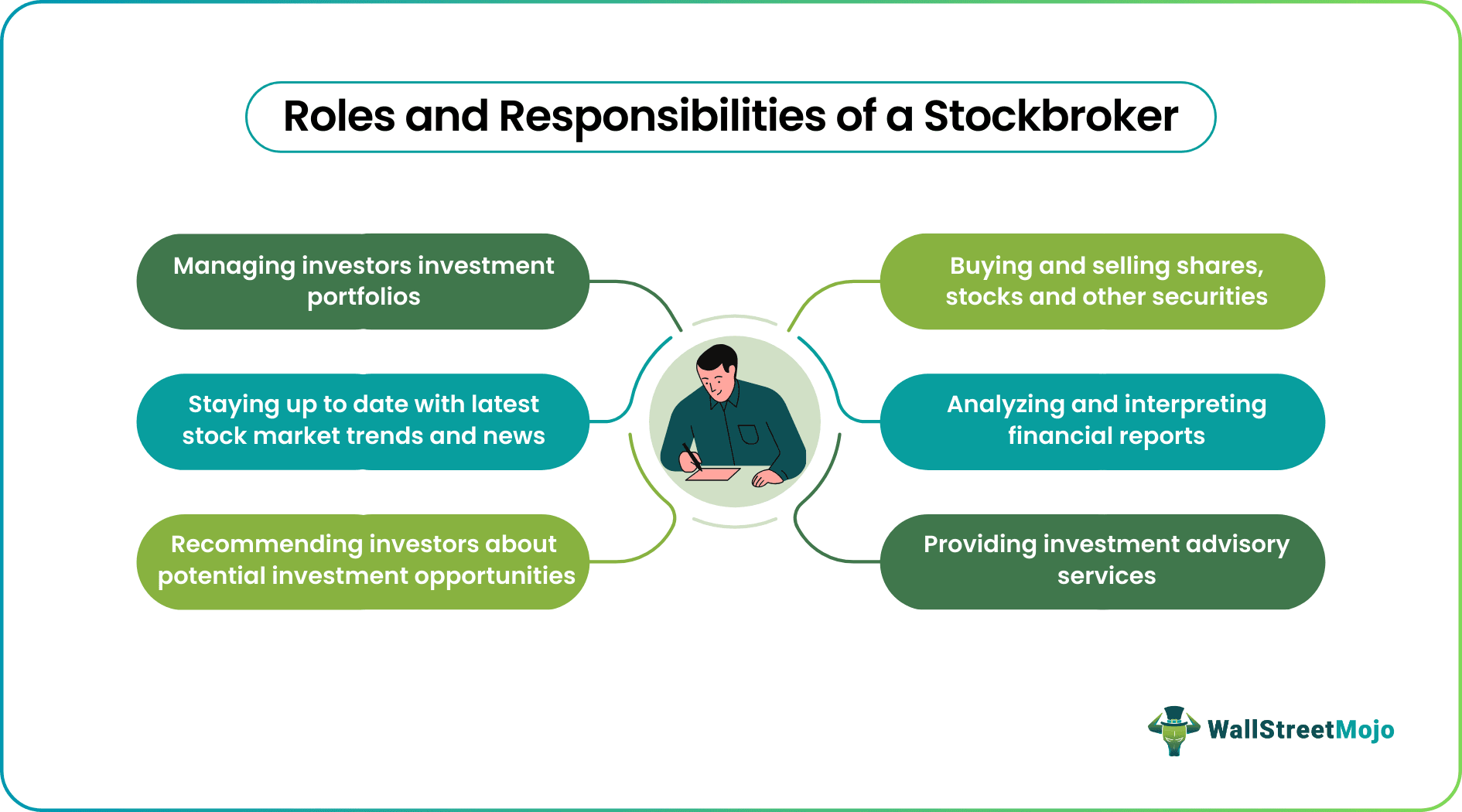
Becoming a broker-dealer involves a great deal of effort, from acquiring relevant educational qualifications to obtaining the required license. Let us look at their responsibilities in quick points:
- Buying and selling shares, stocks, and other securities on behalf of investors
- Analyzing and interpreting financial reports
- Advising clients on investment strategies based on market conditions
- Managing the investment portfolio of investors
- Following the latest trends and news in the stock market
- Recommending clients about potential investment opportunities
Often referred to as a registered representative or investment advisor, a stockbroker can open a separate trading account to assist firms in purchasing shares.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Example
An investor must first open a trading account to participate in stock market trading. Registered representatives have complete access to this account and take care of it.
For example, Karen wants to buy stocks of Apple Inc. from NASDAQ. As she cannot directly trade it from the exchange, she connects with John, the stockbroker. Karen discusses her budget with John and clears the rate at which she wants to buy and sell those stocks. It helps her investment advisor to purchase shares of the concerned company keeping in mind the budget.
When stock prices go up, John sells it to Rob on behalf of Karen, reaping profits for her client. This way, a broker-dealer also acts as a link between a buyer and seller. For his services, John charged a commission from Karen.
Types Of Stockbroker
Every investor has its own set of trading requirements. On top of that, investing in shares, stocks, and other securities is complicated and full of risks. Therefore, there are three types of stockbrokers to cater to the trading needs of investors and help them earn profits:
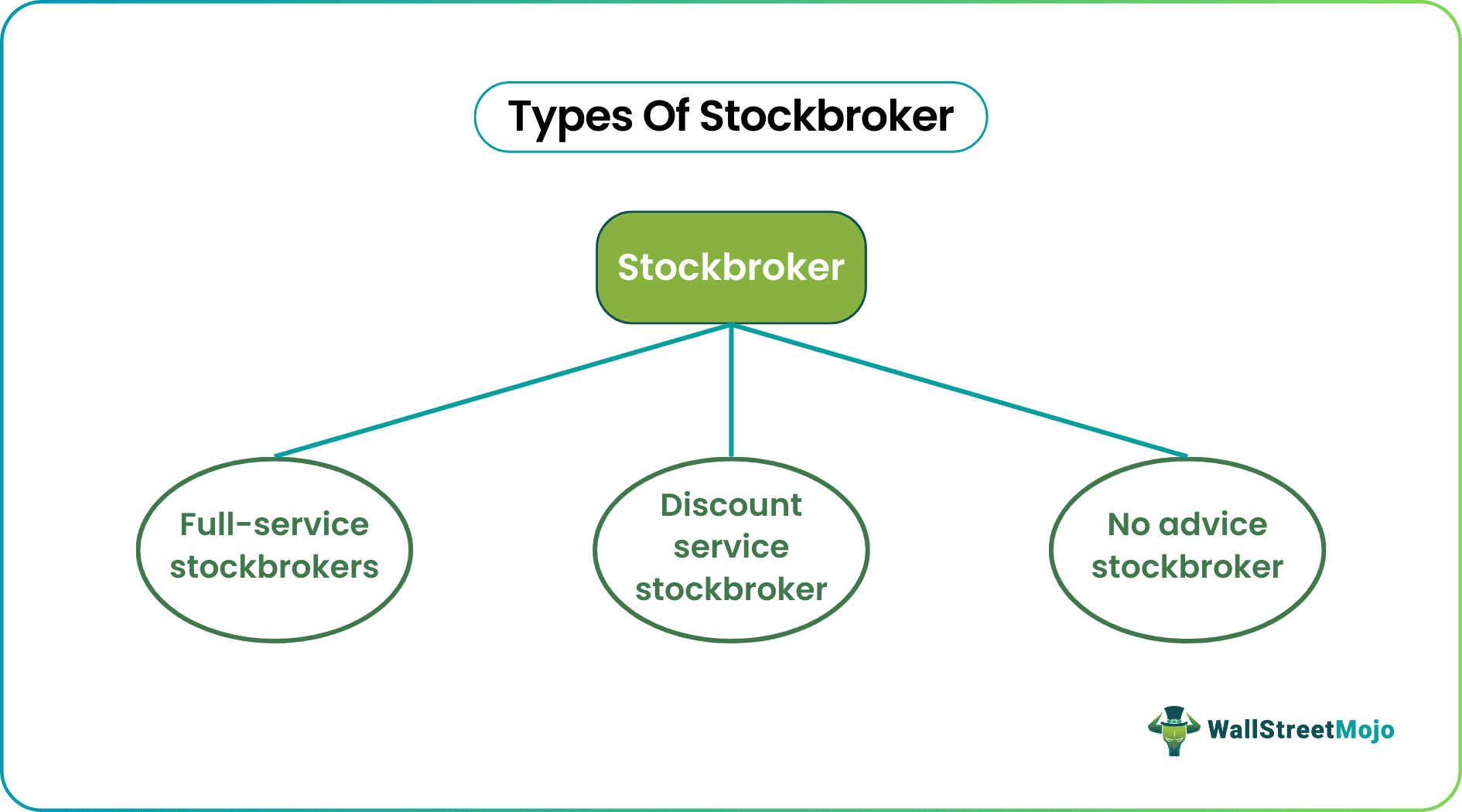
#1 - Full-Service Stockbrokers
These brokers may or may not be affiliated with brokerage firms. They advise clients on how to make appropriate stock investments and recommend relevant investment opportunities. These registered representatives serve as an all-in-one resource for investors, helping them with everything from understanding the stock market to providing stock investment advice. If it is a stockbroking firm, it will have its licensed brokers handle client transactions.
Besides trading securities and offering investment advice, they provide portfolio management services and manage capital gains taxes. These brokers also offer other financial products, including banking and insurance services.
Their core clients are wealthy and institutional investors. An investor can buy mutual funds directly from them and shares through initial public offerings. Also, active day traders can access only a few trading tools, but they need to pay higher commissions for professional services.
#2 - Discount Service Stockbroker
These registered representatives execute securities trading but do not offer any advisory services to investors. However, the rest of the functions are similar to the full-service stockbroking firms with licensed broker-dealers. They provide mutual funds access and other financial products and services at a comparatively cheaper commission.
Swing traders and active day traders usually prefer discount brokers for accessing various trading tools and options.
#3 - No Advice Stockbroker
This set of registered representatives does not offer any additional services as provided by the other two categories. They also do not guide about or recommend what investments clients should make. Instead, they act as a link between the purchase and sale of securities on their clients' behalf.
A stockbroker online is the best example of a no-service broker. Their services are specially for active day traders, who can manage and execute orders online at a minimal commission.
Education Requirement of Stockbroker
A lucrative stockbroker salary is often the reason behind individuals opting for this profession. However, one needs to possess the following educational qualification and background to join a stock brokerage firm as a professional:
- A bachelor's degree in business administration or finance
- A solid grasp of accounting principles, tax regulations, financial laws, financial analysis, planning, reporting, forecasting, etc
- Excellent command of arithmetic, calculations, and statistics
Licensing Requirement
A thorough understanding of finance and a graduate degree may not be enough for an aspirant to begin working as a broker-dealer. Then, how become a stockbroker?
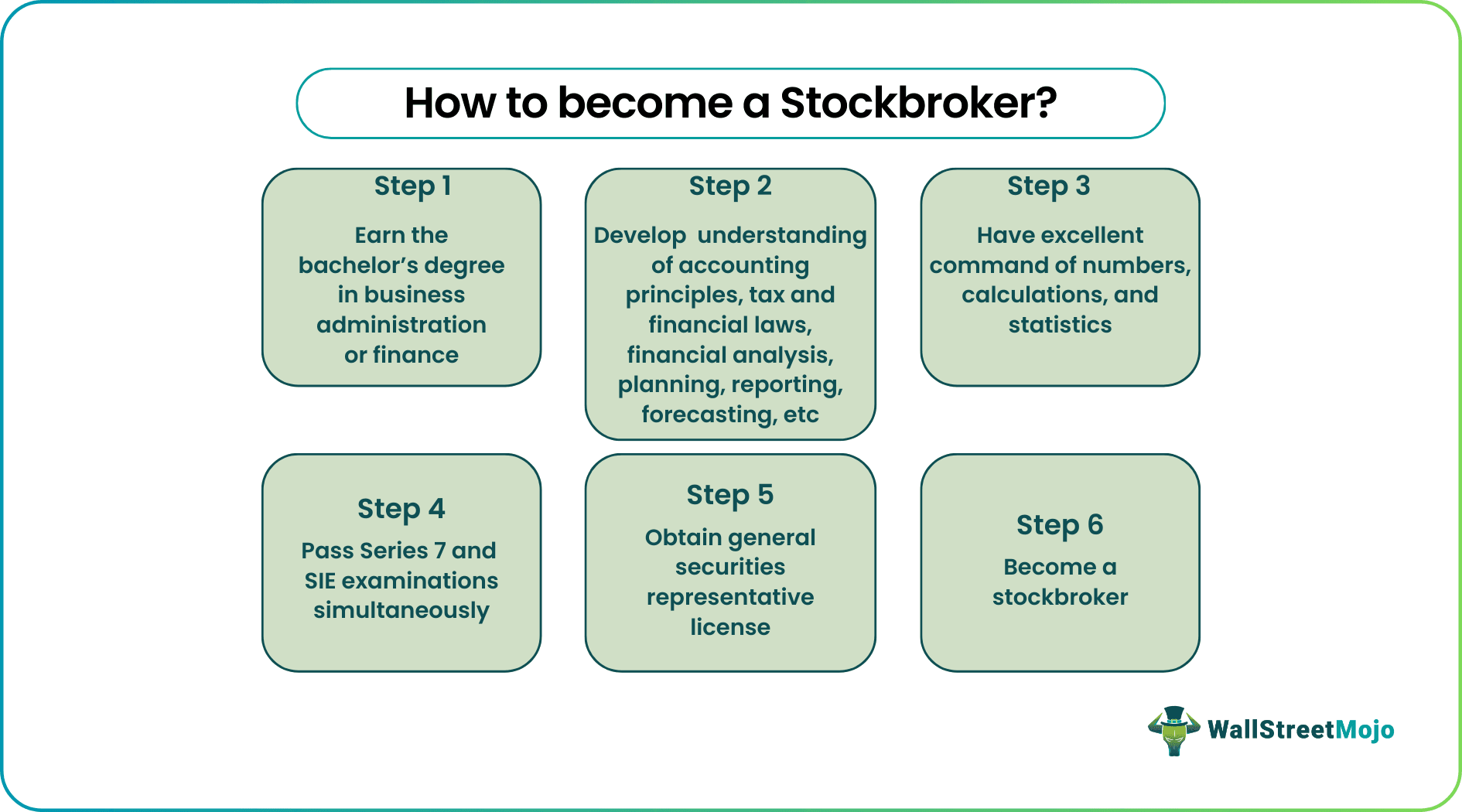
The licensing requirements for registered representatives vary with countries. To become a broker-dealer, the candidate must qualify Series 7 exam, also known as the General Securities Representative Qualification Examination. And to be eligible for this exam, they need to be sponsored by a FINRA member firm or other associated self-regulatory organization.
This examination assesses the skills and knowledge of candidates needed to serve the general securities representative position post-qualification. The test questions cover topics like sales of different types of securities, including corporate, municipal, investment company products, options, government securities, etc. Along with Series 7, candidates must also clear the Securities Industry Essentials (SIE) exam to acquire the license.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Stockbrokers are individuals or companies that buy or sell shares, stocks, and other securities, as instructed by their clients. Since investors cannot directly trade securities in a financial marketplace, they need to connect with a broker-dealer or brokerage firm to execute trade orders.
Aspiring candidates must have a bachelor's degree in finance or business administration, along with a license obtained after clearing the Series 7 exam and the SIE exam. Both exams assess the candidate's knowledge about different types of securities, including municipal, corporate, options, government securities, etc.
A stockbroker must understand accounting principles, taxation regulations, financial laws, financial analysis, planning, reporting, forecasting, etc. In addition, the person should be comfortable with numbers, calculations, and statistics.

