Table Of Contents
Stock Halt Meaning
Stock halt, also termed a trading halt, refers to a scenario when security or stock is temporarily suspended from trading in the respective market it was getting traded. During such phases, open orders are canceled. However, options are usually exercised.
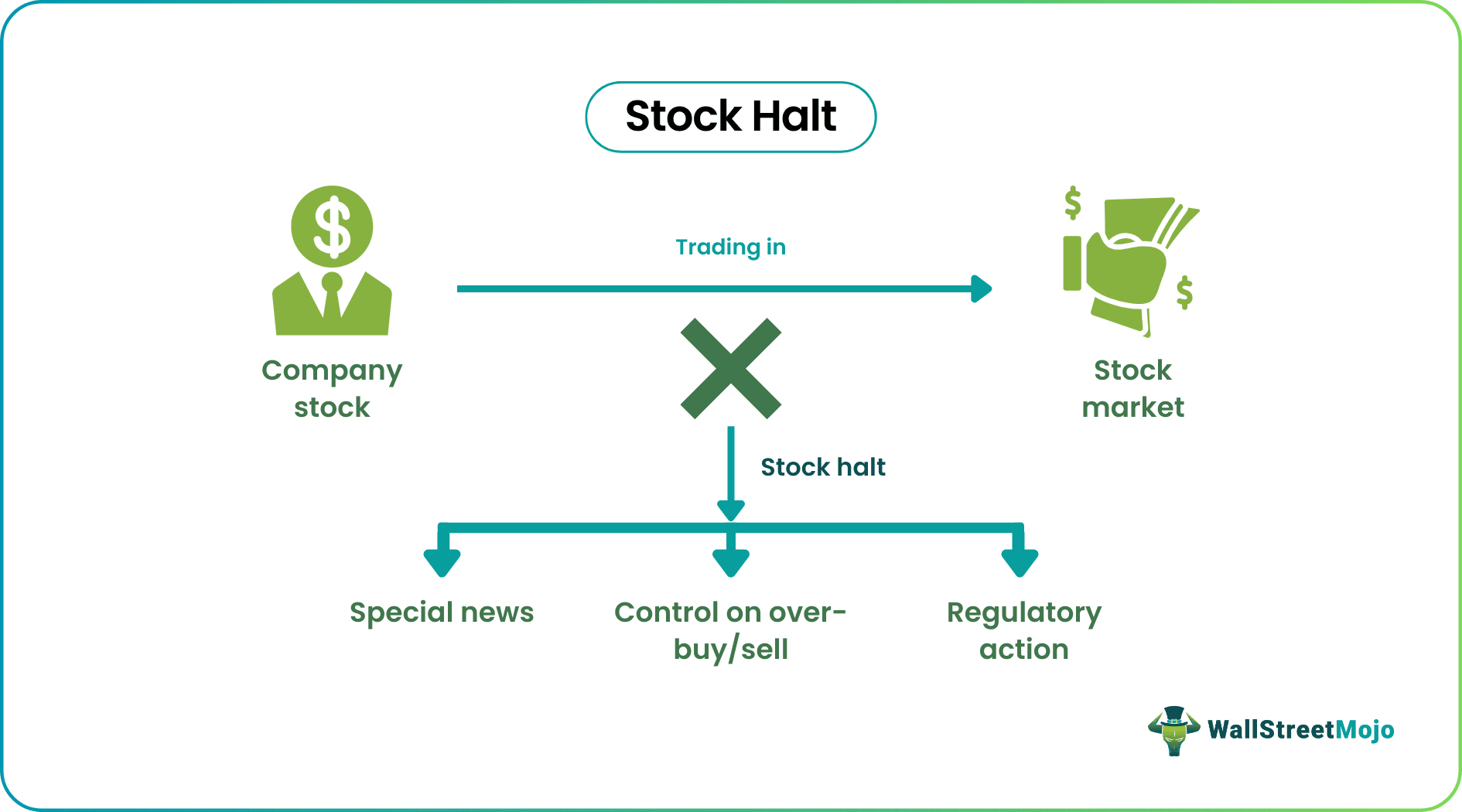
Such a situation may arise on account of factors like the imposition of regulatory actions, significant news which is being anticipated, or to rectify a phase where there is excessive buying or selling of the particular security, and even at times when a company goes for merger and acquisition, the trading may be put to a halt for the time being till the merger or acquisition is over.
Table of contents
Stock Halt Explained
A stock halt alerts are a rare scenario where a stock exchange will announce a prohibition on trading a particular share. During this phase, brokers will not be allowed to trade on the stock, i.e., buy or sell the security for themselves or retail investors like us. Again, there are limited pre-prescribed scenarios when an exchange can announce a trading halt, and again there is a fixed set of rules which need to be followed for the stock to trade again after the halt.
During exceptional events, an entire exchange may also halt trading. The main purpose is to match the demand and supply of the stock, i.e., to match the buyers and sellers for the particular security and ensure smooth execution of the trade.
Both NASDAQ and NYSE have got the best of their interest to keep trading smooth and orderly. It is the motto of all exchanges around the world. Thus when there is some big and significant news based on security that can lead to trading orders going out of balance, exchanges can freeze or halt the trading of a particular stock to prevent investors from suffering considerable financial losses. It is primarily done so that the investors don't blame the exchanges for such huge losses.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Rules
There are generally few scenarios when the trading halt occurs, and securities are coded with a unique identification number. When the exchange halts a share, it will inform all the brokers and the market about suspending the stock from trading. When a stock is trading at more than one exchange, then during such stock halt times, the halt applies to all sales. Brokers then cannot quote the stock price or do trading from their accounts. Again when the exchange plans to lift the halt, they will issue another announcement a few minutes before they lift the halt. As discussed, when a halt takes place, a stock gets marked by a code which is as follows:
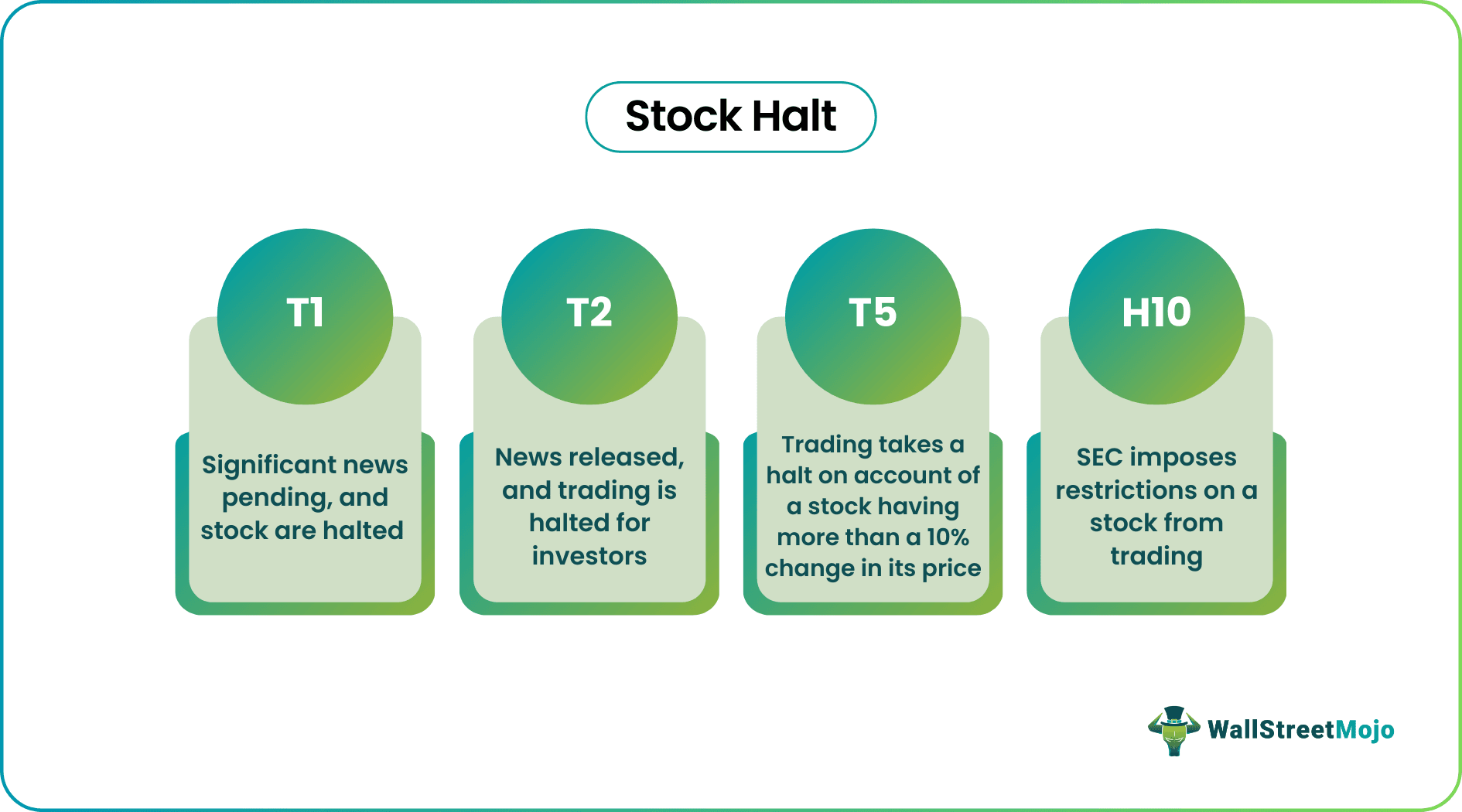
- T1: Significant news is pending, and shares are halted pending the release of the news.
- T2: News is released, and trading is halted for investors to get adjusted to the news and prevent them from panic selling.
- T5: Trading takes a halt because a stock has more than a 10% change in its price within five minutes.
- H10: This type of halt occurs when the Security Exchange Commission or SEC imposes restrictions on a particular share from trading.
Examples
A few examples stock halt alerts are as follows:
#1 - NSE(India)
Due to the CoronaVirus pandemic, when oil prices went for a toss and hit rock bottom, the stock market took a hit, and stocks were impacted badly by falling share prices. This was an example of stock halt times when the entire exchange was halted for trading for thirty minutes to return to a balance of buy and sell and resume after 30 mins.
#2 - Sundance Resource Limited (Australia)
In a tragic accident in 2010 due to a plane crash, the CEO and Chairman were victims of the accident. The share was halted immediately from Australian stock exchanges to prepare the investors to confront the news and not create a panic situation, which would have led otherwise to excessive selling of the stock.
Triggers
- The trading halt is primarily an effect of news and price volatility.
- When the price of a stock is changing, impacting its prices by 10% or more within five minutes, it is a situation when a stock halt scenario gets triggered, and an exchange can put a halt to its trading.
- The stock price can fluctuate up and down and get halted from trading due to frequent changes in volatility or circuit breaker scenarios. SEC can suspend many penny stocks from trading when they doubt any stock promotion or fraudulent activity.
- Also, a type of T12 halt is applied, which is considered a bad halt, for the share, which had traded a lot, but there was so much ground for the long run. Generally, in these cases, when the halt is lifted, the stock comes crashing down.
What Happens When A Stock Is Halted
When trading is halted, the particular security will no longer be able to trade on the stock exchanges. It has been listed till the time the halt is lifted back. It means brokers and retail investors will not be able to trade in that particular stock, i.e., buy or sell the securities for a specific period. Also, on rare occasions, after a share halt is implied on a share like, for example, a T12 category halt, stock prices will generally come crashing down after the lift is halted. A T12 halt is a bad halt applied to overstock, which has gained the long run for no concrete reasons. Thus after the longest stock halt, the market will make corrections, which leads to the downfall of its prices.
Why Does A Stock Halt?
Let us try to understand what causes a stock halt.
- Merger and acquisition.
- Important news or information, be it positive or negative, about the company in the market.
- SEC may impose regulatory imposition and prohibit the stock from doing business on rounds of doubt or fraudulent activities.
- An occasion when massive or materialistic changes happen to the company's financial health.
Thus, from the above explanations we can understand what causes a stock halt.
Advantages
- To provide the entire market participant to be aware of some vital information about a stock or security.
- To eradicate any illegal practice of arbitrage options.
- To provide other markets or exchanges, receive the news simultaneously.
- To protect investors from suffering substantial monetary losses.
- To prevent the stock from becoming a victim of panic buying or panic selling.
Disadvantages
- There are specific scenarios when the share price comes plummeting down after a halt is lifted.
- A longest stock halt may lead to losses in the form of interested investors to the share who lose the opportunity of trading.
- The investor is at a loss as they cannot buy the stock at rock bottom prices and profit from the rise in the stock price.
Stock Halt Vs Suspension
Stock halt is usually stopping the trading session for a short time and suspension is a halt in trading for a long time. Let us look at the differences between them.
| Stock Halt | Suspension |
|---|---|
| The halt is usually for an hour or a couple of hours. | It is usually for a longer period, which may be a few days. |
| It is for reasons like news of corporate action. | It is for some serious reasons like irregularity or fraud. |
| It does not have any serious consequence. | It may lead to delisting from stock exchange. |
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to Stock Halt meaning. We explain its rules, differences with suspension, why a stock halts, triggers, examples and advantages. You may learn more about financing from the following articles –

