Table Of Contents
What is Stock Exchange?
A stock exchange is a market setup where the buyers and sellers trade securities. The securities could be equity, bonds, debt instruments, or exchange-traded funds. The stock market works on the basic principle of matching supply and demand through an auction process.
The trading platforms follow the rules and regulations enforced by an authoritative body. The Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) oversees trading in the US. The online exchange has made trading convenient even for small investors and traders. Now they can easily keep track of their purchases. They can buy or sell securities within seconds.
Table of contents
- What is Stock Exchange?
- A stock exchange is a market arrangement that facilitates the trading of securities among the participants. It is a medium for the interaction of buyers and sellers.
- It is governed by stock regulatory bodies like the Securities Exchange Commission (SEC).
- Listed companies are able to acquire funds, all thanks to the stock market. This is done through Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) released in the primary market. Using this facility, Investors, traders, and speculators generate revenue from stock trading.
Stock Exchange Explained
A stock exchange is a mediator or facilitator that connects various market participants. The traded products include shares of a publicly-traded company, debt instruments, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), indices, equity swaps, single-stock futures, and stock index futures. Just like the SEC, European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) regulates exchanges in Europe.
An exchange can be bifurcated into two: the primary market and the secondary market. In the primary market, new issues or the initial public offerings (IPOs) are announced. This is referred to as “going public.” The secondary market facilitates the procurement and sale of existing securities that debuted during their IPO.
A stock market involves various participants: the brokers who invest clients’ money; the dealers who trade on their behalf; the broker-dealers who buy and sell stocks for themselves and their clients; and finally the market makers who aim to reap profit and improve the market's efficiency.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
History of Stock Exchanges
The history of stock exchanges can be traced back to the 1300s when the Venetian lenders offered debt issues to various investors and lenders. Their role was similar to that of the brokers. The Venetians kept a record of all sales. Evidently, the first exchange was set up in Belgium in the 1500s. It was named “Sans the Stock” and facilitated the trade of bonds and promissory notes.
In the 1600s, the East India Company issued stocks to raise money for the sea journey, which was a risk. The investment was subject to weather turmoil, pirate invasions, and loss of direction. Nevertheless, the investors were promised a percentage of sales if the ship reached its destination.
Ultimately in 1791, a well-channelized stock market. came into existence. The US stock exchange and National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations (NASDAQ) were formed. It trades all kinds of securities and has an electronic trading system. It had competitors; the more advanced New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), formed in 1793. The NYSE further facilitated the trading of securities on a global scale.
Features of Stock Exchange
The stock market is a central government-recognized framework and functions under the guidance of an authoritative body. It aims to ensure fair trading practices and safeguards the interest of retail and institutional investors. This is achieved by keeping track of every transaction. Moreover, brokers act as mediators between the companies and traders.
In such a marketplace, the buyers and sellers can exchange any listed securities, whether offered by companies or government organizations. The benchmark index indicates the ups and downs of the market. Besides, the stock market also deals in secondary securities, i.e., the ones which the companies have already issued.
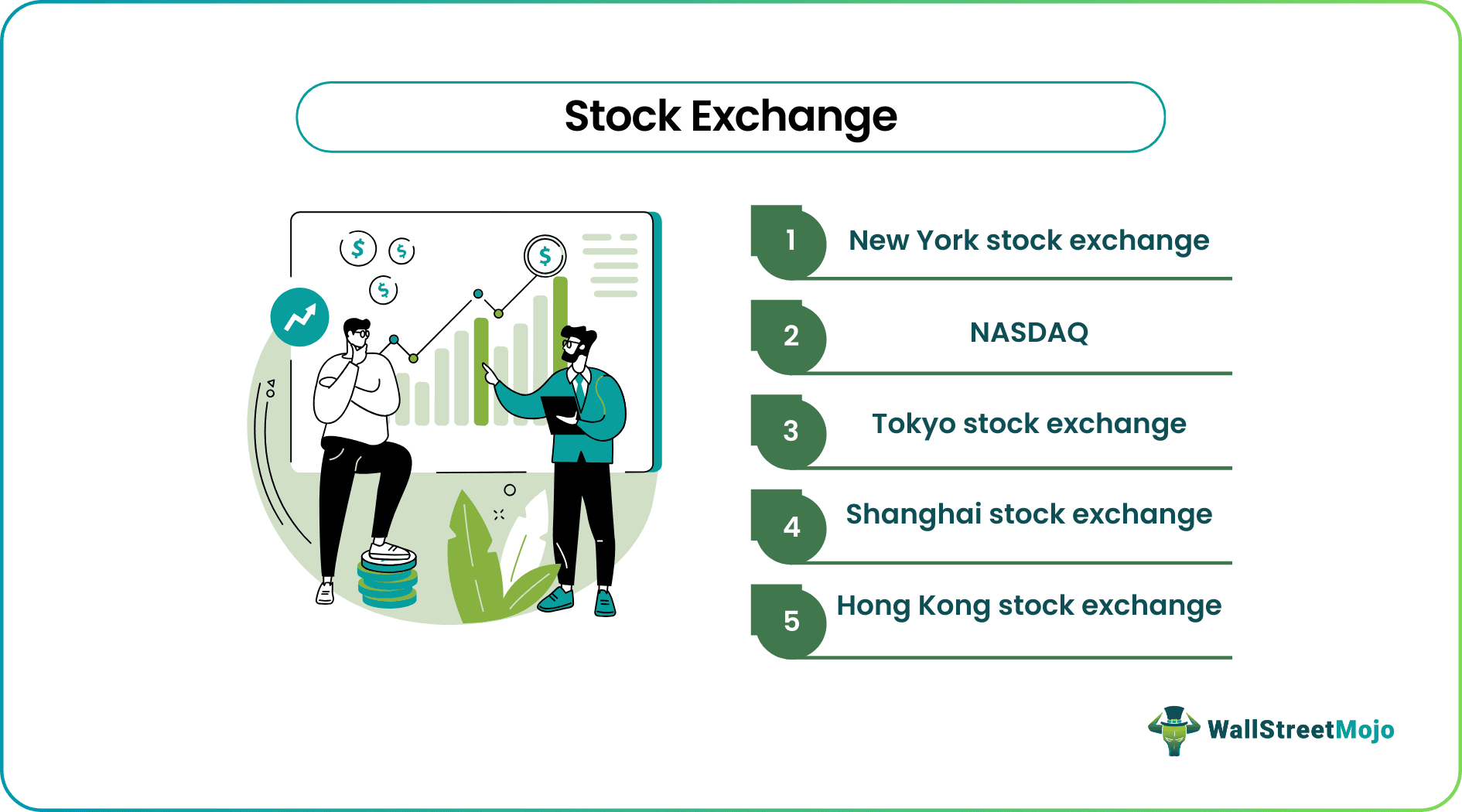
Biggest Stock Exchanges in World
Given below is a list of the top 5 exchanges in the world:
- New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), USA: NYSE is the world’s largest stock market located in the US. It was founded in 1792 and has a market capitalization of $24.5 trillion with 2400 listed companies.
- National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations (NASDAQ), USA: The NASDAQ came into existence in 1791. With a listing of 3000 companies and a market capitalization of 19.34 trillion, it became the world’s second-largest stock exchange.
- Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE), China: Although the third-largest in the world, SSE is the top stock market in China. It was formed in 1990 and possessed a market cap of $6.98 trillion. It is an exchange operating independently in the People's Republic of China.
- European New Exchange Technology (EURONEXT), pan-Europe: EURONEXT is an exchange operational across the different states of Europe. Its MCap values $6.65 trillion and lists different kinds of securities, especially debt and funds.
- Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEX), Hong Kong: HKEX, established in 1891, has a market cap worth $6.48 trillion. The Hang Seng index is its benchmark.
Types
Stock markets are further classified into the following four categories:
- Dealer Market: A market where the dealers are the price setters as they declare the purchase or sale price of securities at a specific value. This type focuses on market movement and efficiency.
- Auction Market: In such a marketplace, the price is determined by the highest bid made by a broker and the lowest selling price that the seller accepts.
- Over The Counter Exchange: The OTC exchange facilitates securities trading via broker-dealers. These are stocks that are not part of top stock markets. Companies that fail to get listed, sell their securities over the counter.
- Electronic Exchange: It is a form of direct selling and buying of securities on a virtual trading platform. Here, the market makers have no role to play. The Electronic Communication Network (ECN) plays the role of a broker. In the present era, almost all stock markets have an electronic trading facility.
Functions of Stock Exchange
The role of a stock market is not limited to capital accumulation; it is much more than that. Let us see how:
#1 – Validation and Authentication of Transactions
There are numerous buying and selling requests on the stock market, which could sometimes lead to an inefficient transaction. Hence, it is the responsibility of the stock market to validate each transaction. Furthermore, they make sure that the transactions are processed correctly, eliminating any room for error.
#2 – Price Determination
Prices of shares and other financial instruments depend on the prevailing demand and supply. So, it is one of the functions of the stock market to accurately determine the price of a particular product. Thus, any blunder in such a mechanism could lead to more or less pay for the product.
#3 – Acts as Economic Barometer
Every stock market is a reflection of the country’s economy. It keeps a check over the ups and downs of the market, price variation of stocks, and the impact of price variation on the economy.
#4 – Ensures Economic Growth
It facilitates the purchase and sale of securities and other financial instruments in the open market. This, in turn, indicates a constant circulation of money in the economy. Circulation is seen as a sign of a healthy economy.
#5 – Provides Liquidity
Stock exchanges offer flexibility to investors and traders. They can purchase and sell securities at any time (during trading hours). Thus, it is a marketplace that ensures the liquidity of funds put in by the participants.
#6 – Promotes Investment
The stock market motivates retail investors to participate in trading activities. In addition, it nudges investors into investing in stocks so that they can generate a passive income.
#7 – Encourages Healthy Speculation
Now, speculation is not always illegal; instead, a stock market strategically encourages a certain level of speculation. Speculation is essential for accelerating the demand and supply of stocks.
Importance of Stock Exchange
The price movement of the listed stocks determines economic fluctuations prevailing within a nation. In addition, various companies require funding to carry out businesses and start new ventures. In order to raise capital, they issue different financial instruments, shares, and debentures.
Moreover, investors often seek handsome returns on their money. The stock market provides them an option. The stock market is a popular choice for generating passive income.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The stock market is a platform that facilitates buying and selling of financial instruments under the regulations of an authoritative body. In the US, The Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) oversees trading.
The exchange is a medium for the listed companies to issue securities and acquire funds from the investors. These funds are then put into the business for generating revenue. Ultimately the profits provide returns to the shareholders.
The world’s three most prominent exchanges are as follows.
1. New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
2. National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations (NASDAQ)
3. Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE)
Investors buy securities, and the securities yield returns in two different ways. Some financial instruments like equity make money by capital appreciation (the profit adds up to the stock value), while others such as bonds and debentures offer regular dividends.

